User:John R. Brews/Draft: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>John R. Brews (New page: A '''semiconductor diode''' is a two-terminal device that conducts current in only one direction, made by joining a ''p''-type semiconducting layer to an ''n''-type semiconducting layer.) |
imported>John R. Brews No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<br> | |||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
A '''semiconductor diode''' is a two-terminal device that conducts current in only one direction, made by joining a ''p''-type semiconducting layer to an ''n''-type semiconducting layer. | A '''semiconductor diode''' is a two-terminal device that conducts current in only one direction, made by joining a ''p''-type semiconducting layer to an ''n''-type semiconducting layer. | ||
==Electrical behavior== | |||
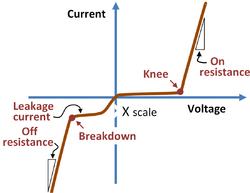
{{Image|Nonideal diode current-voltage behavior.PNG|right|250px|Nonideal diode current-voltage characteristics.}} | |||
The ideal diode has infinite resistance (conducts zero current) for the ''reverse voltage polarity'' and has zero resistance for the ''forward bias polarity''. The ''pn-diode'' is not ideal. | |||
Revision as of 16:54, 8 January 2011
A semiconductor diode is a two-terminal device that conducts current in only one direction, made by joining a p-type semiconducting layer to an n-type semiconducting layer.
Electrical behavior
The ideal diode has infinite resistance (conducts zero current) for the reverse voltage polarity and has zero resistance for the forward bias polarity. The pn-diode is not ideal.