Gamma function: Difference between revisions
imported>Fredrik Johansson |
imported>Fredrik Johansson |
||
| Line 229: | Line 229: | ||
There was in fact little practical need for anything but real values of the gamma function until the 1930s, when applications for the complex gamma function were discovered in theoretical physics. As electronic computers became available for the production of tables in the 1950s, several extensive tables for the complex gamma function were published to meet the demand, including a table accurate to 12 decimal places from the U.S. [[National Bureau of Standards]].<ref>Davis</ref> | There was in fact little practical need for anything but real values of the gamma function until the 1930s, when applications for the complex gamma function were discovered in theoretical physics. As electronic computers became available for the production of tables in the 1950s, several extensive tables for the complex gamma function were published to meet the demand, including a table accurate to 12 decimal places from the U.S. [[National Bureau of Standards]].<ref>Davis</ref> | ||
Like for many other special functions, ''[[Abramowitz and Stegun]]'' became the standard reference after its publication in 1964. | |||
==Notes and references== | ==Notes and references== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 05:11, 13 May 2007
The gamma function is a mathematical function that extends the domain of factorials to non-integers. The factorial of a positive integer n, written n!, is the product 1·2·3···n. The gamma function, denoted by , is defined to satisfy for all positive integers n and to smoothly interpolate the factorial between the integers. The gamma function is one of the most commonly occurring examples of a nonelementary function; that is, a function that cannot be expressed in finite terms using algebraic operations, exponentials, and logarithms. Its study dates back to Leonhard Euler, who gave a formula for its calculation in 1729.
Motivation
A famous anecdote tells that Carl Friedrich Gauss as a child found that the sum can be calculated from the formula . He was thereby able to quickly sum all the integers between 1 and 100, to the astonishment of his teacher. Such a formula, in which the number of operations does not depend on the size of , is called a closed-form expression. Is there a closed-form expression for factorials? If we had one, we could not only calculate factorials less tediously, but also generalize the concept of a factorial to numbers that are not integers. The formula , for comparison, describes a parabola when plotted for a continuously changing variable .
By plotting the factorial of a few small integers, it becomes apparent that the dots can be connected with a smooth curve. We could, very roughly, calculate fractional factorials by just inspecting the graph. The problem is that it is not so easy to find a formula that exactly describes the curve. In fact, we now know that no simple such formula exists — "simple" meaning that no finite combination of elementary functions such as the usual arithmetic operations and the exponential function will do. Considering the simple solution for sums, it may come as surprise that changing "+" to "·" makes such a difference. But it is possible to find a general formula for factorials, if we deploy tools from calculus.
Basic properties of the gamma function
Euler's integral definition
The gamma function is commonly defined by a definite integral due to Leonhard Euler,
where is interpreted as if is not an integer.[1] Using standard theorems from mathematical analysis, it can be shown that Euler's integral defines to be a continuous function if is positive, or indeed any complex number with positive real part.[2] To see that it corresponds to the factorial at integers, we can insert instead of and perform an integration by parts to obtain
This relation is called the recurrence formula or recurrence relation of the gamma function. The equation is an example of a functional equation — an equation to be solved for the function for all values of . It is analogous to the recurrence satisfied by factorials, , the only difference being that the function argument has been shifted by 1. A repeated application of the gamma function's recurrence formula gives
which together with the initial value establishes that
for positive integers . We can of course equivalently write . We may use these formulas to explicitly calculate or, conversely, to define for non-integers in terms of the gamma function.
Real and complex numbers
The behavior of for an increasing positive variable is simple: it grows quickly — faster than an exponential function. Asymptotically as , the magnitude of the gamma function is given by Stirling's formula
The behavior for nonpositive is more intricate. Euler's integral does not converge for , but the function it defines in the positive complex half-plane has a unique analytic continuation to the negative half-plane. One way to find that analytic continuation is to use Euler's integral for positive arguments and extend the domain to negative numbers by repeated application of the recurrence formula,
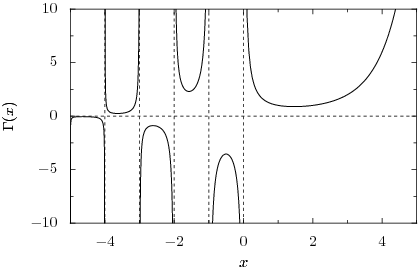
choosing such that is positive. The product contains a factor that blows up due to division by zero as approaches any of the integers . Thus, the gamma function must be undefined at those points; it is a meromorphic function with poles at the nonpositive integers. The following image shows the graph of the gamma function along the real line:
The gamma function is nonzero everywhere along the real line, although it comes arbitrarily close as . There is in fact no complex number z for which , and hence the reciprocal gamma function is an entire function, with zeros at . We see that the gamma function has a local minimum at where it attains the value . The gamma function must alternate sign between the poles because the product in the forward recurrence contains an odd number of negative factors if the number of poles between and is odd, and an even number if the number of poles is even.
| Interval | Sign | Local extreme xm | Γ(xm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (0, ∞) | + | 1.4616321449683623413 | 0.88560319441088870028 |
| (-1, 0) | - | -0.50408300826445540926 | -3.5446436111550050891 |
| (-2, -1) | + | -1.5734984731623904588 | 2.3024072583396801358 |
| (-3, -2) | - | -2.6107208684441446500 | -0.88813635840124192010 |
| (-4, -3) | + | -3.6352933664369010979 | 0.24512753983436625044 |
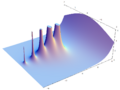
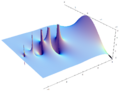
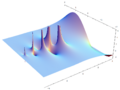
Plotting the gamma function in the complex plane yields beautiful graphs:
The reflection formula
The recurrence relation is not the only functional equation satisfied by the gamma function. Another important property is the reflection formula
which gives a concise relation between the gamma function of positive and negative numbers. The division by a sine, which is periodically zero, again indicates the existence of the gamma function's periodically occurring poles. Further, inserting z = 1/2 reveals the surprising fact that
Hence, by the recurrence formula, the gamma function or factorial of any half-integer is a rational multiple of .
Applications
Opening a random page in an advanced table of formulas, one may be as likely to spot the gamma function as a trigonometric function. One author describes the gamma function as "Arguably, the most common special function, or the least 'special' of them. The other transcendental functions listed below are called 'special' because you could conceivably avoid some of them by staying away from many specialized mathematical topics. On the other hand, the Gamma function is most difficult to avoid."[3]
Integration problems
The gamma function finds application in such diverse areas as quantum physics, astrophysics and fluid dynamics.[4] The gamma distribution, which is formulated in terms of the gamma function, is used in statistics to model a wide range of processes; for example, the expected time between occurrences of earthquakes.[5]
The primary reason for the gamma function's usefulness in such contexts is the prevalence of expressions of the type which describe processes that decay exponentially in time or space. Integrals of such expressions can occasionally be solved in terms of the gamma function when no elementary solution exists. For example, if is a power function and is a linear function, a simple change of variables gives the evaluation
The fact that the integration is performed along the entire positive real line might signify that the gamma function describes the cumulation of a time-dependent process that continues indefinitely, or the value might be the total of a distribution in an infinite space.
It is of course frequently useful to take limits of integration other than 0 and to describe the cumulation of a finite process, in which case the ordinary gamma function is no longer a solution; the solution is then called an incomplete gamma function. (The ordinary gamma function, obtained by integrating across the entire positive real line, is sometimes called the complete gamma function for contrast).
An important category of exponentially decaying functions is that of Gaussian functions and integrals thereof, such as the error function. There are many interrelations between these functions and the gamma function; notably, the square root of we obtained by evaluating is the "same" as that found in the normalizing factor of the error function and the normal distribution.
The integrals we have discussed so far involve transcendental functions, but the gamma function also arises from integrals of purely algebraic functions. In particular, the arc lengths of ellipses and of the lemniscate, which are curves defined by algebraic equations, are given by elliptic integrals that in special cases can be evaluated in terms of the gamma function.
Another important special case is that of the beta function
Expressing products
The gamma function's ability to and generalize factorial products immediately leads to applications in many areas of mathematics; in combinatorics, and by extension in areas such as probability theory and the calculation of power series. Many expressions involving products of successive integers can be written as some combination of factorials, the most important example perhaps being that of the binomial coefficient
We can replace the factorial by a gamma function to extend any such formula to the complex numbers. More generally, any product where each factor is a rational function of the index variable is susceptible to the same treatment. If and are monic polynomials of degree and with respective roots and , we have
If we have a way to calculate the gamma function numerically, it is a breeze to calculate numerical values of such products. The number of gamma functions in the right-hand side depends only on the degree of the polynomials, so it does not matter whether equals 5 or .
By taking limits, infinite products of rational functions can be evaluated in terms of the gamma function as well. Due to the Weierstrass factorization theorem, many simple analytic functions can be written as infinite products of rational factors, and hence can be represented as finite products or quotients of the gamma function. We have already seen one striking example: the reflection formula essentially represents the sine function as the product of two gamma functions. Starting from this formula, the exponential function as well as all the trigonometric and hyperbolic functions can be expressed in terms of the gamma function.
More functions yet, including the hypergeometric function and special cases thereof, can be represented by means of complex contour integrals of products and quotients of the gamma function, called Mellin-Barnes integrals.
Analytic number theory
An elegant and deep application of the gamma function is in the study of the Riemann zeta function. A fundamental property of the Riemann zeta function is its functional equation:
Among other things, this provides an explicit form for the analytic continuation of the zeta function to a meromorphic function in the complex plane and leads to an immediate proof that the zeta function has infinitely many so-called "trivial" zeros on the real line. Borwein et al. call this formula "one of the most beautiful findings in mathematics".[6] Another champion for that title might be
Both formulas were derived by Bernhard Riemann in his seminal 1859 paper "Über die Anzahl der Primzahlen unter einer gegebenen Grösse" ("On the Number of Prime Numbers less than a Given Quantity"), one of the milestones in the development of analytic number theory — the branch of mathematics that studies prime numbers using the tools of mathematical analysis. Factorial numbers, considered as discrete objects, are an important concept in classical number theory due to containing many prime factors, but Riemann found a use for their continuous extension that arguably turned out to be even more important.
Historical development
The gamma function has caught the interest of some of the most prominent mathematicians of all time. Its history, researched for instance by P. J. Davis[7], reflects many of the major developments within mathematics since the 18th century. In the words of Davis, "each generation has found something of interest to say about the gamma function. Perhaps the next generation will also."
Defining the gamma function
The problem of extending the factorial to non-integer arguments was apparently first considered by Daniel Bernoulli and Christian Goldbach in the 1720s, and was solved at the end of the same decade by Leonhard Euler.[7]
Euler's integral establishes that it is possible to define a continuous extension of the factorial, but an important question needs to be addressed: is the gamma function the unique such extension? The answer is no: there are infinitely many ways to connect any discrete set of points with a smooth curve. Infinitely many solutions remain if we demand that must hold for all numbers z, not just integers, so this extra criterion is not strong enough.
The pragmatic reason for using Euler's particular extension of the factorial is that his integral often turns up in applications, whereas other extensions do not.
There is a complication, however: although Euler's function is arguably the most natural extension of the factorial, his integral is not the only formula that can be used to represent it. Other mathematicians who studied the gamma function have used different formulas as definitions, and although those formulas describe the same function, it is not entirely straightforward to prove the equivalence. Euler himself gave two different definitions: the first was not his integral but an infinite product,
of which he informed Goldbach in a letter dated October 13, 1729. He wrote to Goldbach again on January 8, 1730, to announce his discovery of the integral representation
which is valid for . By the change of varibles , this becomes the familiar Euler integral. Euler published his results in the paper "De progressionibus transcendentibus seu quarum termini generales algebraice dari nequeunt" ("On transcendental progressions, that is, those whose general terms cannot be given algebraically"), submitted to the St. Petersburg Academy on November 28, 1729.[8]
James Stirling, a contemporary of Euler, also attempted to find a continuous expression for the factorial and came up with what is now known as Stirling's formula. Although Stirling's formula gives a good estimate of , also for non-integers, it does not provide the exact value. Stirling made several attempts to refine his approximation, and eventually found a solution, although he never managed to prove that the extended version of his formula indeed corresponds exactly to Euler's gamma function. A proof was first given by Charles Hermite in 1900.[9]
Other definitions that have been given include the infinite products
and
where is Euler's constant. They are due, respectively, to Carl Friedrich Gauss and Karl Weierstrass.
A definite and generally applicable characterization of the gamma function was not given until 1922. Harald Bohr and Johannes Mollerup then proved what is known as the Bohr-Mollerup theorem: that the gamma function is the unique solution to the factorial recurrence relation that is also logarithmically convex for positive z. That is, if a function interpolates the factorial, and its logarithm is a convex function for positive , it must be the gamma function. The gamma function is also uniquely defined for negative numbers, and everywhere else in the complex plane, since it can be shown to be an analytic function and analytic functions are uniquely defined by analytic continuation from any region of the complex plane.
The Bohr-Mollerup theorem is useful because it is relatively easy to prove logarithmic convexity for any of the different formulas used to define the gamma function. Taking things further, instead of defining the gamma function by any particular formula, we can choose the conditions of the Bohr-Mollerup theorem as the definition, and then pick any formula we like that satisfies the conditions as a starting point for studying the gamma function. This approach was used by the Bourbaki group.
Notation
The name gamma function and the symbol were introduced by Adrien-Marie Legendre around 1811; Legendre also rewrote Euler's integral definition in its modern form. Although the symbol is an upper-case Greek Gamma, there is no accepted standard for whether the function name should be written "Gamma function" or "gamma function" (some authors simply write "-function"). The alternative "Pi function" notation due to Gauss is sometimes encountered in older literature, but Legendre's notation is dominant in modern works.
It is justified to ask why we distinguish between the "ordinary factorial" and the gamma function by using distinct symbols, and particularly why the gamma function should be normalized to instead of simply using "". Legendre's motivation for the normalization does not appear to be known, and has been criticized as cumbersome by some (the 20th-century mathematician Cornelius Lanczos, for example, called it "void of any rationality" and would instead use [10]). The normalization does simplify some formulas, but complicates others.
Numerical calculation
Algorithms
It is a relatively convenient business to numerically calculate the gamma function for small arguments: given an approximation that holds on some interval of unit width, say for , or a complex strip with real part in such an interval, the value anywhere else can be computed easily via the recurrence and reflection formulas, using only a few multiplications or an evaluation of the sine in the reflection formula. In advanced numerical software that computes the gamma function with double precision (16 digits), the unit-interval approximation is usually an optimally chosen rational function, but for moderate precision an approximating polynomial works just as well. The gamma function can also be computed from any of several series representation, or even by direct numerical integration of Euler's integral, but either approach is generally less efficient than using a pre-computed approximation if a fixed precision is used.
For large arguments, say , it is best to use an asymptotic expansion; the most popular is Stirling's series
This is Stirling's formula multiplied by a series that corrects the error. The series coefficients can be calculated in terms of Bernoulli numbers. The "" sign denotes an asymptotic equality: the series diverges for every z, but yields arbitrarily accurate approximations of the gamma function as if the series is truncated at the smallest term. We can use Stirling's series to calculate the gamma function for small numbers as well, using the recurrence relation. Taking and calculating from , using the three first terms in Stirling's series, we obtain ≈ 1.000003 and ≈ 1.000002; this particular approximation is good to five decimal places on the interval . With larger and more terms, Stirling's series permits calculating the gamma function with arbitrary precision.
Other practical methods for high-precision calculation include the Lanczos approximation and Spouge's approximation, which are both similar in form to Stirling's series but have different convergence characteristics.
It should be noted that it may be convenient to work with the logarithm of the gamma function instead of the gamma function itself, since the raw gamma function grows quickly and can cause overflow in computer arithmetic. It is common to encounter a quotient of two large gamma function values, which is most safely computed by subtracting two logarithms. Stirling's, Lanczos's and Spouge's approximations can all be calculated directly in logarithmic form.
Available software and tables
Double-precision floating-point implementations of the gamma function and its logarithm are available in most scientific computing software and special functions libraries, for example Matlab, GNU Octave, and the GNU Scientific Library. The gamma function was also added to the C mathematics library (math.h) as part of the C99 standard, but is not implemented by all C compilers. Arbitrary-precision implementations are available in most computer algebra systems, such as Mathematica and Maple. Pari/GP, MPFR and MPFUN contain free arbitrary-precision implementations.
Although the gamma function can be calculated virtually as easily as any mathematically simpler function with a modern computer — even with a programmable pocket calculator — this was of course not always the case. Until the mid-20th century, mathematicians relied on hand-made tables; in the case of the gamma function, notably a table computed by Gauss in 1813 and one computed by Legendre in 1825.
Tables of complex values of the gamma function, as well as hand-drawn graphs, were given in Tables of Higher Functions by Jahnke and Emde, first published in Germany in 1909. According to Michael Berry, "the publication in J&E of a three-dimensional graph showing the poles of the gamma function in the complex plane acquired an almost iconic status."[11]
There was in fact little practical need for anything but real values of the gamma function until the 1930s, when applications for the complex gamma function were discovered in theoretical physics. As electronic computers became available for the production of tables in the 1950s, several extensive tables for the complex gamma function were published to meet the demand, including a table accurate to 12 decimal places from the U.S. National Bureau of Standards.[12]
Like for many other special functions, Abramowitz and Stegun became the standard reference after its publication in 1964.
Notes and references
- ↑ Here, "log" denotes the natural logarithm. For complex arguments, it should be interpreted as the principal value.
- ↑ In the remainder of this article, "positive" will be understood to mean either a positive real number or a complex number with positive real part
- ↑ Michon, G. P. "Trigonometry and Basic Functions". Numericana. Retrieved May 5, 2007.
- ↑ Chaudry, M. A. & Zubair, S. M. (2001). On A Class of Incomplete Gamma Functions with Applications. p. 37
- ↑ Rice, J. A. (1995). Mathematical Statistics and Data Analysis (Second Edition). p. 52–53
- ↑ Borwein, J., Bailey, D. H. & Girgensohn, R. (2003). Experimentation in Mathematics. A. K. Peters, 133. ISBN 1-56881-136-5.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Davis, P. J. (1959). "Leonhard Euler's Integral: A Historical Profile of the Gamma Function", The American Mathematical Monthly, Vol. 66, No. 10 (Dec., 1959), pp. 849-869
- ↑ Euler's paper was published in Commentarii academiae scientiarum Petropolitanae 5, 1738, 36—57. See E19 -- De progressionibus transcendentibus seu quarum termini generales algebraice dari nequeunt, from The Euler Archive, which includes a scanned copy of the original article. An English translation by S. Langton is also available.
- ↑ Knuth, D. E. (1997). The Art of Computer Programming, volume 1 (Fundamental Algorithms). Addison-Wesley.
- ↑ Lanczos, C. (1964). "A precision approximation of the gamma function." J. SIAM Numer. Anal. Ser. B, Vol. 1.
- ↑ Berry, M. "Why are special functions special?". Physics Today, April 2001
- ↑ Davis











![{\displaystyle \Gamma (z+1)=\left[-e^{-t}t^{z}\right]_{0}^{\infty }+z\int _{0}^{\infty }e^{-t}t^{z-1}dt=z\Gamma (z).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9fa02312da3f296e53b4e84c5597ad4b6b8beb01)