Gabapentin: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
''' | {{Chem infobox | ||
|align=right | |||
|image=[[Image:Gabapentin.jpg|center|thumb|220px]] | |||
|width=220px | |||
|molname=gabapentin | |||
|synonyms= '''neurontin''' | |||
|molformula= C<sub>9</sub>H<sub>17</sub>NO<sub>2</sub> | |||
|molmass= 171.24 | |||
|uses=epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia | |||
|properties= | |||
|hazards= | |||
|iupac= 1-(aminomethyl)cyclohexaneacetic acid | |||
|casnumber= | |||
}} | |||
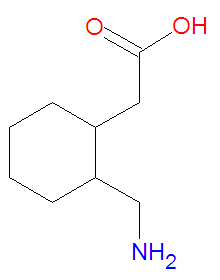
In [[pharmacology]], '''gabapentin''', trademarked '''Neurontin''', is structurally similar to [[pregabalin]]. It is an analog of [[gamma-aminobutyric acid]] (GABA), the major inhibitory [[neurotransmitter]] in the [[central nervous system]]. Gabapentin is centrally active agonist of GABA.<ref>McNamara James O, "Chapter 19. Pharmacotherapy of the Epilepsies" (Chapter). Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL: Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 11e: http://www.accessmedicine.com/content.aspx?aID=939716.</ref> Gabapentin is used for [[epilepsy]] and [[neurogenic pain]]. | |||
==History== | |||
Neurontin brand of gabapentin was approved by the [[Food and Drug Administration]] in the [[United States of America]] with a [http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDevelopedandApproved/ApprovalApplications/NewDrugApplicationNDA/ New Drug Application] (NDA) for Pfizer in 1993.<ref>[http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.SearchAction&SearchType=BasicSearch&Search_Button=Submit&searchTerm=020235 Drugs@FDA]. U S Food and Drug Administration</ref> A generic version was approved with a [http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDevelopedandApproved/ApprovalApplications/AbbreviatedNewDrugApplicationANDAGenerics/ Abbreviated New Drug Application] (ANDA) in 2003.<ref>[http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/drugsatfda/index.cfm?fuseaction=Search.SearchAction&SearchType=BasicSearch&Search_Button=Submit&searchTerm=075350 Drugs@FDA]. U S Food and Drug Administration</ref> | |||
==Pharmacology== | |||
===Administration=== | |||
===Distribution=== | |||
===Metabolism=== | |||
===Excretion=== | |||
===Toxicity=== | |||
==Effectiveness== | ==Effectiveness== | ||
===Pain=== | |||
Regarding the treatment of [[diabetic neuropathy]] or [[postherpetic neuralgia]], a [[randomized controlled trial]] found that while gabapentin was not as effective as morphine, the combination of the two medications was more effective than either alone and allowed for a lower dose of morphine.<ref name="pmid15800228">{{cite journal |author=Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Weaver DF, Houlden RL |title=Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=352 |issue=13 |pages=1324–34 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15800228 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa042580 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=15800228&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn=}}</ref> | Regarding the treatment of [[diabetic neuropathy]] or [[postherpetic neuralgia]], a [[randomized controlled trial]] found that while gabapentin was not as effective as morphine, the combination of the two medications was more effective than either alone and allowed for a lower dose of morphine.<ref name="pmid15800228">{{cite journal |author=Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Weaver DF, Houlden RL |title=Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=352 |issue=13 |pages=1324–34 |year=2005 |month=March |pmid=15800228 |doi=10.1056/NEJMoa042580 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=15800228&promo=ONFLNS19 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
Regarding the treatment of [[low back pain]], a [[systematic review]] found that gabapentin may be effective.<ref name="pmid17909211">{{cite journal |author=Chou R, Huffman LH |title=Medications for acute and chronic low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society/American College of Physicians clinical practice guideline |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=147 |issue=7 |pages=505–14 |year=2007 |month=October |pmid=17909211 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=reprint&pmid=17909211 |issn=}}</ref> | Regarding the treatment of [[low back pain]], a [[systematic review]] found that gabapentin may be effective.<ref name="pmid17909211">{{cite journal |author=Chou R, Huffman LH |title=Medications for acute and chronic low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society/American College of Physicians clinical practice guideline |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=147 |issue=7 |pages=505–14 |year=2007 |month=October |pmid=17909211 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=reprint&pmid=17909211 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
For partial [[epilepsy]], the SANAD [[randomized controlled trial]] compared [[carbamazepine]], gabapentin, [[lamotrigine]], [[oxcarbazepine]], or [[topiramate]] and concluded that gabapentin was less effective.<ref name="pmid17382827">{{cite journal |author=Marson AG, Al-Kharusi AM, Alwaidh M, ''et al'' |title=The SANAD study of effectiveness of carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, or topiramate for treatment of partial epilepsy: an unblinded randomised controlled trial |journal=Lancet |volume=369 |issue=9566 |pages=1000–15 |year=2007 |month=March |pmid=17382827 |pmc=2080688 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60460-7 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(07)60460-7 |issn=}}</ref> | ===Seizures=== | ||
For partial [[epilepsy]], the SANAD [[randomized controlled trial]] compared [[carbamazepine]], gabapentin, [[lamotrigine]], [[oxcarbazepine]], or [[topiramate]] and concluded that gabapentin was less effective.<ref name="pmid17382827">{{cite journal |author=Marson AG, Al-Kharusi AM, Alwaidh M, ''et al'' |title=The SANAD study of effectiveness of carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, or topiramate for treatment of partial epilepsy: an unblinded randomised controlled trial |journal=Lancet |volume=369 |issue=9566 |pages=1000–15 |year=2007 |month=March |pmid=17382827 |pmc=2080688 |doi=10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60460-7 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(07)60460-7 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
===Comparison to antidepressants=== | ===Comparison to antidepressants=== | ||
Regarding the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury, a [[randomized controlled trial]] found that [[amitriptyline]] was more effective than active placebo and possibly better than gabapentin among patients with symptoms of [[depression]] while neither gabapentin nor [[amitriptyline]] helped patients without depression although there was a statistically insignificant trend favoring [[amitriptyline]].<ref name="pmid18047869">{{cite journal |author=Rintala DH, Holmes SA, Courtade D, Fiess RN, Tastard LV, Loubser PG |title=Comparison of the effectiveness of amitriptyline and gabapentin on chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury |journal=Arch Phys Med Rehabil |volume=88 |issue=12 |pages=1547–60 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18047869 |doi=10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.038 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0003-9993(07)01541-9 |issn=}}</ref> | Regarding the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury, a [[randomized controlled trial]] found that [[amitriptyline]] was more effective than active placebo and possibly better than gabapentin among patients with symptoms of [[depression]] while neither gabapentin nor [[amitriptyline]] helped patients without depression although there was a statistically insignificant trend favoring [[amitriptyline]].<ref name="pmid18047869">{{cite journal |author=Rintala DH, Holmes SA, Courtade D, Fiess RN, Tastard LV, Loubser PG |title=Comparison of the effectiveness of amitriptyline and gabapentin on chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury |journal=Arch Phys Med Rehabil |volume=88 |issue=12 |pages=1547–60 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18047869 |doi=10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.038 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0003-9993(07)01541-9 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
In a randomized | In a randomized [[cross-over study]], [[amitriptyline]] provided moderate or greater pain relief in 67% of patients as compared to 52% with gabapentin. In this small study, this result did not have [[statistical significance]].<ref name="pmid10493324">{{cite journal |author=Morello CM, Leckband SG, Stoner CP, Moorhouse DF, Sahagian GA |title=Randomized double-blind study comparing the efficacy of gabapentin with amitriptyline on diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain |journal=Arch. Intern. Med. |volume=159 |issue=16 |pages=1931–7 |year=1999 |month=September |pmid=10493324 |doi= |url=http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10493324 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
===Veterinary use=== | |||
As an off-label indication, it is finding considerable use as a general-purpose oral pain reliever in [[cat]]s and [[dog]]s. | |||
==Legal action== | ==Legal action== | ||
In the case of ''United States ex. rel David Franklin vs. Pfizer, Inc., and Parke-Davis, Division of Warner-Lambert Company'', "in 2004 the Pfizer subsidiary Warner-Lambert settled litigation and admitted guilt in connection to charges that during the 1990s it violated federal regulations by promoting the drug for [[pain]], psychiatric conditions, [[migraine]], and other unapproved uses."<ref name="pmid16908919">{{cite journal |author=Steinman MA, Bero LA, Chren MM, Landefeld CS |title=Narrative review: the promotion of gabapentin: an analysis of internal industry documents |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=145 |issue=4 |pages=284–93 |year=2006 |month=August |pmid=16908919 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=reprint&pmid=16908919 |issn=}}</ref> | In the case of ''United States ex. rel David Franklin vs. Pfizer, Inc., and Parke-Davis, Division of Warner-Lambert Company'', "in 2004 the Pfizer subsidiary Warner-Lambert settled litigation and admitted guilt in connection to charges that during the 1990s it violated federal regulations by promoting the drug for [[pain]], psychiatric conditions, [[migraine]], and other unapproved uses."<ref name="pmid16908919">{{cite journal |author=Steinman MA, Bero LA, Chren MM, Landefeld CS |title=Narrative review: the promotion of gabapentin: an analysis of internal industry documents |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=145 |issue=4 |pages=284–93 |year=2006 |month=August |pmid=16908919 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=reprint&pmid=16908919 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
==External links== | |||
{{CZMed}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 19 August 2024
|
| |||||||
| gabapentin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | epilepsy, postherpetic neuralgia | ||||||
| Properties: | |||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
In pharmacology, gabapentin, trademarked Neurontin, is structurally similar to pregabalin. It is an analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Gabapentin is centrally active agonist of GABA.[1] Gabapentin is used for epilepsy and neurogenic pain.
History
Neurontin brand of gabapentin was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in the United States of America with a New Drug Application (NDA) for Pfizer in 1993.[2] A generic version was approved with a Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) in 2003.[3]
Pharmacology
Administration
Distribution
Metabolism
Excretion
Toxicity
Effectiveness
Pain
Regarding the treatment of diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia, a randomized controlled trial found that while gabapentin was not as effective as morphine, the combination of the two medications was more effective than either alone and allowed for a lower dose of morphine.[4]
Regarding the treatment of low back pain, a systematic review found that gabapentin may be effective.[5]
Seizures
For partial epilepsy, the SANAD randomized controlled trial compared carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, or topiramate and concluded that gabapentin was less effective.[6]
Comparison to antidepressants
Regarding the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury, a randomized controlled trial found that amitriptyline was more effective than active placebo and possibly better than gabapentin among patients with symptoms of depression while neither gabapentin nor amitriptyline helped patients without depression although there was a statistically insignificant trend favoring amitriptyline.[7]
In a randomized cross-over study, amitriptyline provided moderate or greater pain relief in 67% of patients as compared to 52% with gabapentin. In this small study, this result did not have statistical significance.[8]
Veterinary use
As an off-label indication, it is finding considerable use as a general-purpose oral pain reliever in cats and dogs.
Legal action
In the case of United States ex. rel David Franklin vs. Pfizer, Inc., and Parke-Davis, Division of Warner-Lambert Company, "in 2004 the Pfizer subsidiary Warner-Lambert settled litigation and admitted guilt in connection to charges that during the 1990s it violated federal regulations by promoting the drug for pain, psychiatric conditions, migraine, and other unapproved uses."[9]
External links
The most up-to-date information about Gabapentin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Gabapentin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Gabapentin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Gabapentin - Detailed information from DrugBank.
References
- ↑ McNamara James O, "Chapter 19. Pharmacotherapy of the Epilepsies" (Chapter). Brunton LL, Lazo JS, Parker KL: Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, 11e: http://www.accessmedicine.com/content.aspx?aID=939716.
- ↑ Drugs@FDA. U S Food and Drug Administration
- ↑ Drugs@FDA. U S Food and Drug Administration
- ↑ Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Weaver DF, Houlden RL (March 2005). "Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain". N. Engl. J. Med. 352 (13): 1324–34. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa042580. PMID 15800228. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Chou R, Huffman LH (October 2007). "Medications for acute and chronic low back pain: a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society/American College of Physicians clinical practice guideline". Ann. Intern. Med. 147 (7): 505–14. PMID 17909211. [e]
- ↑ Marson AG, Al-Kharusi AM, Alwaidh M, et al (March 2007). "The SANAD study of effectiveness of carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, oxcarbazepine, or topiramate for treatment of partial epilepsy: an unblinded randomised controlled trial". Lancet 369 (9566): 1000–15. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60460-7. PMID 17382827. PMC 2080688. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Rintala DH, Holmes SA, Courtade D, Fiess RN, Tastard LV, Loubser PG (December 2007). "Comparison of the effectiveness of amitriptyline and gabapentin on chronic neuropathic pain in persons with spinal cord injury". Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88 (12): 1547–60. DOI:10.1016/j.apmr.2007.07.038. PMID 18047869. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Morello CM, Leckband SG, Stoner CP, Moorhouse DF, Sahagian GA (September 1999). "Randomized double-blind study comparing the efficacy of gabapentin with amitriptyline on diabetic peripheral neuropathy pain". Arch. Intern. Med. 159 (16): 1931–7. PMID 10493324. [e]
- ↑ Steinman MA, Bero LA, Chren MM, Landefeld CS (August 2006). "Narrative review: the promotion of gabapentin: an analysis of internal industry documents". Ann. Intern. Med. 145 (4): 284–93. PMID 16908919. [e]