Clean Water Act: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) (starting) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Clean Water Act''' usually refers to the ''Federal Water Pollution Control Act Amendments'' of 1972, | {{subpages}} | ||
The '''Clean Water Act''' usually refers to the ''Federal Water Pollution Control Act Amendments'' of 1972<ref>Clean Water Act Legislation https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-water-act</ref>, | |||
the overarching federal law for managing surface water quality in the [[United States of America/Definition|U.S.A.]]. The fundamental purpose of the Clean Water Act of 1972 has been widely communicated as making the nation’s waters “fishable and swimmable”. | |||
The 1972 Act was a major revision of the ''Federal Water Pollution Control Act'' of 1948. Later amendments were the ''Clean Water Act'' of 1977 and the ''Water Quality Act'' (WQA) of 1987. | |||
The 1972 Act employs regulatory and non-regulatory tools to reduce point sources of pollutant discharges into waterways, finance municipal wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The legislation's goal is to “restore and maintain the chemical, physical and biological integrity of the Nation’s waters” so as to improve “water quality which provides for the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish and wildlife and provides for recreation in and on the water”, wherever attainable. | |||
Numerous court cases about the law and its associated regulations have been fought, and continue to be fought, many through appeals up to the [[Supreme Court of the United States |Supreme court]]. | |||
==Statutory Provisions of the CWA== | |||
The CWA includes several major programs and delegations of authority. Below is a summary of the major statutory provisions related to coastal management: | |||
*'''NPDES permit program''' | |||
Covers point sources of pollution discharging into a surface water body. | |||
*'''Section 311''' | |||
Addresses oil spill pollution by providing EPA and the Coast Guard with authority to prevent and respond to oil spills. | |||
*'''Section 319 ''' | |||
Provides grants to address nonpoint sources of pollution, from sources such as farming and forestry operations. | |||
*'''Section 404''' | |||
Gives the US Army Corps of Engineers regulatory power over the placement of dredged or fill materials into wetlands. | |||
*'''Section 401''' | |||
Requires federal agencies to obtain certification from the states before issuing permits that would result in increased pollutant loads to a water body. | |||
*'''State Revolving Funds (SRF)''' | |||
Provides sizable federal loans to municipalities to address point and nonpoint sources. | |||
'''The CWA Signaled a Dramatically Different Approach to Pollution Abatement.''' The Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899 preceded the CWA as the principal mechanism by which water use permits were issued, including permits to discharge wastes to water bodies. Until 1872 the regulation of discharges to water bodies by the federal government, and by complementary legislation adopted by individual states, was based on the principle that any limitations to such discharges required a scientifically convincing demonstration that the discharge had an adverse impact on the receiving water body. This science-based requirement for cause and effect linkages was very difficult to demonstrate – particularly where multiple sources of pollution were flowing into a polluted water body. There was increasing evidence that this approach was producing increasingly severe water pollution in some areas and was not reducing pollution in others. After many years of debate a consensus emerged that water quality regulation should be based on the universal application of the best available pollution control technology to all discharges. This technology-based approach lies at the heart of the CWA. Application of best available technology has been a successful strategy for reducing point sources of pollution. It has been less successful for non-point sources which are not regulated under the CWA. | |||
'''Water Quality Standards.''' The first national water quality standards (WQS) were defined in 1965 and applied only to interstate waters – not water bodies that were contained within the boundaries of a single state. The water quality standards specified the uses of a water body and the attainment and maintenance of these uses was to be the basis for regulating discharges. This system proved to be ineffective due to its limitation to interstate waters and a lack of enforcement. Water quality standards continue to be used under the CWA and are used to designate the uses of the water body – recreation, water supply or agriculture - and specify the quantifiable pollutant concentrations to achieve the specified uses. However, under the CWA, these use standards are only used to condition permits after the technology-based standards have been met. If a water body continues to be impaired, permits may be changed based on more stringent WQS that require increased reductions in pollutants. | |||
==The Regulation of Point Sources of Water Pollution== | |||
'''The National Pollution Discharge Elimination System (NPDES)''' is the major mechanism for implementing the CWA. This requires that all industrial and government discharge facilities as well as animal feedlots obtain a permit for discharging pollutants to surface waters. Amendments to the act have added industrial and urban stormwater dischargers to the NPDES. Stringent regulations have been developed to address wet weather point sources like urban storm sewer systems and construction sites. The EPA administers the NPDES in partnership with the states. Forty-five states have been granted the authority by EPA to issue permits. | |||
'''The Evolution of CWA Strategies.''' | |||
Reducing point source pollutant discharge was the initial focus of the programs developed to implement the CWA with the assumption that control of point sources of pollution would lead to fishable and swimmable waters. Massive amounts of federal funds were directed to the states for construction of publically owned waste water treatment plants and industries had to make large investments in applying the best available treatment technologies to their effluents. Over time it was recognized that nonpoint sources of pollutants are as or more important that point sources. Figure 1 highlights the importance of addressing nonpoint sources of pollutants for various types of waters. | |||
'''Reduction of Nonpoint Sources of Pollution.''' | |||
Pollutants from nonpoint sources (NPS) include contamination from agriculture and urban stormwater runoff. The NPDES does not address these sources. However, in 1998, EPA reported that NPS were responsible for more than 40 percent of all impaired waters, while only 10 percent was caused by point source discharges <ref>EPA Watershed Academy Website: Introduction to the Clean Water Act https://cfpub.epa.gov/watertrain/pdf/modules/introtocwa.pdf</ref>. | |||
[[Image:Ranking of Sources Contributing to Water Quality Impairment.jpg|thumb|350px|center|Figure 1. Ranking of Sources Contributing to Water Quality Impairment]] | |||
In 1987, the EPA through the authority of the CWA created a federal grants program (Section 319) to address nonpoint sources of pollution. This voluntary program encourages states to develop nonpoint source (NPS) management programs. Funds provided to the states for NPS programs are used to create state regulations for NPS and to implement Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs). The federal government has applied only voluntary measures to address NPS. | |||
'''The Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) Strategy.''' The CWA mandates that if a water body is not meeting WQS through the use of technology-based controls, a means for meeting these standards must be developed. In these instances the most common approach is to produce a ‘pollution budget’ that is the basis for calculating the total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) that will meet the WQS. TMDLs were not applied during the first two decades of the CWA. While NPDES has been effective in reducing point source discharges, water bodies continue to need a more comprehensive strategy to address all sources, specifically nonpoint. TMDLs or equivalent comprehensive strategies for impaired waters are required by the act. EPA is encouraging states to apply TMDLs at the watershed scale in order to promote efficiencies, holistic analysis and collaboration across states. | |||
==The CWA Planning Process== | |||
The state-by-state process of implementing the CWA and planning the many activities that are undertaken is an iterative process with defined steps. One version of this process (which includes nonpoint sources) is shown in Figure 1. The progress made by each state is periodically reviewed and priorities for action are revised accordingly. | |||
[[Image:303d.png|thumb|450px|center|Figure 2. The Water Quality Based Approach to the CWA <ref>[https://www.epa.gov/tmdl/water-quality-based-approach-clean-water-act Water Quality-based Approach of the Clean Water Act] on the US EPA website, last access 8/26/2022</ref>]] | |||
'''Other Strategies to Reduce Nonpoint Sources.''' The CWA has drawn upon other programs administered by the EPA to address nonpoint sources of water pollution. | |||
These include: | |||
*The EPA’s watershed planning program that allows the EPA and states to address additional issues beyond the mandate of the CWA and engage citizens in the planning and implementation | |||
*The National Estuary Program. The CWA was amended in 1987 (Section 320) to establish the National Estuary Program (NEP). This program is designed specifically to improve the water quality of nationally important estuaries. States make a request to EPA to establish an NEP and develop a Comprehensive Conservation and Management Plan. NEPs can make use of TMDLs or other mechanisms to achieve water quality standards. NEPs encourage states to apply a watershed approach to managing and restoring water quality and habitat protection. | |||
*The Coastal Zone Management Act encourages a voluntary program for comprehensive land and water planning in the coastal zone that is designed specifically to contribute to CWA goals and programs. | |||
*Voluntary programs such as cost-sharing and education are other methods for addressing nonpoint runoff. | |||
==See also== | |||
===Internal Links=== | |||
*[[Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary – Case Study]] | |||
*[[US Coastal Zone Management Program]] | |||
*[[Coastal Barrier Resources System]] | |||
*[[Overview of Coastal Habitat Protection and Restoration in the United States]] | |||
*[[Essential Fish Habitat]] | |||
*[[Chesepeake Bay Program]] | |||
*[[US National Estuary Program]] | |||
*[[US National Estuarine Research Reserve System]] | |||
*[[US National Marine Sanctuaries]] | |||
*[[US National Wildlife Refuge System]] | |||
*[[Rhode Island Salt Pond Special Area Management Plan – Case Study]] | |||
*[[US Sea Grant College Program]] | |||
*[[Tampa Bay Estuary Program]] | |||
*[[US Army Corps of Engineers’ Coastal Programs]] | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
{{2Authors | |||
|AuthorID1=19106 | |||
|AuthorName1= Olsen | |||
|AuthorFullName1= Stephen Bloye Olsen | |||
|AuthorID2=19107 | |||
|AuthorName2= Ricci | |||
|AuthorFullName2= Glenn Ricci}} | |||
[[Category:Articles by Glenn Ricci]] | |||
[[Category:Coastal and marine pollution]] | |||
[[Category:Legislation and conventions]] | |||
[[Category:ICZM in the US]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 29 July 2024
The Clean Water Act usually refers to the Federal Water Pollution Control Act Amendments of 1972[1], the overarching federal law for managing surface water quality in the U.S.A.. The fundamental purpose of the Clean Water Act of 1972 has been widely communicated as making the nation’s waters “fishable and swimmable”.
The 1972 Act was a major revision of the Federal Water Pollution Control Act of 1948. Later amendments were the Clean Water Act of 1977 and the Water Quality Act (WQA) of 1987.
The 1972 Act employs regulatory and non-regulatory tools to reduce point sources of pollutant discharges into waterways, finance municipal wastewater treatment facilities, and manage polluted runoff. The legislation's goal is to “restore and maintain the chemical, physical and biological integrity of the Nation’s waters” so as to improve “water quality which provides for the protection and propagation of fish, shellfish and wildlife and provides for recreation in and on the water”, wherever attainable.
Numerous court cases about the law and its associated regulations have been fought, and continue to be fought, many through appeals up to the Supreme court.
Statutory Provisions of the CWA
The CWA includes several major programs and delegations of authority. Below is a summary of the major statutory provisions related to coastal management:
- NPDES permit program
Covers point sources of pollution discharging into a surface water body.
- Section 311
Addresses oil spill pollution by providing EPA and the Coast Guard with authority to prevent and respond to oil spills.
- Section 319
Provides grants to address nonpoint sources of pollution, from sources such as farming and forestry operations.
- Section 404
Gives the US Army Corps of Engineers regulatory power over the placement of dredged or fill materials into wetlands.
- Section 401
Requires federal agencies to obtain certification from the states before issuing permits that would result in increased pollutant loads to a water body.
- State Revolving Funds (SRF)
Provides sizable federal loans to municipalities to address point and nonpoint sources.
The CWA Signaled a Dramatically Different Approach to Pollution Abatement. The Rivers and Harbors Act of 1899 preceded the CWA as the principal mechanism by which water use permits were issued, including permits to discharge wastes to water bodies. Until 1872 the regulation of discharges to water bodies by the federal government, and by complementary legislation adopted by individual states, was based on the principle that any limitations to such discharges required a scientifically convincing demonstration that the discharge had an adverse impact on the receiving water body. This science-based requirement for cause and effect linkages was very difficult to demonstrate – particularly where multiple sources of pollution were flowing into a polluted water body. There was increasing evidence that this approach was producing increasingly severe water pollution in some areas and was not reducing pollution in others. After many years of debate a consensus emerged that water quality regulation should be based on the universal application of the best available pollution control technology to all discharges. This technology-based approach lies at the heart of the CWA. Application of best available technology has been a successful strategy for reducing point sources of pollution. It has been less successful for non-point sources which are not regulated under the CWA.
Water Quality Standards. The first national water quality standards (WQS) were defined in 1965 and applied only to interstate waters – not water bodies that were contained within the boundaries of a single state. The water quality standards specified the uses of a water body and the attainment and maintenance of these uses was to be the basis for regulating discharges. This system proved to be ineffective due to its limitation to interstate waters and a lack of enforcement. Water quality standards continue to be used under the CWA and are used to designate the uses of the water body – recreation, water supply or agriculture - and specify the quantifiable pollutant concentrations to achieve the specified uses. However, under the CWA, these use standards are only used to condition permits after the technology-based standards have been met. If a water body continues to be impaired, permits may be changed based on more stringent WQS that require increased reductions in pollutants.
The Regulation of Point Sources of Water Pollution
The National Pollution Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) is the major mechanism for implementing the CWA. This requires that all industrial and government discharge facilities as well as animal feedlots obtain a permit for discharging pollutants to surface waters. Amendments to the act have added industrial and urban stormwater dischargers to the NPDES. Stringent regulations have been developed to address wet weather point sources like urban storm sewer systems and construction sites. The EPA administers the NPDES in partnership with the states. Forty-five states have been granted the authority by EPA to issue permits.
The Evolution of CWA Strategies. Reducing point source pollutant discharge was the initial focus of the programs developed to implement the CWA with the assumption that control of point sources of pollution would lead to fishable and swimmable waters. Massive amounts of federal funds were directed to the states for construction of publically owned waste water treatment plants and industries had to make large investments in applying the best available treatment technologies to their effluents. Over time it was recognized that nonpoint sources of pollutants are as or more important that point sources. Figure 1 highlights the importance of addressing nonpoint sources of pollutants for various types of waters.
Reduction of Nonpoint Sources of Pollution. Pollutants from nonpoint sources (NPS) include contamination from agriculture and urban stormwater runoff. The NPDES does not address these sources. However, in 1998, EPA reported that NPS were responsible for more than 40 percent of all impaired waters, while only 10 percent was caused by point source discharges [2].
In 1987, the EPA through the authority of the CWA created a federal grants program (Section 319) to address nonpoint sources of pollution. This voluntary program encourages states to develop nonpoint source (NPS) management programs. Funds provided to the states for NPS programs are used to create state regulations for NPS and to implement Total Maximum Daily Loads (TMDLs). The federal government has applied only voluntary measures to address NPS.
The Total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) Strategy. The CWA mandates that if a water body is not meeting WQS through the use of technology-based controls, a means for meeting these standards must be developed. In these instances the most common approach is to produce a ‘pollution budget’ that is the basis for calculating the total Maximum Daily Load (TMDL) that will meet the WQS. TMDLs were not applied during the first two decades of the CWA. While NPDES has been effective in reducing point source discharges, water bodies continue to need a more comprehensive strategy to address all sources, specifically nonpoint. TMDLs or equivalent comprehensive strategies for impaired waters are required by the act. EPA is encouraging states to apply TMDLs at the watershed scale in order to promote efficiencies, holistic analysis and collaboration across states.
The CWA Planning Process
The state-by-state process of implementing the CWA and planning the many activities that are undertaken is an iterative process with defined steps. One version of this process (which includes nonpoint sources) is shown in Figure 1. The progress made by each state is periodically reviewed and priorities for action are revised accordingly.
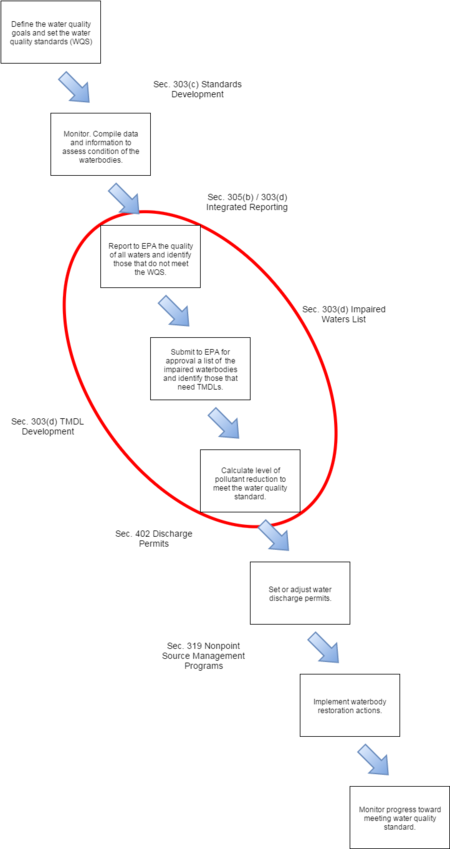
Other Strategies to Reduce Nonpoint Sources. The CWA has drawn upon other programs administered by the EPA to address nonpoint sources of water pollution. These include:
- The EPA’s watershed planning program that allows the EPA and states to address additional issues beyond the mandate of the CWA and engage citizens in the planning and implementation
- The National Estuary Program. The CWA was amended in 1987 (Section 320) to establish the National Estuary Program (NEP). This program is designed specifically to improve the water quality of nationally important estuaries. States make a request to EPA to establish an NEP and develop a Comprehensive Conservation and Management Plan. NEPs can make use of TMDLs or other mechanisms to achieve water quality standards. NEPs encourage states to apply a watershed approach to managing and restoring water quality and habitat protection.
- The Coastal Zone Management Act encourages a voluntary program for comprehensive land and water planning in the coastal zone that is designed specifically to contribute to CWA goals and programs.
- Voluntary programs such as cost-sharing and education are other methods for addressing nonpoint runoff.
See also
Internal Links
- Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary – Case Study
- US Coastal Zone Management Program
- Coastal Barrier Resources System
- Overview of Coastal Habitat Protection and Restoration in the United States
- Essential Fish Habitat
- Chesepeake Bay Program
- US National Estuary Program
- US National Estuarine Research Reserve System
- US National Marine Sanctuaries
- US National Wildlife Refuge System
- Rhode Island Salt Pond Special Area Management Plan – Case Study
- US Sea Grant College Program
- Tampa Bay Estuary Program
- US Army Corps of Engineers’ Coastal Programs
References
- ↑ Clean Water Act Legislation https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-clean-water-act
- ↑ EPA Watershed Academy Website: Introduction to the Clean Water Act https://cfpub.epa.gov/watertrain/pdf/modules/introtocwa.pdf
- ↑ Water Quality-based Approach of the Clean Water Act on the US EPA website, last access 8/26/2022