Nose: Difference between revisions
imported>Michael Benjamin |
imported>Michael Benjamin |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==[[Human nose]]== | ==[[Human nose]]== | ||
==Nasal anatomy== | ==Nasal anatomy== | ||
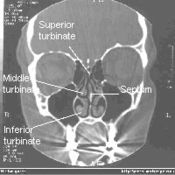
[[ Image:NormalNose-CT-Front-cross-section-common-wiki.jpg|left|175px]] | |||
==Skeletal (bony) components== | ==Skeletal (bony) components== | ||
Revision as of 13:07, 25 February 2007
Template:Disclaim The nose is the portion of the airway preferentially used for inhalation, and contains sense receptors for the sense of smell (olfaction). In humans, the nose is located centrally on the face; on most other mammals, and in reptiles and amphibians, it is on the upper tip of the snout.
The nose acts an interface between air within the body's respiratory passages and the atmosphere of the external world. The nose and associated structures (the paranasal sinuses) are concerned with conditioning the entering air (for instance, by warming and/or humidifying it) and sometimes with reclaiming moisture from the air before it is exhaled (as occurs most efficiently in camels). The nose also acts as a trap for noxious particles and germs (bacteria and viruses) that enter the body by being inhaled.
Newborn human babies breathe "only" through the nose, and are called therefore called "obligate nasal breathers". Crying newborns sometimes are able to breathe in through the mouth, and by several months of age, all normal infants are able to use both the nose and mouth for breathing. Many adults are mouth-breathers. Preferential inhalation through the mouth is generally either a learned habit, or performed because nasal obstruction resists airflow.
In humans, like most mammals, the nose is the primary organ for smelling. As the air is sniffed, it flows in through the nose and over structures called turbinates in the nasal cavity. These turbinates are shaped very much like side-fins. The turbinates slow the air flow and direct it toward the olfactory epithelium. At the surface of the olfactory epithelium, substances carried by the air contact olfactory receptor neurons. When these substances are of a type that the human olfactory system recognizes, the neurons fire and send impulses to the brain. For further information, see sense of smell, olfaction.
In cetaceans, the nose has been reduced to the nostrils, which have migrated to the top of the head, producing a more streamlined body shape and the ability to breathe while the body is almost entirely submerged. Conversely, the elephant's nose has become elaborated into a long, muscular, manipulative organ called the trunk.
Human nose
Nasal anatomy
Skeletal (bony) components
Cartilaginous components
Epithelial membrane
Neurological function
Immunological function
Medical conditions of the nose
Trauma
Deviated septum
Anosmia
Nasal polyp
Culture
Some people choose to get rhinoplasty to change the aesthetic appearance of their nose. Nose piercings are also common, such as nostril, septum or bridge.
In New Zealand, nose pressing ("hongi") is a traditional greeting.
The nose and the voice
References
- Physical Manual: Univ. of Tennessee at Martin
- Eden Warwick (pseudonym of George Jabet), Nasology, or hints towards a classification of Noses, London, Richard Bentley, 1848
- Encyclopedia Britannica Micropedia, 1982
See also
External links
- WebMD: The Sinuses and The Nose
- From the Nose to the Eustachian Tube: Information, videos, tips for diving
- Your Nose: The Guardian Of Your Lungs
- Asian Noses This website discusses the differences in Asian noses.
- The Empty nose syndrome patient association
Template:Respiratory system Template:Human anatomical features