Kansas Nebraska Act: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) (→Background: fixing link to Chicago, Illinois) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Missouri (U.S. state)|Missouri" to "Missouri") |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
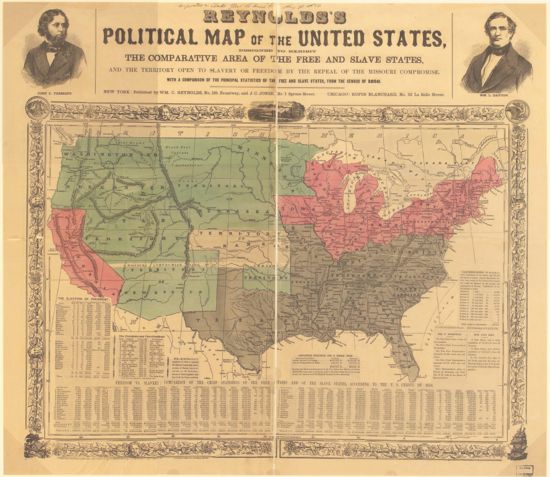
{{Image|us1854.jpg|right|550px|This 1854 map shows slave states (grey), free states (red), and US territories (green) with Kansas in center (white).}} | {{Image|us1854.jpg|right|550px|This 1854 map shows slave states (grey), free states (red), and US territories (green) with Kansas in center (white).}} | ||
The '''Kansas-Nebraska Act''' of | |||
The '''Kansas-Nebraska Act''' was an 1854 [[United States of America|U.S.]] law that created [[Kansas Territory]] and [[Nebraska Territory]], effectively repealed of the [[Missouri Compromise]], and resulted in extensive conflict over whether slavery should exist in the new territories. The new [[Republican Party (United States), history|Republican Party]], formed in reaction against allowing slavery where it had been forbidden, emerged as the dominant force throughout the North. The act was designed by [[Democratic Party (United States), history|Democratic]] Senator [[Stephen A. Douglas]] of Illinois. While not repealing the [[Missouri Compromise]] of 1850, the new law did deem it "inoperative and void". The act established that settlers could decide for themselves whether to allow slavery, in the name of "popular sovereignty" or rule of the people. Opponents denounced the law as a concession to the [[Slave Power]] --that is the political machine of slaveowners that controlled the South and much of the national government. The act and the subsequent civil war in [[Bleeding Kansas]] was a major step on the way to the [[American Civil War]]. | |||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
Douglas was very interested in having a railroad extend from his home city of [[Chicago, Illinois]] to the West, reaching eventually to California. However, many southerners wanted a transcontinental railroad that would start in New Orleans and extend to southern California. Douglas decided to make a compromise with the southern senators. In exchange for having the railroad go through Chicago, he would introduce the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854. At first he proposed one new territory of Nebraska, then two of Kansas and Nebraska. Popular sovereignty would decide whether there would be slavery or not. | Douglas was very interested in having a railroad extend from his home city of [[Chicago, Illinois]] to the West, reaching eventually to California. However, many southerners wanted a transcontinental railroad that would start in New Orleans and extend to southern California. Douglas decided to make a compromise with the southern senators. In exchange for having the railroad go through Chicago, he would introduce the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854. At first he proposed one new territory of Nebraska, then two of Kansas and Nebraska. Popular sovereignty would decide whether there would be slavery or not. | ||
The Douglas bill caused a firestorm of opposition because it allowed slavery north of the line agreed upon in the [[Missouri Compromise]], effectively repealing it. Even before the bill passed, a new grass roots opposition party was being organized in most northern states, the Republican Party. Northern Democrats, southerners, and President [[Franklin Pierce]] supported the bill. Douglas used brilliant parliamentary maneuvers to get the bill passed on May 30, 1854. It was signed into law by Pierce; he was a "doughface" or northerner whose political support came mostly from the South. In effect, there were now three political positions in American politics, represented by Northern Democrats (led by Douglas), the Northern Republicans, and the Southern Democrats. In 1860, they each ran a candidate for [[President of the United States]]. | The Douglas bill caused a firestorm of opposition because it allowed slavery north of the line agreed upon in the [[Missouri Compromise]], effectively repealing it. Even before the bill passed, a new grass roots opposition party was being organized in most northern states, the Republican Party. Northern Democrats, southerners, and President [[Franklin Pierce]] supported the bill. Douglas used brilliant parliamentary maneuvers to get the bill passed on May 30, 1854. It was signed into law by Pierce; he was a "doughface" or northerner whose political support came mostly from the South. In effect, there were now three political positions in American politics, represented by Northern Democrats (led by Douglas), the Northern Republicans, and the Southern Democrats. In 1860, they each ran a candidate for [[President of the United States of America]]. | ||
==Effects== | ==Effects== | ||
[[Image:Forcing Slavery Freesoilers Throats.jpg|thumb|right|550px|''Forcing Slavery Down the Throat of a Freesoiler''<br>An 1856 cartoon depicts a giant free soiler being held down by President Buchanan and Lewis Cass standing on the [[ | [[Image:Forcing Slavery Freesoilers Throats.jpg|thumb|right|550px|''Forcing Slavery Down the Throat of a Freesoiler''<br>An 1856 cartoon depicts a giant free soiler being held down by President Buchanan and Lewis Cass standing on the [[Democratic Party (United States), history|Democratic]] platform marked "Kansas", "Cuba" and "Central America". [[Franklin Pierce]] also holds down the giant's beard as [[Stephen A. Douglas]] shoves a black man down his throat.]] | ||
The act divided the region into the [[Kansas Territory]] (south of the 40th parallel) and the [[Nebraska Territory]] (north of the 40th parallel). The most controversial provision was the stipulation that each territory would separately decide whether to allow slavery within its borders. This provision repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, which had prohibited slavery in any new states to be created north of latitude 36°30' since Kansas and Nebraska would be north of that line and could now choose to allow slavery. | The act divided the region into the [[Kansas Territory]] (south of the 40th parallel) and the [[Nebraska Territory]] (north of the 40th parallel). The most controversial provision was the stipulation that each territory would separately decide whether to allow slavery within its borders. This provision repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, which had prohibited slavery in any new states to be created north of latitude 36°30' since Kansas and Nebraska would be north of that line and could now choose to allow slavery. | ||
===Hostilities=== | ===Hostilities=== | ||
Pro-slavery settlers rushed to Kansas mainly from [[Missouri]]. Their influence in territorial elections was often bolstered by resident Missourians who crossed the border into Kansas purely for the purpose of voting in such ballots. They were called ''border ruffians'' by their opponents, a term coined by [[Horace Greeley]]. [[John Brown]] and his sons helped in the fight against them and killed five pro-slavery farmers in the [[Pottawatomie Massacre]]. Successive territorial governors, usually sympathetic to slavery, attempted unsuccessfully to maintain the peace. The territorial capital of [[Lecompton, Kansas]], the target of much agitation, consequently became such a hostile environment for free-soilers that they set up their own unofficial legislature at Topeka. | Pro-slavery settlers rushed to Kansas mainly from [[[[Missouri (U.S. state)|Missouri]]]]. Their influence in territorial elections was often bolstered by resident Missourians who crossed the border into Kansas purely for the purpose of voting in such ballots. They were called ''border ruffians'' by their opponents, a term coined by [[Horace Greeley]]. [[John Brown]] and his sons helped in the fight against them and killed five pro-slavery farmers in the [[Pottawatomie Massacre]]. Successive territorial governors, usually sympathetic to slavery, attempted unsuccessfully to maintain the peace. The territorial capital of [[Lecompton, Kansas]], the target of much agitation, consequently became such a hostile environment for free-soilers that they set up their own unofficial legislature at Topeka. | ||
The hostilities between the factions reached a state of low-intensity civil war which was extremely embarrassing to Pierce, especially as the nascent Republican Party sought to capitalize on the scandal of [[Bleeding Kansas]]. The routine ballot-rigging and intimidation practiced by pro-slavery settlers failed to deter the immigration of anti-slavery settlers who won a demographic victory by winning the race to populate the state. | The hostilities between the factions reached a state of low-intensity civil war which was extremely embarrassing to Pierce, especially as the nascent Republican Party sought to capitalize on the scandal of [[Bleeding Kansas]]. The routine ballot-rigging and intimidation practiced by pro-slavery settlers failed to deter the immigration of anti-slavery settlers who won a demographic victory by winning the race to populate the state. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
Eventually a new anti-slavery constitution was drawn up. On January 29, 1861, Kansas was admitted to the Union as a free state. Nebraska was admitted to the Union as a state after the Civil War in 1867. | Eventually a new anti-slavery constitution was drawn up. On January 29, 1861, Kansas was admitted to the Union as a free state. Nebraska was admitted to the Union as a state after the Civil War in 1867. | ||
== Provenance == | |||
{{WPAttribution}} | |||
== Notes == | |||
<references />[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 08:12, 7 October 2024
The Kansas-Nebraska Act was an 1854 U.S. law that created Kansas Territory and Nebraska Territory, effectively repealed of the Missouri Compromise, and resulted in extensive conflict over whether slavery should exist in the new territories. The new Republican Party, formed in reaction against allowing slavery where it had been forbidden, emerged as the dominant force throughout the North. The act was designed by Democratic Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois. While not repealing the Missouri Compromise of 1850, the new law did deem it "inoperative and void". The act established that settlers could decide for themselves whether to allow slavery, in the name of "popular sovereignty" or rule of the people. Opponents denounced the law as a concession to the Slave Power --that is the political machine of slaveowners that controlled the South and much of the national government. The act and the subsequent civil war in Bleeding Kansas was a major step on the way to the American Civil War.
Background
The availability of tens of millions of acres of excellent farm land made it necessary to create a territorial infrastructure to allow settlement. Railroad interests were especially eager to start operations since they needed farmers as customers. Four previous attempts to pass legislation had failed. The solution was a bill proposed in January 1854 by Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois. He was the Democratic party leader in the United States Senate, the chairman of the Committee on Territories, an avid promoter of railroads, an aspirant to the presidency, and, above all, a fervent believer in popular sovereignty: the policy of letting the residents of a territory decide whether or not they would permit slavery to exist.
Douglas was very interested in having a railroad extend from his home city of Chicago, Illinois to the West, reaching eventually to California. However, many southerners wanted a transcontinental railroad that would start in New Orleans and extend to southern California. Douglas decided to make a compromise with the southern senators. In exchange for having the railroad go through Chicago, he would introduce the Kansas-Nebraska Act in 1854. At first he proposed one new territory of Nebraska, then two of Kansas and Nebraska. Popular sovereignty would decide whether there would be slavery or not.
The Douglas bill caused a firestorm of opposition because it allowed slavery north of the line agreed upon in the Missouri Compromise, effectively repealing it. Even before the bill passed, a new grass roots opposition party was being organized in most northern states, the Republican Party. Northern Democrats, southerners, and President Franklin Pierce supported the bill. Douglas used brilliant parliamentary maneuvers to get the bill passed on May 30, 1854. It was signed into law by Pierce; he was a "doughface" or northerner whose political support came mostly from the South. In effect, there were now three political positions in American politics, represented by Northern Democrats (led by Douglas), the Northern Republicans, and the Southern Democrats. In 1860, they each ran a candidate for President of the United States of America.
Effects

An 1856 cartoon depicts a giant free soiler being held down by President Buchanan and Lewis Cass standing on the Democratic platform marked "Kansas", "Cuba" and "Central America". Franklin Pierce also holds down the giant's beard as Stephen A. Douglas shoves a black man down his throat.
The act divided the region into the Kansas Territory (south of the 40th parallel) and the Nebraska Territory (north of the 40th parallel). The most controversial provision was the stipulation that each territory would separately decide whether to allow slavery within its borders. This provision repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820, which had prohibited slavery in any new states to be created north of latitude 36°30' since Kansas and Nebraska would be north of that line and could now choose to allow slavery.
Hostilities
Pro-slavery settlers rushed to Kansas mainly from [[Missouri]]. Their influence in territorial elections was often bolstered by resident Missourians who crossed the border into Kansas purely for the purpose of voting in such ballots. They were called border ruffians by their opponents, a term coined by Horace Greeley. John Brown and his sons helped in the fight against them and killed five pro-slavery farmers in the Pottawatomie Massacre. Successive territorial governors, usually sympathetic to slavery, attempted unsuccessfully to maintain the peace. The territorial capital of Lecompton, Kansas, the target of much agitation, consequently became such a hostile environment for free-soilers that they set up their own unofficial legislature at Topeka.
The hostilities between the factions reached a state of low-intensity civil war which was extremely embarrassing to Pierce, especially as the nascent Republican Party sought to capitalize on the scandal of Bleeding Kansas. The routine ballot-rigging and intimidation practiced by pro-slavery settlers failed to deter the immigration of anti-slavery settlers who won a demographic victory by winning the race to populate the state.
Constitution
The pro-slavery territorial legislature ultimately proposed a state constitution for approval by referendum. The constitution was offered in two alternative forms, neither of which made slavery illegal. Free soil settlers boycotted the legislature's referendum and organized their own which approved a free state constitution. The results of the competing referendums were sent to Washington by the territorial governor.
President Buchanan sent the Lecompton Constitution to Congress for approval. The Senate approved the admission of Kansas as a state under the Lecompton Constitution, despite the opposition of Senator Douglas, who believed that the Kansas referendum on the Constitution, by failing to offer the alternative of prohibiting slavery, was unfair. The measure was subsequently blocked in the House of Representatives, where northern congressmen refused to admit Kansas as a slave state. Senator James Hammond of South Carolina characterized this resolution as the expulsion of the state, asking, "If Kansas is driven out of the Union for being a slave state, can any Southern state remain within it with honor?"
Results
The Kansas-Nebraska Act split the nation and pointed it toward civil war. The act itself virtually nullified the Missouri Compromise of 1820 and the Compromise of 1850. The turmoil over the act split both the Democratic and Know Nothing parties and gave rise to the Republican party that soon controlled most of the Northern states.
Eventually a new anti-slavery constitution was drawn up. On January 29, 1861, Kansas was admitted to the Union as a free state. Nebraska was admitted to the Union as a state after the Civil War in 1867.
Provenance
- Some content on this page may previously have appeared on Wikipedia.