Defense Intelligence Agency: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "SIGINT" to "SIGINT") |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "United States Central Command" to "United States Central Command") |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{PropDel}}<br><br> | |||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{TOC|right}} | {{TOC|right}} | ||
| Line 4: | Line 5: | ||
Functional Component Command for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (JFCC-ISR) of the U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). | Functional Component Command for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (JFCC-ISR) of the U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). | ||
As opposed to the [[Central Intelligence Agency]] or Bureau of Intelligence and Research , DIA coordinates but does not necessarily control a wide range of other intelligence agencies. In particular, it draws information from, and supplies information to, the intelligence components of Unified Combatant Commands such as the | As opposed to the [[Central Intelligence Agency]] or Bureau of Intelligence and Research , DIA coordinates but does not necessarily control a wide range of other intelligence agencies. In particular, it draws information from, and supplies information to, the intelligence components of Unified Combatant Commands such as the United States Central Command and U.S. Pacific Command. Those intelligence components, however, are ultimately responsible to their commanders, not DIA. DIA has a more authoritative role in working with national-level specialist organizations such as the National Ground Intelligence Center, run by the Army. Its authority comes from a [[Department of Defense]] directive, rather than explicit legislation. <ref name=DoDdir5105.21-2008>{{citation | ||
| author = Department of Defense | | author = Department of Defense | ||
| title = DoD Directive 5105.21: Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) | | title = DoD Directive 5105.21: Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) | ||
| Line 25: | Line 26: | ||
| first = Jim | last = Garamone | | first = Jim | last = Garamone | ||
| date =21 September 2006 | | date =21 September 2006 | ||
}}</ref> According to Maples, the JFCC is “a place to operate at the defense level with national capabilities, but more importantly to respond to the needs of combatant commanders,” he said. It allows intelligence planners to align defense intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance operations from a global perspective, leveraging DIA’s collection-management experience and capabilities. Historically, USSTRATCOM and its predecessors operated high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft such as the [[U-2 Dragon Lady]], various large airborne SIGINT and | }}</ref> According to Maples, the JFCC is “a place to operate at the defense level with national capabilities, but more importantly to respond to the needs of combatant commanders,” he said. It allows intelligence planners to align defense intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance operations from a global perspective, leveraging DIA’s collection-management experience and capabilities. Historically, USSTRATCOM and its predecessors operated high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft such as the [[U-2 Dragon Lady]], various large airborne SIGINT and MASINT aircraft such as the RC-135 RIVET JOINT and [[RC-135 COBRA BALL]], and now high-altitude [[unmanned aerial vehicle]]s such as the [[RQ-4A Global Hawk]]. Note that the [[National Reconnaissance Office]] retains responsibility for operating ISR systems in space. USSTRATCOM provides the operational view and the DIA provides the combat support view of the closely related ISR assets. | ||
Another responsibility that DIA shares with a Unified Combatant Command, the U.S. Joint Forces Command (USJFCOM), is supporting recovery of [[Prisoner of War|Prisoners of War]] (POW) and [[Missing in Action|personnel Missing in Action (MIA)]]. <ref name=POWMIA>{{citation | Another responsibility that DIA shares with a Unified Combatant Command, the U.S. Joint Forces Command (USJFCOM), is supporting recovery of [[Prisoner of War|Prisoners of War]] (POW) and [[Missing in Action|personnel Missing in Action (MIA)]]. <ref name=POWMIA>{{citation | ||
| Line 191: | Line 192: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist|2}} | {{Reflist|2}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:33, 3 September 2024
| This article may be deleted soon. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
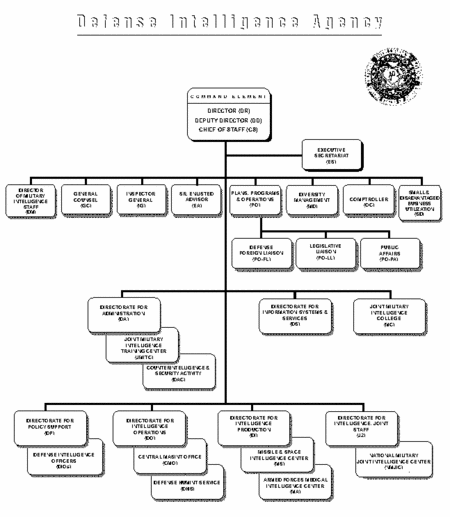
Formed in 1962, the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an organization in the United States Department of Defense. In an ideal world, its responsibilities include those intelligence activities that are of principally military interest but not clearly associated with one military service, intelligence support to the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and participating in the process of producing United States intelligence community (IC) national estimates and other high-level analysis. As of March 2009, the Director is LTG Ronald Burgess, U.S. Army. The DIA director is "dual hatted" as the commander of the Joint Functional Component Command for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (JFCC-ISR) of the U.S. Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). As opposed to the Central Intelligence Agency or Bureau of Intelligence and Research , DIA coordinates but does not necessarily control a wide range of other intelligence agencies. In particular, it draws information from, and supplies information to, the intelligence components of Unified Combatant Commands such as the United States Central Command and U.S. Pacific Command. Those intelligence components, however, are ultimately responsible to their commanders, not DIA. DIA has a more authoritative role in working with national-level specialist organizations such as the National Ground Intelligence Center, run by the Army. Its authority comes from a Department of Defense directive, rather than explicit legislation. [1] In addition, it does have the IC-wide operational control of measurement and signature intelligence, as well as some military-specific human-source intelligence operations. DoD Directive 5105.21, “Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA),” February 18, 1997 (hereby canceled) One could think of DIA is a mini-United States intelligence community (IC), coordinating a set of intelligence organizations within the United States Department of Defense, agencies that directly support commanders or focus on technical areas within the special interest of a service. DIA does not control other major intelligence agencies within DoD, such as the National Security Agency (NSA), National Reconnaissance Office (NRO), or National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). DIA, however, is coequal to NSA, NRO, or NGA in the IC. The Agency is led by a three-star general or flag officer with a senior civilian executive as deputy. The Chief of Staff is a senior civilian executive who oversees the operations of the staff of the headquarters element. There is a Command Staff, but DIA’s intelligence analysis and production capabilities are located in three directorates.
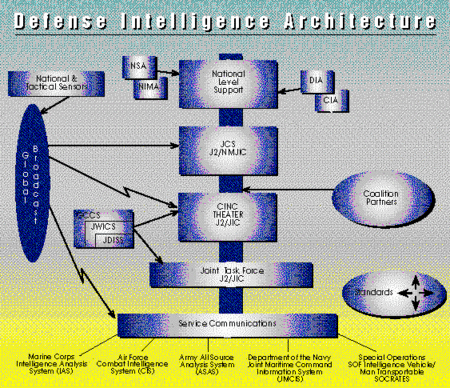
There are also Directorates for Information Systems and Administration, as well as the Joint Military Intelligence College. The DIA Director, currently Army LTG Michael Maples, also heads the U.S. Strategic Command (USSOCOM) Joint Functional Component Command for Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance (ISR).[2] According to Maples, the JFCC is “a place to operate at the defense level with national capabilities, but more importantly to respond to the needs of combatant commanders,” he said. It allows intelligence planners to align defense intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance operations from a global perspective, leveraging DIA’s collection-management experience and capabilities. Historically, USSTRATCOM and its predecessors operated high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft such as the U-2 Dragon Lady, various large airborne SIGINT and MASINT aircraft such as the RC-135 RIVET JOINT and RC-135 COBRA BALL, and now high-altitude unmanned aerial vehicles such as the RQ-4A Global Hawk. Note that the National Reconnaissance Office retains responsibility for operating ISR systems in space. USSTRATCOM provides the operational view and the DIA provides the combat support view of the closely related ISR assets. Another responsibility that DIA shares with a Unified Combatant Command, the U.S. Joint Forces Command (USJFCOM), is supporting recovery of Prisoners of War (POW) and personnel Missing in Action (MIA). [3]. It is quite likely that any clandestine recovery missions would also involve the U.S. Special Operations Command (USSOCOM). It is worth considering the information architecture before going into the work of the Command Staff and the Directorates. ArchitectureDuring a crisis, the formal flow for intelligence requirements from all echelons in support of joint operations is through the National Military Joint Intelligence Center (NMJIC) — the focal point for all Defense Intelligence crisis operations and activities. [4] The Unified Commands’ Joint Intelligence Centers (JICs) and Joint Intelligence Support Elements (JISEs), subordinate to task-organized Joint Task Forces (JTFs), are the principal organizations that support joint warfighting at the operational and tactical levels. Within a UCC, the JIC concept fuses into a one-stop shopping center for intelligence support. A particular JIC cannot be expected to satisfy every intelligence requirement completely; however, it can coordinate support, and draw on resources, from other intelligence organizations above and below its echelon. Because the JIC is the focal point for intelligence operations, the JIC may draw upon additional resources (including military reserves) in coordination with the Joint Staff, DIA and the military services. A subordinate joint force, when established, forms a JISE as a tailored subset of the theater JIC. JISEs are established to meet the particular needs of subordi-nate joint forces and therefore do not replicate every facet of JIC operations.[4] Command StaffThe headquarters or command element of DIA consists of several staffs and offices. For the Director’s Defense Intelligence Community responsibilities, the Director, Military Intelligence Staff (DM), provides plans, policies, and programs to manage the resources that support the Defense Intelligence Agency, Services, and Unified Commands. This management or coordination of pro-grams includes the General Defense Intelligence Program (GDIP) and part of the Joint Military Intelligence Program (JMIP). DM also provides support to the Military Intelligence Board (MIB) and manages the Reserve forces assigned to Defense Intelligence. The Plans, Programs, and Operations Staff (PO) is responsible for internal planning and programming, liaison with Congress, the press and the public, and foreign attaches. The Command Element’s immediate support staff is the Executive Secretariat (ES). ES provides administrative, staff and service support to the Command Element; facilitates effective communications/sup-port links between and among the Command Element and all subordinate line and staff elements; and maintains and manages the Agency-wide Automated Tasking System.The Command Element also contains key offices for legal, fiscal, and oversight responsibilities. J-2 versus Director of DIA functionsThere is a legally and bureaucratically complex relationship among DIA and the Joint Staff. Any senior level military staff, the Joint Staff certainly among them, has an intelligence directorate. The problem comes from the National Security Act of 1947, which created the Joint Staff, but strictly limited its size. Other directorates tend not to be as large as intelligence (J-2), because they are fed by the planning, operations and logistics staffs of Unified Combatant Commands and other organization. The J-2 function, however, has a national-level production function and needs a larger staff, larger than could be accommodated within the Joint Staff limits.[5] Some of the factors that led to intelligence reorganizations in the National Security Act of 1947 were Congressional investigations into C3I that lead to the surprise of the attack on Pearl Harbor "Operational and intelligence work required centralization of authority and clear-cut allocation of responsibility," the joint committee wrote. The National Security Act of 1947 was the first step toward reordering an outmoded system, but it focused on general military organization and the structure of national intelligence, but not specifically military intelligence. In WWII, the JCS had a Joint Intelligence Committee (JIC) within the Joint Staff, rather than the "J-2" directorate that would be typical of a high-level staff. Its purpose had been to furnish "agreed military intelligence" in various forms to other agencies of the JCS and represent them on the Allied wartime Combined Intelligence Committee. The JIC did not unify military intelligence components, and it failed to produce composite national intelligence estimates.[5] The Joint Chiefs of Staff were responsible in their corporate character for providing jointly agreed intelligence to the Secretary of Defense and to the heads of the Unified and Specified Commands, the old name for the Unified Combatant Commands.
The Hoover Commission of 1948 examined the overall national security apparatus, and observed the "National Military Establishment", or the "unified" organization that did not yet have a single strong leader. It lacked "centralized authority" which "should be placed firmly in the Secretary of Defense." This would lead to the Defense Reorganization Act of 1949, which strengthened the authority of the SecDef, although the present system would wait for the Goldwater-Nichols Act of 1996. Moreover, "... the continuance of intense interservice rivalries hampers and confuses sound policy at many points. One of our greatest needs is to elevate military thinking to a plane above individual service aims and ambitions." As for the JCS, they were described as "... too remote from related groups ..." such as the National Security Council and the CIA. "... A spirit of teamwork must govern interagency intelligence relationships." The committee observed that the small size of the JIG led to:
The Department of Defense Reorganization Act of 1958 stemmed from a widespread belief in the 1950's that the Defense Department needed major revision to provide for more effective, efficient, and economical administration, to eliminate duplication, and to encourage more comprehensive policies and programs. The intelligence system was not "in consonance with the objectives of the 1958 Act" which specified strengthening the channels of command from the President to the "combatant forces." Thus, the 1958 Act resolved several asymmetries concerning the "vague authority" of the Secretary of Defense. The Act removed all doubts about the Secretary's authority and placed the JCS in the chain of command, particularly in terms of responsibility for intelligence support to the Unified and Specified Commands. Overall, the Act extended the centralization processes underway in DoD since 1947. J-2 created, 1959In November 1959, seven directorates (J-1 through J-6, plus a directorate for military assistance) had been established in the JCS, including J-2, Directorate for Intelligence. The Joint Staff expanded from 210 to 400 officer billets for the seven directorates as one of the provisos of the 1958 Defense Reorganization Act. Upon taking office in 1961, Secretary of Defense, Robert S. McNamara, conveyed his decision to establish a Defense Intelligence Agency in an 8 February memorandum to the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Significantly, his deputy's recommended method of implementation, that is, an "evolutionary process," was incorporated into the final plan for activating DIA. This included assuming all responsibilities of the J-2 of the JCS. In 1961, the SecDef created DIA with a directive, which stated DIA's primary operational responsibilities, according to the directive establishing it, were: [6] fell within nine general areas. The table below describes these areas, and contrasts them with 2008 missions.
DIA and the J-2--1961-1991The J-2, until its abolishment on 28 June 1963, depended fully upon DIA's Office of Estimates to provide substantive intelligence. During this period, formal JCS actions (such as the review of the operations and contingency plans of the Unified and Specified Commands) continued to be staffed by the J-2, while the Office of Estimates directly received spot intelligence requirements from the commands. Moreover, the Office of Estimates became immediately responsible (in 1961) for producing Defense estimates which were forwarded to the Board of National Estimates (i.e., under the Director of Central Intelligence). Before DIA, the J-2 had merely coordinated the Services' contribution. Reluctant to break with long established procedures, the Services continued to independently submit some of their estimates directly to the Board of National Estimates until 1963, when the practice was ended. DIA revised its charter, DoD Directive 5105.21, on 24 June 1963, to provide for the continuation of intelligence staff support to the JCS following the J-2 disestablishment on 28 June 1963. While the J-2 had existed, DIA had been charged with providing the JCS with military intelligence and discharging such intelligence functions as the JCS assigned. Recharter, 1970By 1970, successive years of internal and external critiques, inspections, and conjecture concerning the DIA raison d'etre had nurtured the presumption that a DIA charter revision was necessary. Central to the arguments for charter revision was the chain-of-command issue. In his 23 December l970 memo, Secretary of Defense Laird believed it necessary to clarify the relationship of DIA to the Secretary of Defense and the JCS:
1976 ReorganizationIn 1976, a DIA-wide reorganization, established a bicameral organization and recast the Deputy Director's position as Vice Director for Plans, Operations and Support (VO). The J-2 Support Office (JS), a former CS/DP function, was subordinated under VO. DIA Director Lieutenant General Samuel Wilson characterized organizational changes in 1977 as "refinements to increase effectiveness." Consequently, the Deputy Director and Chief of Staff positions were reestablished to enhance command and control, and coordination of Agency activities. The J-2 Support Office was realigned and the Director's Staff Group was expanded to provide improved support to OSD and JCS consumers. 1979 ReorganizationAnother reorganization in August 1979, consolidated the Assistant Vice Directorate for Current Intelligence (DN), the Strategic Warning Staff (SWS), and the J-2 Support Office (JS) into a new Assistant Directorate for JCS Support (JS). It combined current intelligence production with the more traditional liaison and support functions generally provided by the J-2. The changes enabled DIA to focus on the operational intelligence needs of the JCS and satisfy them on a more timely basis. JS becomes J-2In retrospect, Secretary of Defense James Schlesinger had told Congress in 1974, "As a Defense agency, DIA had a responsibility to provide intelligence support to the Joint Chiefs of Staff. Abolishment of the J-2 organization, per se, had no effect on DIA's clearly defined role to support the Joint Chiefs. However, it eventually raised some doubt in regard to DIA's role within the Joint Staff itself. I am happy to say that this functional uncertainty has been removed, and that the Director, DIA, is so fully involved--personally and organizationally--as the J-2 of the Joint Staff." In 1991, the JS organization was redesignated J-2. Directorate for IntelligenceThe Directorate for Intelligence (J2) serves the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Secretary of Defense, Joint Staff, and Unified Combatant Commands as the national focal point for crisis intelligence support to military operations and DoD indications and warning (I&W). The J2 also coordinates joint intelligence doctrine and architecture. Indications and warningAs components of the National Military Joint Intelligence Center (NMJIC), J2’s alert center provides real-time I&W assessments and targeting support to key decisionmakers, while the Defense Intelligence Network globally disseminates timely and accurate all-source crisis intelligence via multi-media formats. Directorate for Intelligence ProductionUnder the Directorate for Intelligence Production (DI), the Operational Intelligence Crisis Center (OICC) manages crisis-related military intelligence production, including joint intelligence preparation of the battlespace.
DI also produces or manages the production of all-source military intelligence to support the operational, planning, and policy requirements of the U.S. armed forces, as well as the Services, the Unified Combatant Commands, DoD policymakers, and national-level agencies. As the DoD Production Functional Manager, DI ensures that DoD intelligence production requirements are articulated and resources are programmed and executed in consonance with Defense and national guidance. Production programs are also re-evaluated as missions, technical capabilities, and threat environments change. DI’s analytic expertise includes military capabilities, scientific and technical, missile, medical, estimative, military production and geography, intelligence databases, and operational support and targeting intelligence for tactical, theater, and national consumers. Missile intelligenceThe Missile and Space Intelligence Center (Huntsville, AL) is a DIA activity primarily concerned with missiles of tactical range. Medical intelligenceThe Armed Forces Medical Intelligence Center is the focal point in the Department of Defense for compiling all-source intelligence and producing finished medical intelligence on foreign military and civilian medical capabilities, the health status of foreign military forces, infectious disease and environmental health risks, and scientific and technical developments in biotechnology and biomedical subjects.[7] It also manages the medical aspects of the DoD Foreign Materiel Program (see technical intelligence) Targeting intelligenceOriginally an Air Force program usually called the Strategic Vulnerability Branch, which grew to a full Directorate of Targeting in Air Force Intelligence, DIA eventually took over responsibility for a database called the Bombing Encyclopedia. A criticism of this work is that it focused only on blast damage and did not consider the thermal effects of nuclear weapons, [8] but the document dealt with both nuclear and non-nuclear weapons. Directorate of OperationsDIA, through the Directorate of Operations, also serves as the [[United States intelligence community] Executive Agent for measurement and signature intelligence (MASINT) and the DoD MASINT collection manager. The other operational activity is directing and managing DoD-wide intelligence collection requirements in support of national and theater consumers and the centralized direction and management of the DoD HUMINT Service (DHS), including operation of the Defense Attache System (DAS). Directorate for Policy SupportTo address the needs of the Office of the Secretary of Defense (OSD) and other national-level policymakers, the Directorate for Policy Support (DP) provides direct intelligence support through DIA’s senior analysts, the Defense Intelligence Officers (DIOs), as well as managing special access programs. Additionally, DP provides assistance with foreign disclosure and agreements. References
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||