Gamma-aminobutyric acid: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (stub and structure) |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
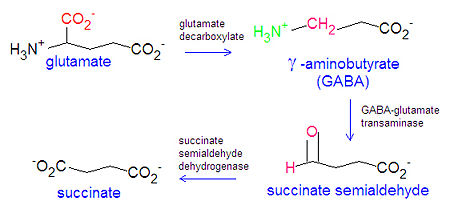
[[Image:GABA synthesis degradation DEVolk.jpg|right|thumb| | [[Image:GABA synthesis degradation DEVolk.jpg|right|thumb|450px|{{#ifexist:Template:GABA synthesis degradation DEVolk.jpg/credit|{{GABA synthesis degradation DEVolk.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Synthesis and degradation of GABA.]] | ||
'''Gamma aminobutyric acid''' (GABA) or <math>\gamma</math>-aminobutyrate, is an inhibitory transmitter in the central nervous system. It is produced from the [[amino acid]] glutamate through the action of the enzyme [[glutamate decarboxylase]], and is inactivated by degradation to [[succinate]] in a two step mechanism involving the enzymes [[GABA-glutamate transaminase]] and [[succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase]]. | '''Gamma aminobutyric acid''' (GABA) or <math>\gamma</math>-aminobutyrate, is an inhibitory transmitter in the central nervous system. It is produced from the [[amino acid]] glutamate through the action of the enzyme [[glutamate decarboxylase]], and is inactivated by degradation to [[succinate]] in a two step mechanism involving the enzymes [[GABA-glutamate transaminase]] and [[succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase]]. | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 22 January 2008
Gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) or -aminobutyrate, is an inhibitory transmitter in the central nervous system. It is produced from the amino acid glutamate through the action of the enzyme glutamate decarboxylase, and is inactivated by degradation to succinate in a two step mechanism involving the enzymes GABA-glutamate transaminase and succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase.