Australopithecus afarensis: Difference between revisions
imported>John S. Murphy |
imported>John S. Murphy |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
==='''Cranial'''=== | ==='''Cranial'''=== | ||
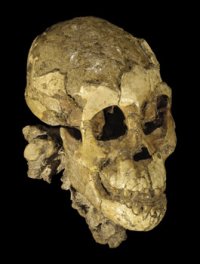
Although the cranium is more primitive than the Australopithecus africanus, it remains classified as a [[gracile]] Australopith instead of a chimpanzee. The hominid has a relatively small brain with an average cranial capacity of 434cc. The brain of A. afarensis was about one-third the size of the average modern human brain, or about the same size as a modern ape's brain.<ref>http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html</ref> It has an [[encephalization quotient]] of 2.5 and is quite chimpanzee-like when looking at it from behind. The compound temporal neutral crests are responsible for a smaller brain capacity and its face is more prognathus when compared to the Australopithecus africanus. Males also typically had large crests (called sagital crests) on top of their skulls while females did not. <ref>http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html</ref><br /> | Although the cranium is more primitive than the Australopithecus africanus, it remains classified as a [[gracile]] Australopith instead of a chimpanzee. The hominid has a relatively small brain with an average cranial capacity of 434cc. The brain of A. afarensis was about one-third the size of the average modern human brain, or about the same size as a modern ape's brain.<ref>http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html</ref> It has an [[encephalization quotient]] of 2.5 and is quite chimpanzee-like when looking at it from behind. The compound temporal neutral crests are responsible for a smaller brain capacity and its face is more prognathus when compared to the Australopithecus africanus. Males also typically had large crests (called sagital crests) on top of their skulls while females did not. <ref>http://WGBH Educational Foundation: 2001 www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html</ref><br /> | ||
A. afarensis provides the first evidence that, with the exception of lower limb features related to bipedalism, australopiths retained a generally apelike skeletal design and body shape(McHenry,1991)<ref>https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf</ref> | A. afarensis provides the first evidence that, with the exception of lower limb features related to bipedalism, australopiths retained a generally apelike skeletal design and body shape(McHenry,1991)<ref>WGBH Educational Foundatio: 2001 https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf</ref> | ||
==='''Dental'''=== | ==='''Dental'''=== | ||
Revision as of 18:42, 30 April 2008
| Australopithecus afarensis |
|---|
| Scientific classification |
|
|
Articles that lack this notice, including many Eduzendium ones, welcome your collaboration! |
Australopithecus afarensis is an extinct hominid species, which to some, is considered to be the "missing link" in human evolution. Although A. afarensis is an older species than A. africanus, it is thought to be one of the closest ancestors to the genus Homo. This is because the species shares a significant amount of traits with both chimpanzees and humans. The monumental remains known as "Lucy" stemmed from one of the most famous paleoanthropological finds in history. The potassium-argon dating found that the ancient species is thought to have lived between 3.76 and 2.9 million years ago with Lucy's remains dating to around 3.2 million years ago. The claim of discovering the potential missing link as well as the name of the species remains the subject of heated discussions within many scholarly circles. A number of scholars with Mary Leakey, in particular, would prefer the official name of this species to be Praeanthropus afarensis.
Distinguished Digs
AL 129-1
1973: Knee joint Kada Hadar, Ethiopia
Discovered in Hadar, Ethiopia by Donald Johanson, the angle of the proximal tibia and distal femur suggests a bipedal hominid. In addition, the bicondylar angle, deep patellar groove and lateral lip of the patellar groove suggest that it is in fact a hominid.
The Hadar site consists of four general members: The Basal member dates older than 3.4 million years old while the Sidi Hakum member dates to 3.22ma and is thought to be a woodland environment. The Denen Dora member dates to 3.18ma and is thought to be a forested/swampy area while the top layer is named Kada Hadar and dates to 2.3ma. The Kada Hadar member is much more open than the other bottom layers.
AL 288-1
1974: Lucy Kada Hadar, Ethiopia
The Lucy find was a singular find and relatively complete (around 40%). Discovered by the International Afar Research Expedition (IARE), Lucy became one of the most notable finds in the history of human biological evolution. Lucy's remains dated to just under 3.18 million years old. The great significance of this find is mainly due to the fact that it was the first time there existed good evidence that humans were bipedal before developing larger brains.
Laetoli
1978: Laetoli Site: Footprints / Holotype Tanzania
The Laetoli site is located in Tanzania and is just south of Olduvai gorge. The site was being excavated by Mary Leakey and her team in 1975 when thirteen specimens of Australopithecus afarensis were discovered, including the current holotype of Australopithecus afarensis (a mandible). When returning to the site in 1978, the team uncovered over 20,000 animal tracks which included hominid footprints. The cluster of footprints found in the tuff dates from 3.76 to 3.49 million years ago.
DIK-1/1
1999: Lucy's Baby Dikika, Ethiopia
This was the first major find by an African scientist. Zeray Alemseged was responsible for this find in Ethiopia and is equally astonishing as Lucy. This find was one of the most complete skeletons ever found, which included a scapula, and dated to around 3.31-3.35 million years old. The thyroid bone in the throat was not even fused yet which suggested a very early age of maturation (thus, the name Lucy's baby). Like adult A. afarensis, the Dikika baby had long, curved fingers. But the fossil also brings new data to the debate in the form of two shoulder blades, or scapulae--bones previously unknown for this species. According to Alemseged, the shoulder blades of the child look most like those of a gorilla. The upward-facing shoulder socket is particularly apelike, contrasting sharply with the laterally facing socket modern humans have. This, Alemseged says, may indicate that the individual was raising its hands above its head--something primates do when they climb.[1]
Morphology
Cranial
Although the cranium is more primitive than the Australopithecus africanus, it remains classified as a gracile Australopith instead of a chimpanzee. The hominid has a relatively small brain with an average cranial capacity of 434cc. The brain of A. afarensis was about one-third the size of the average modern human brain, or about the same size as a modern ape's brain.[2] It has an encephalization quotient of 2.5 and is quite chimpanzee-like when looking at it from behind. The compound temporal neutral crests are responsible for a smaller brain capacity and its face is more prognathus when compared to the Australopithecus africanus. Males also typically had large crests (called sagital crests) on top of their skulls while females did not. [3]
A. afarensis provides the first evidence that, with the exception of lower limb features related to bipedalism, australopiths retained a generally apelike skeletal design and body shape(McHenry,1991)[4]
Dental
The canines show similar wear patterns as humans which may show a possible link between humans and Australopiths. Although the canines are a bit smaller than chimpanzees, they are bigger than other Australopiths which suggests dimorphism. There is minimal metaconid development and the cusps retain an asymmetric shape which is more chimpanzee-like. The megadontia quotient is around 1.7 and they have a shallow palate which is human-like. Although there are human-like characteristics,the tooth rows are more parallel and narrow which is more ape-like. These discrepancies show a possible link between human-like morphologies and ape-like characteristics which is both exciting and frustrating in the attempt to find a definitive answer to human evolution.
The main differences between A. anamensis and A. afarensis relate to mandibular morphology and details of the dentition. The mandibular symphysis of A. anamensis is steeply-sloping compared with the more vertical symphysis of later hominids, including A. afarensis. In some respects the teeth of A. anamensis are more primitive than those of A. afarensis (e.g. asymmetry of the premolar crowns, less posteriorlyinclined canine root, and the relatively simple crowns of the deciduous first mandibular molars), but in others (e.g. the low cross-sectional profiles, and bulging sides of the molar crowns) they show similarities to more derived, and temporally much later, Paranthropus taxa. Compared with A. afarensis, A. anamensis also exhibits a primitive, horizontal tympanic [5]
“The large premolars of A. afarensis suggests they were frugivores, and the thick enamel on the teeth suggests they may have eaten nuts, grains, or hard fruit pies” (Boyd and Silk, p. 334).[6]
Body size
Males average a weight of 100 lbs while females average a weight of 64lbs, meaning that the average female weighed around 64% of a typical male. This indicates a significant amount of sexual dimorphism. Some studies have suggested that there exists such a great deal of dimorphism that it could in fact be two different species. But this has been refuted because although body sizes differ, the morphological features are continuous. In July researchers reported that A. africanus actually had more apelike body proportions than its presumed ancestor, A. afarensis... "The larger forelimbs of africanus might be an adaptation to a more arboreal life," McHenry says. "But the hind limb is adapted to bipedality, and so there's no doubt that they were terrestrial. They probably spent a lot of time in trees--feeding, sleeping, or for protection" ...In afarensis, the apish proportions were not so pronounced--in all probability the presumed ancestor spent less time in the trees than the purported descendant. [7]
Vertebrae
The vertebrae tend to have long, apelike spinous and transverse processes, and the vertebral bodies are intermediate in size compared with the ape and human conditions. Lumbar vertebrae are wedged such that the anterior length of the body is greater than the posterior length. The upper limb of A. afarensis is shorter than a great ape of comparable mass, but long relative to humans. (Jungers, 1994). [8]
Pelvis: bipedal locomotion
Evidence for bipedal locomotion is seen when examining the pelvis structure, knee joint and foramen magnum. The bones are strong and the pelvis is very human-like. When examining the bottom of the foot; there exists a non-opposable hallux (straight big-toe)with a longitudinal arch (for a springy foot). Although a lot of these features indicate a human-like biped, they still posses long arms, short legs and very curved fingers, which may indicate a significant amount of time in trees.
Apelike morphology includes the coronal orientation of the iliac blades, a somewhat long ischium without a raised tuberosity, a reduced acetabular anterior horn, and evidence of weakly developed sacroiliac ligaments. However, the pelvis shares with humans a short, wide ilium, a well developed sciatic notch and anterior inferior iliac spine, and wide sacrum. The femoral head and acetabulum, as well as sacroiliac and lower intervertebral joints, are small relative to humans of comparable size (Jungers, 1988). This evidence for the locomotion of A. afarensis is complemented by the discovery, at Laetoli, of several trails of fossil footprints (Leakey & Hay, 1979).[9]
Social Structure
Australopithecus afarensis had very curved finger bones which are relatively malleable throughout one's life. From this fact , paleoanthropologists can infer that they probably spent a significant amount of time in trees. Some have argued that they may have spent the night in trees as to avoid terrestrial predation.
More arboreal lifestyles are confirmed by the fact that A. afarensis have different inner ear anatomy than humans: "Australopithecines are more similar to chimpanzees than to modern humans in their inner-ear anatomy," asserts C. Fred Spoor of the University of Liverpool in England. "This supports the view that australopithecines combined arboreal and terrestrial movement. Although humans and apes share many aspects of inner-ear anatomy, humans display markedly larger semicircular canals relative to body weight, Spoor holds. These structures support a balanced, upright stance, he says." [10]
"The moderate skeletal dimorphism of A. afarensis (greater than Pan and less than Gorilla) suggests a somewhat longer developmental period in males compared with females and is therefore inconsistent with a chimpanzee-like territorial strategy. At the same time, it is also markedly inconsistent with strategies like those of gorillas and orangutans, in which skeletal dimorphism is much more pronounced. Therefore, the cooccurrence of moderate skeletal dimorphism, such as that found in modern humans and A. afarensis, and a reduced male canine is fully consistent with a pair-bonded reproductive strategy in early hominids; that is, if their reproductive strategy was chimpanzee-like, hominids should show only minimal skeletal dimorphism, or if it was orangutan- or gorilla-like, they should show greater skeletal dimorphism. Canine dimorphism should be present in either case. Early hominid skeletal dimorphism is consistent with another special hominid character, the failure of male canine eruption to be delayed and thereby coincident with somatic maturation (as it is in all other hominoid species) (34, 35). Thus, observed levels of body size dimorphism in A. afarensis do not imply that monogamy is any less probable than polygyny as the fundamental social system of these early hominids." [11]
External Links
1 AL 129-1
2 Lucy's Baby
References
- ↑ Kate Wong. Scientific American: September 20, 2006 http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=special-report-lucys-baby
- ↑ http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html
- ↑ http://WGBH Educational Foundation: 2001 www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/humans/humankind/d.html
- ↑ WGBH Educational Foundatio: 2001 https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf
- ↑ https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf
- ↑ http://www.collegetermpapers.com/TermPapers/Anthropology/Australopithecus_Afarensis.shtml
- ↑ Kathy A. Svitil. Discover: Jan 1999 http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1511/is_1_20/ai_53501819
- ↑ https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf
- ↑ https://melampus.colorado.edu/class/readings/4110/WoodandRichmond2000.pdf
- ↑ http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m1200/is_/ai_15312077
- ↑ http://www.pnas.org/cgi/content/full/100/16/9404
Simpson, S. W., Lovejoy, C. O. & Meindl, R. S. (1990) J. Hum. Evol. 19, 285–297.
Simpson, S. W., Lovejoy, C. O. & Meindl, R. S. (1991) Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 86, 113–120.