imported>David Hume |
|
| (26 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| pisiform bone (''os pisiforme'')
| | {{AccountNotLive}} |
| | {{systemic}} |
|
| |
|
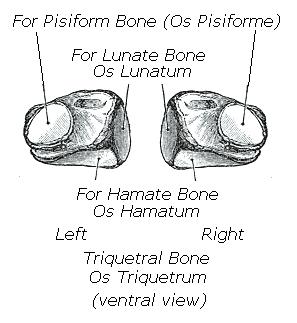
| '''parent article''' - [[wrist]] or [[carpus]] | | The Triangular Bone (os triquetum; cuneiform bone) (Fig. 223).—The triangular bone may be distinguished by its pyramidal shape, and by an oval isolated facet for articulation with the pisiform bone. It is situated at the upper and ulnar side of the carpus. The superior surface presents a medial, rough, non-articular portion, and a lateral convex articular portion which articulates with the triangular articular disk of the wrist. The inferior surface, directed lateralward, is concave, sinuously curved, and smooth for articulation with the hamate. The dorsal surface is rough for the attachment of ligaments. The volar surface presents, on its medial part, an oval facet, for articulation with the pisiform; its lateral part is rough for ligamentous attachment. The lateral surface, the base of the pyramid, is marked by a flat, quadrilateral facet, for articulation with the lunate. The medial surface, the summit of the pyramid, is pointed and roughened, for the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist. 8 |
| | |
| | Articulations.—The triangular articulates with three bones: the lunate laterally, the pisiform in front, the hamate distally; and with the triangular articular disk which separates it from the lower end of the ulna. |
| | |
| | The Triangular Bone (os triquetrum; cuneiform bone) |
| | |
| | {{Image|triquetral.JPG|left|300px|triquetral}} |
| | |
| | {{Infobox Bone | |
| | Name = Triquetral bone | |
| | Latin = os triquetrum, os pyramidale, os triangulare | |
| | GraySubject = 54 | |
| | GrayPage = 224 | |
| | Image = Carpus.png | |
| | Caption = '''BONES OF HAND'''<BR>''Proximal:'' A=[[Scaphoid bone|Scaphoid]], B=[[Lunate bone|Lunate]], C=[[Triquetral bone|Triquetral]], D=[[Pisiform bone|Pisiform]]<BR>''Distal:'' E=[[Trapezium bone|Trapezium]], F=[[Trapezoid bone|Trapezoid]], G=[[Capitate bone|Capitate]], H=[[Hamate bone|Hamate]]<BR> | |
| | Image2 = Gray223.png | |
| | Caption2 = The left triquetal bone. | |
| | Origins = | |
| | Insertions = | |
| | Articulations = articulates with ''three'' bones:<BR>[[lunate]] laterally<BR>[[pisiform]] in front<BR>[[hamate]] distally<BR>triangular [[articular disk]] which separates it from the lower end of the [[ulna]]. | |
| | MeshName = Triquetrum+Bone | |
| | MeshNumber = A02.835.232.087.319.150.831 | |
| | DorlandsPre = o_07 | |
| | DorlandsSuf = 12598819 | |
| | }} |
| | The '''triquetral bone''' (also called '''triquetrum bone''', '''cuneiform bone''', '''pyramidal bone''', '''cubital bone''', '''three-cornered bone''', and '''triangular bone''') is located in the [[wrist]] on the medial side of the proximal row of the [[carpus]] between the [[lunate]] and [[pisiform]] bones. It is on the [[ulnar]] side of the hand, but does not articulate with the [[ulna]]. It connects with the [[pisiform]], [[hamate]], and [[lunate]] bones. It is the 3rd most commonly fractured carpal bone. |
| | |
| | The triangular bone may be distinguished by its pyramidal shape, and by an oval isolated facet for articulation with the pisiform bone. It is situated at the upper and ulnar side of the carpus. To facilitate its palpation in an exam, the hand must be radially deviated so that the triquetrium moves out from under the ulnar styloid process. The triquetrum may be difficult to find, since it also lies under the pisiform. |
| | |
| | The etymology derives from the Latin ''triquetrus'' which means "three-cornered." |
| | |
| | ==Surfaces== |
| | The ''superior surface'' presents a medial, rough, non-articular portion, and a lateral convex articular portion which articulates with the triangular articular disk of the wrist. |
| | |
| | The ''inferior surface'', directed lateralward, is concave, sinuously curved, and smooth for articulation with the hamate. The dorsal surface is rough for the attachment of ligaments. |
| | |
| | The ''volar surface'' presents, on its medial part, an oval facet, for articulation with the pisiform; its lateral part is rough for ligamentous attachment. |
| | |
| | The ''lateral surface'', the base of the pyramid, is marked by a flat, quadrilateral facet, for articulation with the lunate. |
| | |
| | The ''medial surface'', the summit of the pyramid, is pointed and roughened, for the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist. |
| | |
| | == See also == |
| | *[[Bone#Terminology|Bone terminology]] |
| | *[[Terms for anatomical location]] |
| | |
| | ==Additional images== |
| | <gallery> |
| | Image:Gray219.png|Bones of the left hand. Volar surface. |
| | Image:Gray220.png|Bones of the left hand. Dorsal surface. |
| | </gallery> |
| | |
| | {{Bones of upper extremity}} |
| | |
| | [[Category:Skeletal system]] |
| | [[Category:wrist]] |
|
| |
|
| The Pisiform Bone (os pisiforme) The pisiform bone may be known by its small size, and by its presenting a single articular facet. It is situated on a plane anterior to the other carpal bones and is spheroidal in form. Its dorsal surface presents a smooth, oval facet, for articulation with the triangular: this facet approaches the superior, but not the inferior border of the bone. The volar surface is rounded and rough, and gives attachment to the transverse carpal ligament, and to the Flexor carpi ulnaris and Abductor digiti quinti. The lateral and medial surfaces are also rough, the former being concave, the latter usually convex. 10
| |
|
| |
| Articulation.—The pisiform articulates with one bone, the triangular.
| |
|
| |
|
| Volar: Pertaining to both the palm and sole. It comes from word "vola" which the ancient Romans used for "the palm of the hand and the sole of the foot."
| | {{musculoskeletal-stub}} |
|
| |
|
| cf palmar (palm side of hand)and planar (sole of foot)
| | [[fr:Os triquetrum]] |
| | [[nl:Os triquetrum]] |
| | [[sk:Trojhranná kosť]] |
|
| |
|
| The Triangular Bone (os triquetrum; cuneiform bone)
| |
|
| |
|
| By comparison, the term "palm" applies to only the palm (the grasping side) of the hand. The Romans actually used the word "palma" for the outstretched palm of the hand. | | By comparison, the term "palm" applies to only the palm (the grasping side) of the hand. The Romans actually used the word "palma" for the outstretched palm of the hand. |
|
| |
|
| ==topics in anatomy== | | ==Topics in Anatomy== |
| SYSTEMIC ANATOMY | | |
| INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
| | '''SYSTEMIC ANATOMY''' |
| integumentary system | | Introduction and Systemic Overview |
| SKELETAL SYSTEM
| | *Anatomical Nomenclature |
| full skeleton | | *Basic Structure and Function of Cells |
| skull | | *Integrating Cells into Tissues |
| vertebral column | | Systemic Overview |
| ribcage | | *Nervous System |
| shoulder & arm | | *Blood, Lymphoid Tissues and Haemopoiesis |
| hand & wrist | | *Functional Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System |
| pelvis | | *Smooth Muscle and the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic systems |
| leg & ankle | | *Skin and its Appendages |
| foot | | *Endocrine System |
| MUSCULAR SYSTEM
| | *Principles of Hormone Production and Secretion |
| full body | | *Embryology |
| muscle histology | | **Embryogenesis |
| head & neck | | **Prenatal and Neonatal Growth |
| thorax | | |
| shoulder & upper arm | | [[Integumentary System]] |
| giceps brachii
| | *[[integumentary system]] |
| forearm & hand | | |
| abdomen | | [[Skeletal System]] |
| pelvis, thigh & knee | | *[[full skeleton]] |
| leg & foot | | *[[axial skeleton]] |
| THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
| | *[[skull]] |
| nervous system
| | *[[vertebral column]] |
| brain
| | *[[ribcage]] |
| spinal cord
| | *[[appendicular skeleton]] |
| autonomic nervous system
| | *[[shoulder & arm]] |
| eye
| | *[[hand & wrist]] |
| ear
| | *[[pelvis]] |
| nose
| | *[[leg & ankle]] |
| ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
| | *[[foot]] |
| endocrine sytem
| | |
| hypothalamus & pituitary
| | [[Muscular System]] |
| thyroid & parathyroids
| | *[[full body]] |
| adrenal glands
| | *[[muscle histology]] |
| pancreas
| | *[[head & neck]] |
| ovaries
| | *[[thorax]] |
| testes
| | *[[shoulder & upper arm]] |
| CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
| | *[[biceps brachii]] |
| cardiovascular system
| | *[[forearm & hand]] |
| lymphatic system
| | *[[abdomen]] |
| RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
| | *[[pelvis]] |
| respiratory system
| | *[[thigh & knee]] |
| mouth, nose & throat
| | *[[leg & foot]] |
| lungs
| |
|
| |
|
| DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
| | [[Nervous System]] |
| digestive system
| | *[[nervous system]] |
| alimentary canal
| | *[[brain]] |
| accessory organs
| | *[[spinal cord]] |
| mouth & throat
| | *[[autonomic nervous system]] |
| esophagus & stomach
| | *[[eye]] |
| liver, gallbladder
| | *[[ear]] |
| pancreas & duodenum
| | *[[nose]] |
| small intestine
| |
| large intestine
| |
| URINARY SYSTEM
| |
| urinary system
| |
| kidneys
| |
| REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
| |
| male reproductive systerm
| |
| female reproductive system
| |
|
| |
|
| REGIONAL ANATOMY
| | [[Endocrine System]] |
| THE HEAD & NECK
| | *[[endocrine system]] |
| the head & neck
| | *[[hypothalamus & pituitary]] |
| the brain
| | *[[thyroid & parathyroids]] |
| the eye
| | *[[adrenal glands]] |
| the ear
| | *[[pancreas]] |
| THE THORAX
| | *[[ovaries]] |
| the thorax
| | *[[testes]] |
| the lungs
| |
| the hearg
| |
| THE ABDOMEN
| |
| the abdomen
| |
| stomach
| |
| liver & gallbladder
| |
| spleen
| |
| small intestine
| |
| large intestine
| |
| kidney
| |
| THE PELVIS
| |
| pelvis
| |
| THE UPPER LIMB
| |
| arm & elbow
| |
| forearm & hand
| |
| hand
| |
| THE LOWER LIMB
| |
| thigh & knee
| |
| leg & foot
| |
| foot
| |
|
| |
|
| More Regional Anatomy
| | [[Cardiovascular System]] ([[Circulatory System]]) |
| | *[[cardiovascular system]] |
| | *[[lymphatic system]] |
|
| |
|
| HEAD, NECK AND BRAIN
| | [[Lymphatic System]] |
| skull skull bones
| |
| head and neck
| |
| nose
| |
| pharynx
| |
| larynx
| |
| cranial cavity
| |
| eye
| |
| ear
| |
| brain
| |
| radiographs
| |
| VERTEBRAL COLUMN AND SPINAL CORD
| |
| vertebrae
| |
| sacrum and coccyx
| |
| vertebral column and spinal cord muscles radiographs
| |
| UPPER LIMB
| |
| bones
| |
| shoulder
| |
| radiographsaxilla
| |
| upper arm
| |
| elbow
| |
| radiographsaxillaforearm
| |
| hand
| |
| radiographs
| |
| THORAX
| |
| bones
| |
| thoracic walls
| |
| heart
| |
| arteriograms
| |
| mediastinum and lungs
| |
| inlet, diaphragm and vessels
| |
| joints
| |
| radiographsaxilla
| |
| ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
| |
| anterior abdominal wall
| |
| upper abdominal viscera
| |
| liver
| |
| spleen
| |
| appendix
| |
| smal intestine
| |
| kidneys and suprarenal glands
| |
| posterior abdominal and pelvic wals
| |
| male inguinal region
| |
| female inguinal region
| |
| male pelvis
| |
| female pelvis
| |
| male perineum
| |
| female perineum
| |
| radiographs
| |
| LOWER LIMB
| |
| bones
| |
| gluteal region
| |
| thigh
| |
| hip joint
| |
| radiographsknee
| |
| radiograph
| |
| leg
| |
| ankle and foot
| |
| radiographs
| |
| APPENDIX
| |
| skeleton
| |
| arteries
| |
| veins
| |
| nerves
| |
| lymphatic system
| |
| muscles
| |
| skull foramina
| |
|
| |
|
| CYTOLOGY
| | [[Immune System]] |
| introduction
| |
| cell structure
| |
| epithelial tissues
| |
| connective tissues
| |
| blood and haemopoiesis
| |
| EMBRYOLOGY
| |
| introduction
| |
| sixual reproduction
| |
| growth and differentiation
| |
| the female gamete
| |
| the male gamete
| |
| fertilization
| |
| heredity and human genetics
| |
| early development fo the human embryoLOGYdifferentiation of the embryonic area
| |
| formation of the embryoLOGYnutrition of the embryoLOGYimplantation and placentation
| |
| skeletal development
| |
| branchial apparatus
| |
| development of locomotor structures
| |
| nerovous system and special sense organs
| |
| vascular system
| |
| digestive and respriatory system
| |
| urogenital system
| |
| prenatal growth
| |
| OSTEOLOGY
| |
| human skeletal morphology
| |
| skeletal connective tissues
| |
| structure of cartilage
| |
| bone as a tissue
| |
| histogenesis of bone
| |
| verebral characteristics
| |
| sternum and ribs
| |
| the skull
| |
| exterior of the skull
| |
| interior ofr th cranium
| |
| individual cranial bones
| |
| cranial growth and variation
| |
| appendicular skeleton
| |
| skeleton of upper limb
| |
| skeleton of lower limb
| |
| ARTHROLOGY
| |
| fibrous and cartlaginous joints
| |
| structure of synovial joints
| |
| movements and mechanisms of joints
| |
| temporomandibular joint
| |
| vertebral andthoracic articulations
| |
| joints of the upper limb
| |
| joints of the lower limb
| |
| MYOLOGY
| |
| introduction
| |
| skeletal muscle
| |
| cardiac muscle
| |
| non-striated muscle
| |
| form and actions fo skeletal muscle
| |
| fasciae and muscles of the hea
| |
| anterolateral nuchal muscles and fasciae
| |
| fasciae and muscles of the trunk
| |
| fasciae and muslces of th upper limb
| |
| fasciae and muscles of the lower limb
| |
| ANGIOLOGy
| |
| introduction and vascular structuresvascular patterns'
| |
| thoracic cavity and pericardium
| |
| the heart
| |
| aortic arch
| |
| carotid arterial system
| |
| subclavian arterial system
| |
| thoracic aorta
| |
| abdomanal aorta
| |
| ilia arterial system
| |
| cranial venous system
| |
| veins of the upper limb
| |
| thoracic veins
| |
| veins of the lower limb
| |
| abdominal veins
| |
| reticulo-endothelial and lymphatic system
| |
| the spleen
| |
| the thymus
| |
| regional lymph nodes and vessels
| |
| NEUROLOGY
| |
| general principles
| |
| neuroanatomical techniques
| |
| neurocytology
| |
| nervous system – divisions
| |
| spinal medulla or cord
| |
| myelencephalon – medulla oblongata
| |
| metencephalon-pons
| |
| cerebellum
| |
| mesencephalon-midbrain
| |
| reticular formation
| |
| diencaphalon
| |
| dorsal thalamus
| |
| epithalamus
| |
| ventral thalamus
| |
| hypothalamus
| |
| metathalamus
| |
| crebral surfaces
| |
| limbic lobe
| |
| crebral cortex-structure
| |
| cerebral cortex-areas
| |
| basal nuclei
| |
| meninges-cranial and spinal
| |
| peripheral nervous system
| |
| individual cranial nerves
| |
| mophology of cranial nerves
| |
| spinal nerves
| |
| dorsal spinal rami
| |
| cervical ventral spinal rami
| |
| thoracic ventral spinal rami
| |
| lumbar ventral spinal rami
| |
| sacral and coccygeal ventral spinal rami
| |
| autonomic nervous system
| |
| parasympathetic nervous system
| |
| sympathetic nervous system
| |
| major autonomic plexuses
| |
| gustatory apparatus
| |
| olfactory apparatus
| |
| visual apparatus
| |
| auditory and vestiular apparatus
| |
| integument-skin
| |
| SPLANCHNOLOGY
| |
| respiratory system
| |
| larynx
| |
| trachea and bronchi
| |
| pleurae
| |
| the mediastinum
| |
| lungs
| |
| alimentary system
| |
| the teeth
| |
| tongue, pharynx and oesophagus
| |
| the abdomen
| |
| peritoneum
| |
| gastro-intestinal tract
| |
| pancreas
| |
| liver
| |
| urogenital system
| |
| the urinary tract
| |
| reproductive organs – male
| |
| reproductive organs – female
| |
| endocrine glands
| |
|
| |
|
| | [[Respiratory System]] |
| | *[[respiratory system]] |
| | *[[mouth]] |
| | *[[nose & throat]] |
| | *[[lung]] |
|
| |
|
| I. INTRODUCTION AND SYSTEMIC OVERVIEW
| | [[Digestive System]] |
| Anatomical Nomenclature • Basic Structure and Function of Cells • Integrating Cells into Tissues
| | *[[digestive system]] |
| Systemic Overview:
| | *[[alimentary canal]] |
| Nervous System • Blood, Lymphoid Tissues and Haemopoiesis • Functional Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System • Smooth Muscle and the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic systems • Skin and its Appendages • Endocrine System: Principles of Hormone Production and Secretion • Embryogenesis • Prenatal and Neonatal Growth
| | *[[accessory organs]] |
| II. NEUROANATOMY
| | *[[mouth & throat]] |
| Overview of the Organization of the Nervous System • Autonomic Nervous System • Development of the Nervous System • Cranial Meninges • Ventricular System and Cerebrospinal Fluid • Vascular Supply of the Brain • Spinal Cord • Brain Stem • Cerebellum • Diencephalon • Cerebral Hemisphere • Basal Ganglia • Special Senses
| | *[[esophagus & stomach]] |
| III. HEAD AND NECK
| | *[[liver]] |
| Surface Anatomy of the Head and Neck • Overview of the Development of the Head and Neck
| | *[[gallbladder]] |
| Head:
| | *[[pancreas & duodenum]] |
| Skull and Mandible • Development of the Skull • Face and Scalp • Infratemporal Region and Temporomandibular Joint
| | *[[small intestine]] |
| Neck and Upper Aerodigestive Tract:
| | *[[large intestine]] |
| Neck • Nose, Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses and Pterygopalatine Fossa • Oral Cavity • Development of the Face and Neck • Pharynx • Larynx • Development of the Pharynx, Larynx and Oesophagus
| |
| Ear and Auditory and Vestibular Apparatus:
| |
| External and Middle Ear • Inner Ear • Development of the Ear
| |
| The Bony Orbit and Peripheral and Accessory Visual Apparatus:
| |
| The Orbit and its Contents • The Eye • Development of the Eye
| |
| IV. BACK AND MACROSCOPIC ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Back • The Back • Macroscopic Anatomy of the Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves • Development of the Vertebral Column
| |
| V. PECTORAL GIRDLE AND UPPER LIMB
| |
| General Organization and Surface Anatomy of the Upper Limb • Pectoral Girdle, Shoulder Region and Axilla • Upper Arm • Elbow • Forearm • Wrist and Hand • Overview of Development of the Limbs • Development of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb
| |
| VI. THORAX
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Thorax • Chest Wall • Breast Heart and Mediastinum:
| |
| Mediastinum • Heart and Great Vessels • Development of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
| |
| Lungs and Diaphragm:
| |
| Microstructure of the Trachea, Bronchi and Lungs • Pleura, Lungs, Trachea and Bronchi • Diaphragm and Phrenic Nerve • Development of the Trachea, Lungs and Diaphragm
| |
| VII. ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
| |
| Introduction:
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Abdomen and Pelvis • Anterior Abdominal Wall • Posterior Abdominal Wall and Retroperitoneum • Peritoneum and Peritoneal Cavity
| |
| Gastrointestinal Tract:
| |
| General Microstructure of the Gut Wall • Stomach and Abdominal Oesophagus
| |
| Small Intestine:
| |
| Microstructure of the Small Intestine • Duodenum • Jejunum and Ileum
| |
| Large Intestine:
| |
| Microstructure of the Large Intestine • Overview of the Large Intestine • Caecum • Vermiform Appendix • Ascending Colon • Transverse Colon • Descending Colon • Sigmoid Colon • Rectum • Anal Canal
| |
| Hepatobiliary System
| |
| Liver • Gall Bladder and Biliary Tree
| |
| Pancreas, Spleen and Suprarenal Gland:
| |
| Pancreas • Spleen • Suprarenal (Adrenal) Gland
| |
| Development of the Peritoneal Cavity, Gastrointestinal Tract and its Adnexae:
| |
| Development of the Peritoneal Cavity, Gastrointestinal Tract and its Adnexae
| |
| Kidney and Ureter:
| |
| Kidney • Ureter
| |
| Bladder, Prostate and Ureter:
| |
| Bladder • Male Urethra • Female Urethra • Prostate
| |
| Male Reproductive System:
| |
| Testes and Epididymes • Vas Deferens and Ejaculatory Ducts • Spermatic Cords and Scrotum • Penis • Accessory Glandular Structures
| |
| Female Reproductive System:
| |
| Ovaries • Uterine Tubes • Uterus • Implantation, Placentation, Pregnancy and Parturition • Vagina • Female External Genital Organs
| |
| True Pelvis, Pelvic Floor and Perineum:
| |
| True Pelvis, Pelvic Floor and Perineum
| |
| Development of the Urogenital System:
| |
| Development of the Urogenital System
| |
| VIII. PELVIC GIRDLE AND LOWER LIMB
| |
| General Organization and Surface Anatomy of the Lower Limb • Pelvic Girdle, Gluteal Region and Hip Joint • Thigh • Knee • Leg • Foot and Ankle • Development of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb
| |
| Eponyms
| |
| Index
| |
|
| |
|
| | [[Reproductive System]] |
| | *[[male reproductive systerm]] |
| | *[[female reproductive system]] |
|
| |
|
| I. INTRODUCTION AND SYSTEMIC OVERVIEW
| | *[[Excretory System]] ([[Urinary System]]) |
| Anatomical Nomenclature • Basic Structure and Function of Cells • Integrating Cells into Tissues
| | *[[urinary system]] |
| Systemic Overview:
| | *[[kidneys]] |
| Nervous System • Blood, Lymphoid Tissues and Haemopoiesis • Functional Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System • Smooth Muscle and the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic systems • Skin and its Appendages • Endocrine System: Principles of Hormone Production and Secretion • Embryogenesis • Prenatal and Neonatal Growth
| |
| II. NEUROANATOMY
| |
| Overview of the Organization of the Nervous System • Autonomic Nervous System • Development of the Nervous System • Cranial Meninges • Ventricular System and Cerebrospinal Fluid • Vascular Supply of the Brain • Spinal Cord • Brain Stem • Cerebellum • Diencephalon • Cerebral Hemisphere • Basal Ganglia • Special Senses
| |
| III. HEAD AND NECK
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Head and Neck • Overview of the Development of the Head and Neck
| |
| Head:
| |
| Skull and Mandible • Development of the Skull • Face and Scalp • Infratemporal Region and Temporomandibular Joint
| |
| Neck and Upper Aerodigestive Tract:
| |
| Neck • Nose, Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses and Pterygopalatine Fossa • Oral Cavity • Development of the Face and Neck • Pharynx • Larynx • Development of the Pharynx, Larynx and Oesophagus
| |
| Ear and Auditory and Vestibular Apparatus:
| |
| External and Middle Ear • Inner Ear • Development of the Ear
| |
| The Bony Orbit and Peripheral and Accessory Visual Apparatus:
| |
| The Orbit and its Contents • The Eye • Development of the Eye
| |
| IV. BACK AND MACROSCOPIC ANATOMY OF THE SPINAL CORD
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Back • The Back • Macroscopic Anatomy of the Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves • Development of the Vertebral Column
| |
| V. PECTORAL GIRDLE AND UPPER LIMB
| |
| General Organization and Surface Anatomy of the Upper Limb • Pectoral Girdle, Shoulder Region and Axilla • Upper Arm • Elbow • Forearm • Wrist and Hand • Overview of Development of the Limbs • Development of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limb
| |
| VI. THORAX
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Thorax • Chest Wall • Breast Heart and Mediastinum:
| |
| Mediastinum • Heart and Great Vessels • Development of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
| |
| Lungs and Diaphragm:
| |
| Microstructure of the Trachea, Bronchi and Lungs • Pleura, Lungs, Trachea and Bronchi • Diaphragm and Phrenic Nerve • Development of the Trachea, Lungs and Diaphragm
| |
| VII. ABDOMEN AND PELVIS
| |
| Introduction:
| |
| Surface Anatomy of the Abdomen and Pelvis • Anterior Abdominal Wall • Posterior Abdominal Wall and Retroperitoneum • Peritoneum and Peritoneal Cavity
| |
| Gastrointestinal Tract:
| |
| General Microstructure of the Gut Wall • Stomach and Abdominal Oesophagus
| |
| Small Intestine:
| |
| Microstructure of the Small Intestine • Duodenum • Jejunum and Ileum
| |
| Large Intestine:
| |
| Microstructure of the Large Intestine • Overview of the Large Intestine • Caecum • Vermiform Appendix • Ascending Colon • Transverse Colon • Descending Colon • Sigmoid Colon • Rectum • Anal Canal
| |
| Hepatobiliary System
| |
| Liver • Gall Bladder and Biliary Tree
| |
| Pancreas, Spleen and Suprarenal Gland:
| |
| Pancreas • Spleen • Suprarenal (Adrenal) Gland
| |
| Development of the Peritoneal Cavity, Gastrointestinal Tract and its Adnexae:
| |
| Development of the Peritoneal Cavity, Gastrointestinal Tract and its Adnexae
| |
| Kidney and Ureter:
| |
| Kidney • Ureter
| |
| Bladder, Prostate and Ureter:
| |
| Bladder • Male Urethra • Female Urethra • Prostate
| |
| Male Reproductive System:
| |
| Testes and Epididymes • Vas Deferens and Ejaculatory Ducts • Spermatic Cords and Scrotum • Penis • Accessory Glandular Structures
| |
| Female Reproductive System:
| |
| Ovaries • Uterine Tubes • Uterus • Implantation, Placentation, Pregnancy and Parturition • Vagina • Female External Genital Organs
| |
| True Pelvis, Pelvic Floor and Perineum:
| |
| True Pelvis, Pelvic Floor and Perineum
| |
| Development of the Urogenital System:
| |
| Development of the Urogenital System
| |
| VIII. PELVIC GIRDLE AND LOWER LIMB
| |
| General Organization and Surface Anatomy of the Lower Limb • Pelvic Girdle, Gluteal Region and Hip Joint • Thigh • Knee • Leg • Foot and Ankle • Development of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limb
| |
| Eponyms
| |
| Index
| |
The account of this former contributor was not re-activated after the server upgrade of March 2022.
Template:Systemic
The Triangular Bone (os triquetum; cuneiform bone) (Fig. 223).—The triangular bone may be distinguished by its pyramidal shape, and by an oval isolated facet for articulation with the pisiform bone. It is situated at the upper and ulnar side of the carpus. The superior surface presents a medial, rough, non-articular portion, and a lateral convex articular portion which articulates with the triangular articular disk of the wrist. The inferior surface, directed lateralward, is concave, sinuously curved, and smooth for articulation with the hamate. The dorsal surface is rough for the attachment of ligaments. The volar surface presents, on its medial part, an oval facet, for articulation with the pisiform; its lateral part is rough for ligamentous attachment. The lateral surface, the base of the pyramid, is marked by a flat, quadrilateral facet, for articulation with the lunate. The medial surface, the summit of the pyramid, is pointed and roughened, for the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist. 8
Articulations.—The triangular articulates with three bones: the lunate laterally, the pisiform in front, the hamate distally; and with the triangular articular disk which separates it from the lower end of the ulna.
The Triangular Bone (os triquetrum; cuneiform bone)
Template:Infobox Bone
The triquetral bone (also called triquetrum bone, cuneiform bone, pyramidal bone, cubital bone, three-cornered bone, and triangular bone) is located in the wrist on the medial side of the proximal row of the carpus between the lunate and pisiform bones. It is on the ulnar side of the hand, but does not articulate with the ulna. It connects with the pisiform, hamate, and lunate bones. It is the 3rd most commonly fractured carpal bone.
The triangular bone may be distinguished by its pyramidal shape, and by an oval isolated facet for articulation with the pisiform bone. It is situated at the upper and ulnar side of the carpus. To facilitate its palpation in an exam, the hand must be radially deviated so that the triquetrium moves out from under the ulnar styloid process. The triquetrum may be difficult to find, since it also lies under the pisiform.
The etymology derives from the Latin triquetrus which means "three-cornered."
Surfaces
The superior surface presents a medial, rough, non-articular portion, and a lateral convex articular portion which articulates with the triangular articular disk of the wrist.
The inferior surface, directed lateralward, is concave, sinuously curved, and smooth for articulation with the hamate. The dorsal surface is rough for the attachment of ligaments.
The volar surface presents, on its medial part, an oval facet, for articulation with the pisiform; its lateral part is rough for ligamentous attachment.
The lateral surface, the base of the pyramid, is marked by a flat, quadrilateral facet, for articulation with the lunate.
The medial surface, the summit of the pyramid, is pointed and roughened, for the attachment of the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist.
See also
Additional images
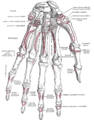
Bones of the left hand. Volar surface.
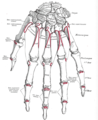
Bones of the left hand. Dorsal surface.
Template:Bones of upper extremity
Template:Musculoskeletal-stub
fr:Os triquetrum
nl:Os triquetrum
sk:Trojhranná kosť
By comparison, the term "palm" applies to only the palm (the grasping side) of the hand. The Romans actually used the word "palma" for the outstretched palm of the hand.
Topics in Anatomy
SYSTEMIC ANATOMY
Introduction and Systemic Overview
- Anatomical Nomenclature
- Basic Structure and Function of Cells
- Integrating Cells into Tissues
Systemic Overview
- Nervous System
- Blood, Lymphoid Tissues and Haemopoiesis
- Functional Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
- Smooth Muscle and the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic systems
- Skin and its Appendages
- Endocrine System
- Principles of Hormone Production and Secretion
- Embryology
- Embryogenesis
- Prenatal and Neonatal Growth
Integumentary System
Skeletal System
Muscular System
Nervous System
Endocrine System
Cardiovascular System (Circulatory System)
Lymphatic System
Immune System
Respiratory System
Digestive System
Reproductive System