United Kingdom: Difference between revisions
imported>John Stephenson ({{UK}} template restored) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (286 intermediate revisions by 27 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
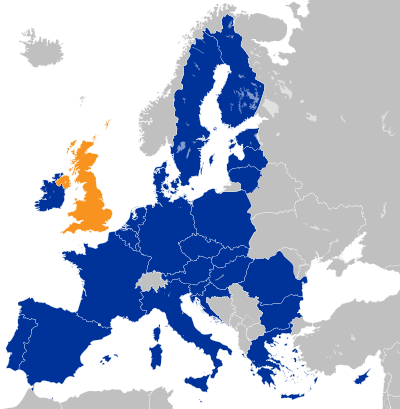
{{ | {{Image|Location map of the United Kingdom and the European Union.svg|right|400px|The United Kingdom is shown in orange, and for context, the official countries of the European Union are shown in dark blue. Some overseas territories that are included in the European Union are outside the boundaries of the map.}} | ||
The '''United Kingdom | The '''United Kingdom''' is a political union of the countries of [[England]], [[Wales]], [[Scotland]] and [[Northern Ireland]]. Its formal title is "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland". It is often referred to as "Britain", including by the government. Its principal language is [[English language|English]], but the [[Welsh language]] is also officially recognised. Other indigenous languages include [[Scots language|Scots]], [[Scottish Gaelic]] and [[British Sign Language]]. Its citizens are called Britons (or, informally, "Brits"), and their nationality is referred to as "British". It is located off the north-western coast of [[Europe]], and it is geographically and politically a part of the continent. It is a member of the [[British Commonwealth]] and the [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation]] and is a founder member of the [[United Nations]] with a permanent seat on the [[United Nations Security Council]]. In 2016, a majority of British voters opted to [[United Kingdom exit from the European Union|leave the European Union]], and this was implemented in 2020. | ||
{{TOC|left}} | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
The | The British people have acquired a genetic inheritance from immigrants including Celts, Romans, Saxons, Danes, Normans, and many others. | ||
An early cultural inheritance came from the [[Celts]] of central [[Europe]] and a further contribution came when missionaries established monasteries in the [[British Isles]]. Little cultural progress was made during the five centuries of [[Anglo-Saxon]] rule in England, however, and the technological knowledge that was lost when the Romans left was only slowly regained. Intellectual thought was dominated for several centuries by a religious establishment concerned mainly with the preservation of orthodoxy, and it was not until the [[Renaissance]] that inductive modes of reasoning became acceptable. The British constitutional inheritance has been the outcome of an intermittent progression from an unruly conglomeration of uncoordinated kingships into an orderly democratic nation. A transition from autocracy to constitutional monarchy happened by the transfer of power to deliberative assemblies in a succession of discrete steps that included the [[Magna Carta]] of 1215, the Bill of Rights of 1688, the Reform Act of 1867, and the Representation of the People Act of 1928. The dissolution of the rigid hierarchical structure of rights and obligations of the feudal system happened at an earlier stage in Britain than in other European countries and the resulting increase in labour mobility made possible the earlier development of the [[Industrial Revolution]] -and gave it a decisive, although temporary, economic advantage. As a result it was for a time, the world's richest and most powerful country. It acquired - and then lost - responsibility for managing the world's financial system, and for ruling an [[British Empire|Empire]] of almost a quarter of the world's population, covering a larger area than any other empire in history. In the course of the 20th century, it suffered major losses of its economic resources in two world wars and it gave independence to nearly all the former members its empire, and devolved a degree of legislative independence to [[Northern Ireland]], [[Wales]] and [[Scotland]]. It joined the [[European Union]] but did not adopt its common currency. It joined with the [[United States of America]] in the [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation]], and supported it in wars in [[Korea]], Afghanistan and Iraq, but not [[Vietnam]]. | |||
==Government and politics== | ==Government and politics== | ||
===The Constitution=== | |||
=== | Parliamentary sovereignty is the ruling principle of the constitution<ref>The British constitution is not codified into a single document but is recorded in the form of an extensive a body of common-and state law.</ref> of the United Kingdom. Parliament is the country's supreme legal authority, and it can create or end any law. It has from time to time passed laws that limit the application of its sovereignty, but it is not bound by those laws. nor by any other of its past decisions | ||
The | <ref>[http://www.parliament.uk/about/how/sovereignty/ ''Parliamentary sovereignty'', www.parliament.uk]</ref>. | ||
The | The [[Parliament of the United Kingdom|UK parliament]] is bicameral, consisting of a wholly-elected [[House of Commons (United Kingdom)|House of Commons]] and a mainly-appointed [[House of Lords]], of which the House of Commons is its primary legislative assembly, and the functions of the House of Lords are mainly deliberative. Once elected, the House of Commons serves for a fixed term of five years unless the government loses a [[House of Commons (United Kingdom)/Addendum#Votes of confidence|vote of no confidence]], and unless a new government does not receive a vote of confidence within a fortnight, or two thirds of its members vote for its dissolution<ref>[http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2011/14/contents/enacted ''Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011'']</ref>. | ||
The | The political head of the [[Government of the United Kingdom|UK government]] is its [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|Prime Minister]] who is a member of one of the Houses of Parliament, appointed by the [[Monarchy|Monarch]] on the presumption that he or she would able to command the support of a majority of the members of the House of Commons. (The appointee is expected to submit his or her resignation if he or she is unable to win the of confidence of the House of Commons). It is nowadays understood that the Prime Minister must be in the House of Commons. (Apart from a very short period in 1963,<ref>The Earl of Home completed the legal formalities of disclaiming his peerage four days after being appointed Prime Minister, and was elected to the Commons in a by-election shortly after.</ref> this has always been the case since 1902.) The person chosen to be Prime Minister is normally the elected leader of one of the country's [[political party|political parties]]. | ||
The monarch is the | The [[Monarchy of the United Kingdom|British monarch]] is the country's [[Head of State]]. The functions of the monarchy are mainly ceremonial, but the Sovereign, as its embodiment, has the | ||
right to advise the Prime Minister in private. The Sovereign has the personal power to resolve an otherwise intractable constitutional crisis but is bound, in all other circumstances, to give way to ministerial advice. In other respects, the [[Monarchy of the United Kingdom/Addendum#The Royal Prerogatives| royal prerogative]], which includes the power to declare war, is effectively exercised by ministers. The ancient feudal functions of the monarchy continue to be reflected in constitutional and legal terminology and usage. For those purposes, the term "The Crown", refers to a legal fiction that makes the [[state]] a legal entity that can be a party to a legal transaction or a legal action<ref>[http://www.duhaime.org/LegalDictionary/C/Crown.aspx ''Crown Definition'', Duhaime's Legal Dictionary]</ref>. | |||
The | ===The conduct of government=== | ||
It is the Prime Minister's responsibility to select those members of the [[Parliament of the United Kingdom|Houses of Parliament]] who are to become [[Minister (government)|Ministers]] and serve as political managers of government departments, and to decide who among them are to serve in the top decision-making body known as "the Cabinet". With rare exceptions, a government's business is conducted in accordance with the "doctrine of collective responsibility"<ref>[http://www.parliament.uk/documents/commons/lib/research/rp2004/rp04-082.pdf Oonagh Gay and Thomas Powell: ''The collective responsibility of Ministers - an outline of the issues'', House of Commons Research Paper, 15 November 2004]</ref>, under which ministers are bound to defend Cabinet decisions, whether or not they agree with them. The conduct of ministers is governed by a ministerial code<ref>[http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/+/http://www.cabinetoffice.gov.uk/media/409215/ministerialcodemay2010.pdf ''Ministerial Code'', Cabinet Office, May 2010]</ref> covering their personal conduct, the presentation of policy, and their relations with Parliament and the civil service. Ministers receive political advice from "special advisers", and impartial advice from permanent civil servants. Permanent civil servants are recruited by open competition under the supervision of an independent Commission<ref>[http://civilservicecommission.independent.gov.uk/About_us/index.html The Civil Service Commission]</ref>, and their appointment does not change with changes of government; whereas special advisers are temporary civil servants who are appointed by ministers, and whose tenure ends when there is a change of government<ref>[http://civilservicecommission.independent.gov.uk/admin/assets/spaw2/uploads/files/Constitutional-Reform-Governance-Act.pdf ''Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010'']</ref>. | |||
In 2010/11 there were 68 special advisors<ref>[http://www.parliament.uk/documents/commons/lib/research/briefings/snpc-03813.pdf Oonagh Gay ''Special Advisers'', House of Commons Library, November 2010]</ref> within a total of about 440,000 civil servants. Legislation is normally initiated by government departments and piloted through the legislative process by the party [[Whip (political)|Whips]]. Legislative proposals by a Government with a substantial majority in the House of Commons are usually enacted. Government Whips warn members who rebel against its motions that they are damaging their prospects of promotion. | |||
===Political parties=== | |||
Nearly all MPs belong to political parties; often all do. Currently, 10 parties are represented in the Commons, of which the only two that have been in power alone recently are the [[Conservative Party (UK)|Conservative Party]] and the [[Labour Party (UK)|Labour Party]]. The Liberal Democrats were in a coalition government from 2010 to 2015. Among the others, the [[Scottish National Party]] and [[Plaid Cymru]] campaign for the independence of Scotland and Wales respectively; the [[Democratic Unionist Party]](DUP) represent unionist, and Sinn Féin and the Social Democratic an Labour Party represent nationalist interests in Northern Ireland, while the Alliance Party tries to bridge the divide. The Green Party is also represented in the Commons. Many other parties are represented in other elected positions, or were formerly represented in Parliament. Analysts have remarked upon the apparent lack of ideological differences among the three major national parties<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/4904198.stm Bob Tyrrell: ''Is British politics ideology-free?'', BBC News, 13 April 2006]</ref>, an impression that is supported by a comparison of their 2010 election manifestoes<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/8515961.stm ''Where They Stand: Guide to party election policies'', Election 2010, BBC News]</ref>. | |||
=== | ===The current administration=== | ||
The [[2019 United Kingdom general election]] resulted in a majority for the [[Conservative Party]] led by [[Boris Johnson]]. He was succeeded as [[Prime Minister of the United Kingdom|Prime Minister]] by [[Liz Truss]] on 6th September 2022, and she in turn was succeeded by [[Rishi Sunak]] on 25th October. | |||
===Regional Structure=== | |||
====Devolution==== | |||
Following [[/Addendum#Devolution|devolution]] referendums in Scotland and Wales in 1997, and in both parts of Ireland in 1998, the United Kingdom Parliament transferred a range of powers to national parliaments or assemblies<ref>[http://www.direct.gov.uk/en/Governmentcitizensandrights/UKgovernment/Devolvedgovernment/DG_073306. ''Devolved government in the UK'', DirectGov, 2012]</ref>. The arrangements are different in the three parts of the country, reflecting their history and administrative structures. The Scottish Government develops and implements policy on matters that include health, education, justice, rural affairs and transport<ref>[http://home.scotland.gov.uk/home ''The Scottish Government'']</ref>, and is accountable to the Scottish Parliament<ref>[http://www.scottish.parliament.uk/ ''The Scottish Parliament'', 2012]</ref>. | |||
The Welsh Assembly Government<ref>[http://new.wales.gov.uk/?lang=en ''Welsh Government'', 2012]</ref> has responsibilities which include health, education, economic development, culture, the environment and transport, and is accountable to the National Assembly for Wales<ref>[http://www.assemblywales.org/ ''National Assembly for Wales'', 2012]</ref>. The Northern Ireland Executive<ref>[http://www.northernireland.gov.uk/ ''Northern Ireland Executive'', 2012]</ref> is responsible for economic and social matters, agriculture and rural development, culture, arts, education, health, social services and public safety, and is accountable to the Northern Ireland Assembly<ref>[http://www.niassembly.gov.uk/ ''Northern Ireland Assembly'', 2012]</ref>. The United Kingdom Parliament is still able to pass legislation for any part of the United Kingdom, though in practice it only deals with devolved matters with the agreement of the devolved governments. | |||
====Local Government==== | |||
The United Kingdom is divided, for the purposes of government, into a set of | |||
further [[/Addendum#Administrative subdivisions|administrative subdivisions]]. In most of England there are two levels of local government: a county council and a district council. County councils cover large areas and provide public services that include schools, social services, and public transportation. District councils cover smaller areas and provide more local services, including council housing, gyms and leisure facilities, local planning, recycling and trash collection. In most large towns and cities, and in some small counties, there is only one level of local government responsible for all local services. In London, each borough is a unitary authority, but the Greater London Authority provides London-wide services including transport and police. In Scotland there is a unitary system with one level of local government. In Northern Ireland there are local councils, but most services are carried out by other organisations. In some parts of England and Wales there are also town and parish councils that are responsible for services like allotments, public toilets, parks and ponds, war memorials, and local halls and community centres. In Wales, they are called community councils. In Scotland there are community councils with fewer powers. There is no equivalent in Northern Ireland. | |||
==Law== | ==Law== | ||
The | The United Kingdom has three systems of law: one for England and Wales, one for Northern Ireland and one for Scotland. In England and Wales and Northern Ireland they are "common law systems", under which decisions are determined by precedent, except where precedent is overruled by legislation (as distinct from "civil law systems" under which decisions are determined exclusively by legislative enactment). Scotland has a "mixed jurisdiction system" which is a mixture of common law and civil law. Each system has a hierarchy of courts, and each permits appeal to a higher court against a decision of a lower court. In England and Wales, the court system includes the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). In Scotland, the principal courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases, and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases, and the sheriff court is the Scottish equivalent of the English county court. The United Kingdom's highest court is the [[Supreme Court (United Kingdom)|Supreme Court]],<ref>[http://www.supremecourt.gov.uk/ ''The Supreme Court'', 2012]</ref> roughly speaking. The provisions of the European Communities Act 1972 require United Kingdom courts to apply European law, and to give it preference when it conflicts with previous parliamentary legislation<ref>[http://www.leeds.ac.uk/law/hamlyn/european.htm ''European Law as a source of UK Law'', UK Law online, 2012]</ref>. The Human Rights Act 1998<ref>[http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1998/42/contents ''Human Rights Act 1998'', Legislation.gov.uk]</ref> embodies the provisions of the [[European Convention on Human Rights]]. | ||
The | ==Geography== | ||
The United Kingdom comprises the island of [[Great Britain]], [[Northern Ireland]], and numerous smaller islands in the surrounding seas. It is bounded by the [[Atlantic Ocean]] and its ancillary bodies of water, including the [[North Sea]], the [[English Channel]], the [[Celtic Sea]], and the [[Irish Sea]]. On the island of Ireland, Northern Ireland has a land border with the [[Republic of Ireland]] to the south and west. There are several islands which are not part of the United Kingdom, including the Isle of Man, Jersey, Guernsey and Alderney). They are all [[British Crown Dependencies]], which means that they are effectively self-governing with their own legislature and tax systems: the UK remains responsible for foreign policy and in certain circumstances has legal authority superior to the parliaments. | |||
Most of England consists of rolling lowland, divided east from west by mountains in the Northwest ([[Cumbrian Mountains]] of the [[Lake District]]) and north (the upland moors of the [[Pennines]]) and limestone hills of the [[Peak District]] by the [[Tees-Exe line]]. The lower limestone hills of the [[Isle of Purbeck]], [[Cotswolds]], [[Lincolnshire]] and [[chalk]] downs of the [[Southern England Chalk Formation]]. The main rivers and estuaries are the [[Thames]], [[Severn]] and the [[Humber|Humber Estuary]]. The largest urban area is [[Greater London]]. Near [[Dover, England|Dover]], the [[Channel Tunnel]] links the UK to [[France]].<ref> [https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/uk.html#Geo Geography of the United Kingdom] CIA, Accessed May 22 2006</ref> The highest mountain in England is [[Scafell Pike]] in the [[Lake District]], at 978m (3,208 ft). | |||
Most of England consists of rolling lowland, divided east from west by mountains in the Northwest ([[Cumbrian Mountains]] of the [[Lake District]]) and north (the upland moors of the [[Pennines]]) and limestone hills of the [[Peak District]] by the [[Tees-Exe line]]. The lower limestone hills of the [[Isle of Purbeck]], [[Cotswolds]], [[Lincolnshire]] and [[chalk]] downs of the [[Southern England Chalk Formation]]. The main rivers and estuaries are the [[Thames]], [[Severn]] and the [[Humber|Humber Estuary]]. The largest urban area is [[Greater London]]. Near [[Dover, England|Dover]], the [[Channel Tunnel]] links the UK to [[France]]. <ref> [https://www.cia.gov/cia/publications/factbook/geos/uk.html#Geo Geography of the United Kingdom] CIA, Accessed May 22 2006</ref> The highest mountain in England is [[Scafell Pike]] in the [[Lake District]], at 978m (3,208 ft). | |||
[[Scotland's geography]] is varied, with lowlands in the south and east and highlands in the north and west, including [[Ben Nevis]], the highest mountain in the British Isles at 1,343m (4,406 ft). There are many long and deep-sea arms, [[firth]]s, and [[loch]]s. Scotland has nearly 800 [[Scottish islands|islands]], mainly west and north of the mainland, notably the [[Hebrides]], [[Orkney Islands]] and [[Shetland Islands]]. The capital city is [[Edinburgh]], the centre of which is a [[World Heritage | [[Scotland's geography]] is varied, with lowlands in the south and east and highlands in the north and west, including [[Ben Nevis]], the highest mountain in the British Isles at 1,343m (4,406 ft). There are many long and deep-sea arms, [[firth]]s, and [[loch]]s. Scotland has nearly 800 [[Scottish islands|islands]], mainly west and north of the mainland, notably the [[Hebrides]], [[Orkney Islands]] and [[Shetland Islands]]. The capital city is [[Edinburgh]], the centre of which is a [[World Heritage site]]. The largest city is [[Glasgow]].<ref> [http://www.heritage-of-scotland.com/geog.htm Geography of Scotland] Heritage of Scotland, Accessed May 22 2006</ref> The UK has about 1,000 islands, with 700 in Scotland alone.<ref> [http://www.celticlegend.co.uk/dialysis/scotland.htm Dialysis Scotland] Accessed May 22, 2006</ref> | ||
Wales (''Cymru in [[Welsh language|Welsh]]'') is mostly mountainous, the highest peak being [[Snowdon]] (Yr Wyddfa) at 1,085m (3,560 ft) above sea level. North of the mainland is the island of [[Anglesey]] (Ynys Môn). The largest city, [[Cardiff]] (Caerdydd), has been the Welsh capital since 1955.<ref> [http://www.bbc.co.uk/wales/culture/sites/aboutwales/pages/geography.shtml Geography of Wales] [[BBC]] Wales, Accessed May 22 2006</ref> The greatest concentration of people live in the south, in the cities of [[Swansea]] and [[Newport]], as well as Cardiff, and the South Wales Valleys. The largest town in North Wales is [[Wrexham]]. | Wales (''Cymru in [[Welsh language|Welsh]]'') is mostly mountainous, the highest peak being [[Snowdon]] (Yr Wyddfa) at 1,085m (3,560 ft) above sea level. North of the mainland is the island of [[Anglesey]] (Ynys Môn). The largest city, [[Cardiff]] (Caerdydd), has been the Welsh capital since 1955.<ref> [http://www.bbc.co.uk/wales/culture/sites/aboutwales/pages/geography.shtml Geography of Wales] [[BBC]] Wales, Accessed May 22 2006</ref> The greatest concentration of people live in the south, in the cities of [[Swansea]] and [[Newport]], as well as Cardiff, and the South Wales Valleys. The largest town in North Wales is [[Wrexham]]. | ||
Northern Ireland, making up the north-eastern part of Ireland, is mostly hilly. The capital is [[Belfast]] ('Béal Feirste' in [[Irish language|Irish]]), with other major cities being [[Derry|Londonderry/Derry]] ('Doire' in [[Irish language|Irish]]) and Armagh. The province includes one of the UK’s [[World Heritage | Northern Ireland, making up the north-eastern part of Ireland, is mostly hilly. The capital is [[Belfast]] ('Béal Feirste' in [[Irish language|Irish]]), with other major cities being [[Derry|Londonderry/Derry]] ('Doire' in [[Irish language|Irish]]) and Armagh. The province includes one of the UK’s [[World Heritage sites]], the [[Giant's Causeway]], which consists of more than 40,000 hexagonal basalt columns up to 40 feet (12 m) high. [[Lough Neagh]], the largest body of water in the [[British Isles]] (388 km² / 150 mi²), can be found in [[Northern Ireland]].<ref> [http://cain.ulst.ac.uk/ni/geog.htm Geography of Northern Ireland] [[University of Ulster]] Accessed May 22 2006]] </ref> The highest peak is [[Slieve Donard]] at 849m (2,786 ft) in the [[Mourne Mountains]]. | ||
===Climate=== | ===Climate=== | ||
England has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. The seasons are quite variable in temperature, but temperatures rarely fall below −5°C (23°F) or rise above 30°C (86°F). The prevailing wind is from the | England has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. The seasons are quite variable in temperature, but temperatures rarely fall below −5°C (23°F) or rise above 30°C (86°F). The prevailing wind is from the south-west, bringing mild and wet weather regularly from the Atlantic Ocean. It is driest in the east and warmest in the south-east. Snowfall can occur in Winter and early Spring, though it is uncommon away from high ground. The highest temperature recorded in England is 38.5 °C (101.3 °F) on 10 August 2003 at Brogdale, near Faversham, in Kent. [1]. The lowest temperature recorded is −26.1 °C (−15.0 °F) on 10 January 1982 at Edgmond, near Newport, in Shropshire. [2] | ||
Wales' climate is similar, with the highest temperature recorded at 35.2°C (95.4°F) in Hawarden Bridge, Flintshire on 2 August 1990, and the lowest temperature at -23.3°C (-10°F) in Rhayader, Radnorshire on 21 January 1940. [1] | Wales' climate is similar, with the highest temperature recorded at 35.2°C (95.4°F) in Hawarden Bridge, Flintshire on 2 August 1990, and the lowest temperature at -23.3°C (-10°F) in Rhayader, Radnorshire on 21 January 1940. [1] | ||
| Line 93: | Line 70: | ||
===Cities=== | ===Cities=== | ||
Due to differences between the administrative boundaries and metropolitan areas of cities, and because of merging of settlements into conurbations, there are many different statistics and debates on which cities are the UK's largest. The capitals of the UK's constituent countries are London (England), Edinburgh (Scotland), Cardiff (Wales) and Belfast (Northern Ireland). London is by far the UK's largest city, whilst [[Birmingham]] is considered, population-wise, the 'second city'. | Due to differences between the administrative boundaries and metropolitan areas of cities, and because of merging of settlements into conurbations, there are many different statistics and debates on which cities are the UK's largest. The capitals of the UK's constituent countries are London (England), Edinburgh (Scotland), Cardiff (Wales) and Belfast (Northern Ireland). London is by far the UK's largest city,<ref>using the term in an objective sense; officially, Greater London is not a city, the population of the official "City" of London is in four figures, and Birmingham is the largest city</ref> whilst [[Birmingham]] is considered, population-wise, the 'second city'. | ||
==Demography== | ==Demography== | ||
The UK population according to the 2011 census was 63,181,775.<ref>[http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/dcp171778_292378.pdf]</ref> In 2007 birth per woman were 1.84 (up from 1.74 in 2005); the net annual migration was 190,000 (up from 145,000 in 2005), and the life expectancy at birth for females was 86.2 years (up from 85.0). | |||
Its overall population density is one of the highest in the world. About a quarter of the population lives in the south-east <ref>[http://www.statistics.gov.uk/census2001/pyramids/pages/j.asp Census 2001: South East], Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 14 May 2006.</ref> and is predominantly urban and suburban, with an estimated 7,517,700 in the capital of London. <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nomisweb.co.uk/reports/lmp/la/2038431860/subreports/pop_time_series/report.aspx |title=All people population: City of London |publisher=Office for National Statistics |accessdate=2006-08-31}}</ref> The United Kingdom's high literacy rate (99%) <ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.humana.org/Article.asp?TxtID=223&SubMenuItemID=183&MenuItemID=43 |title=United Kingdom |publisher=Humana |accessdate=2006-05-18}}</ref> is attributable to universal public education | Its overall population density is one of the highest in the world. About a quarter of the population lives in the south-east<ref>[http://www.statistics.gov.uk/census2001/pyramids/pages/j.asp Census 2001: South East], Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 14 May 2006.</ref> and is predominantly urban and suburban, with an estimated 7,517,700 in the capital of London.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.nomisweb.co.uk/reports/lmp/la/2038431860/subreports/pop_time_series/report.aspx |title=All people population: City of London |publisher=Office for National Statistics |accessdate=2006-08-31}}</ref> The United Kingdom's high literacy rate (99%)<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.humana.org/Article.asp?TxtID=223&SubMenuItemID=183&MenuItemID=43 |title=United Kingdom |publisher=Humana |accessdate=2006-05-18}}</ref> is attributable to universal public education established by law for the primary level in 1870 (though in fact nearly all children of primary age were already attending school) and secondary level in 1900 (except in Scotland where it was introduced in 1696). Education is mandatory from ages four or five (dependent on birth date) to sixteen. | ||
===Population history=== | |||
The lands now constituting the UK have been subject to many invasions and migrations, especially from Scandinavia and the continent of Europe, including Roman occupation for several centuries. The Romans, however, left a minimal long-term impact on the culture. The Celtic, Anglo-Saxon, and Norse cultural traditions were blended under the Normans after that French-speaking group invaded and conquered England in 1066. | |||
===Immigration=== | |||
Immigration has come through interaction with continental Europe and ties forged by the British Empire. Continuous waves of immigration have brought people to the UK, with Europe, Africa and South-East Asia being the biggest areas from where people emigrate. The UK has amongst the highest immigration rates in Europe, along with Italy and Spain<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.guardian.co.uk/immigration/story/0,,1852513,00.html|title=Immigration fails to stem European population loss | date=2006-08-17| accessdate=2006-08-20| publisher=[[The Guardian]]}}</ref> In the Greater London area the 2011 census found only 45% of the population identifying themselves as "White British"<ref>[http://www.standard.co.uk/news/uk/census-reveals-white-britons-as-minority-in-capital-for-first-time-8405998.html]</ref> and only about 43% identifying as English. The latest wave of immigration began in May 2004 when the European Union was expanded. From May 2004 to June 2006, around 600,000 people from Central and Eastern Europe emigrated to the UK to work; this figure is for arrivals only and does not take account of people leaving, so net migration will be lower.<ref>[http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/uk_politics/5273356.stm 'Nearly 600,000' new EU migrants], BBC, 22 August 2006. Retrieved 22 August 2006.</ref> In 2004 net migration from EU states stood at 74,000.<ref>[http://www.statistics.gov.uk/cci/nugget.asp?id=1311 International migration: Net inflow rose in 2004], ONS, 15 December 2005. Retrieved 24 August 2006.</ref> | |||
Immigration has come through interaction with continental Europe and ties forged by the British Empire. | |||
The UK has amongst the highest immigration rates in Europe, along with | |||
The latest wave of immigration began in May 2004 when the European Union was expanded. From May 2004 to June 2006, around 600,000 people from | |||
===Language=== | ===Language=== | ||
[[English language|English]] is understood and used everyday by the vast majority of British people. Its continued use is therefore of some cultural importance; the British enjoy the prestige and status of being a major English-speaking nation whose language acts as a ''[[lingua franca]]'' for millions worldwide. | [[English language|English]] is understood and used everyday by the vast majority of British people. Its continued use is therefore of some cultural importance; the British enjoy the prestige and status of being a major English-speaking nation whose language acts as a common ''[[lingua franca]]'' for millions worldwide. | ||
Various laws and procedures award some degree of recognition to other indigenous languages of the UK: for example, | Various laws and procedures award some degree of recognition to other indigenous languages of the UK: for example, in 2011, Welsh became an [[official language]] of Wales through legislation passed by the [[Welsh Assembly]]<ref>''BBC News'': '[http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/uk-wales-11934239 'Historic' assembly vote for new Welsh language law]'. 7th December 2010.</ref>, and Scottish law promotes [[Scots Gaelic]] with a view to making it official. In Northern Ireland, [[Irish language|Irish]] and [[Ulster Scots]] are officially-recognised minority varieties. European Union legislation designed to protect ''[[minority language]]s'' has also granted some legislative protection to such languages as [[Scots language|Scots]], [[Cornish language|Cornish]] and [[British Sign Language]] (BSL). In contrast, though English is recognised in Scotland and Wales, no legal document explicitly defines it as an official language of the whole UK, meaning that the tongue of the overwhelming majority is protected by its sheer number of speakers rather than any act of parliament (though all acts of the British Parliament are in English). | ||
The UK's native languages, aside from BSL, can be divided into two families: English and Scots are two closely-related [[Germanic languages]], while Welsh, Scots Gaelic, | The UK's native languages, aside from BSL, can be divided into two families: English and Scots are two closely-related [[Germanic languages]], while Welsh, Scots Gaelic, Irish and Cornish are [[Celtic languages|Celtic]].<ref> The [[Indo-Aryan languages|Indo-Aryan language]] [[Romani language|Romani]], which is spoken by the [[Roma]] minority, is not native to the UK, though its speakers are mostly British.</ref> | ||
Romani is a language brought to the UK's shores through immigration, but in the UK the term ''[[immigrant languages]]'' is generally reserved for more recent arrivals. The open passport system in the Commonwealth enabled immigration from former colonies. | Romani is a language brought to the UK's shores through immigration, but in the UK the term ''[[immigrant languages]]'' is generally reserved for more recent arrivals. The open passport system in the Commonwealth enabled immigration from former colonies. The UK includes the largest groups of Hindi and Punjabi speakers outside Asia. Such groups may maintain ties with historic homelands while playing an active part in all aspects of British life. | ||
Even more recently, the expansion of the [[European Union]] in 2004 to accommodate ten mainly Eastern European countries has led to increased, although predominantly temporary, immigration. In a typical British urban area, therefore, languages such as Polish may be heard alongside Urdu and Bengali; likewise, English as a first or second language will be common to most of these speakers. Polish is currently the UKs second most spoken language, though this may cease to be true after the UK leaves the EU. | |||
=== Religion === | === Religion === | ||
The | The United Kingdom is an increasingly secular society. Numbers saying they have no religion vary substantially with the exact form of the question, but time series indicate a substantial increase, and some surveys now give a majority. However, this overall decline masks increases, sometimes substantial, in non-Christian religions.<ref>2011 census data give the following percentage increases in absolute numbers over the 2001 census: Muslims 75, Buddhists 72, Hindus 49, Sikhs 29, Jews 1, total other religions 47; for comparison, the total for no religion or not stated (in 2001, these were not separated in all parts of the country) increased by 52%, while the figure for Christians decreased by 11%. What would have been the 2021 census for Scotland was postponed for a year because of the Covid-19 pandemic, but the rest of the country went ahead. As a result, there are no UK-wide figures for any one date. However, the figures for England and Wales, which include most of the population, clearly show even nominal Christians now a minority. Other religions have continued to grow (religions added together still include the majority of the population), with the highest proportionate growth being for Shamanism, though it still has small absolute numbers.</ref> Similarly, the decline in Christianity masks growth in some forms, particularly some Evangelical/Pentecostal churches. | ||
The | In terms of actual religious practice, 62 percent of those surveyed say that they never attend a religious service<ref>[http://data.gov.uk/dataset/british-social-attitudes-survey ''The British Social Attitudes Survey'', data.gv.uk 2011]</ref> | ||
The Church of England is the officially [[established church]] in England, and is the senior branch of the worldwide Anglican Communion<ref>[http://www.anglicancommunion.org/ ''The Anglican Community'']</ref>. The [[Presbyterian]] [[Church of Scotland]] (known as "The Kirk") is the official national church of Scotland. In Wales, the [[Church in Wales]] is disestablished from the Church of England, but remains a member of the Anglican communion. The Roman Catholic Church is the country's second largest Christian denomination and is the largest denomination in Northern Ireland. | |||
The Presbyterian Church in Ireland is closely linked to the Church of Scotland, and is the province's largest Protestant denomination. The United Kingdom's Christian denominations also include the Methodists and Baptists, and there are substantial numbers of [[Islam|Muslims]], [[Hinduism|Hindus]] and [[Sikhism|Sikhs]] with [[Judaism]], [[Buddhism]] and other religions occurring in smaller numbers. | |||
In Wales, the [[Church in Wales]] | |||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
''(the numbers quoted in this paragraph come from the OECD 2010 factbook[http://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/oecd-factbook-2010_factbook-2010-en], unless otherwise stated)'' | |||
The United Kingdom has an open [[market economy]] with limited natural resources and a proficient workforce. It is an industrialised economy with a small agricultural sector. In more precise terms, trade in goods and services amounts to around 30 percent of GDP, and there are no trade restrictions except for agricultural products. Seventy percent of the working age population is in employment, with proficiency levels in reading, mathematics and science that are close to the [[OECD]] average. Agricultural products account for less than one percent of the value of domestic output, as compared with 39 percent for production and distribution, 17 percent for government, health and education, and 8 per cent for finance and insurance<ref>Blue book par 2.1</ref>. It is a heavily indebted economy with a household debt burden among the highest in the world at about 160 percent of disposable income, and government debt in line with the OECD average at about 100 percent of GDP; and the debt burden is expected to rise<ref>[http://budgetresponsibility.independent.gov.uk/wordpress/docs/household%20debt%20paper% ''Household debt forecast. Office of Budget Responsibility, April 2011]</ref>. As percentages of GDP, total tax revenue, and taxation on corporate income are about the same as the OECD average, and the revenue from taxation on personal income is about 10 per cent higher. The economy is currently running at below capacity with an [[output gap]] of 4.4 percent, compared with a 3.4 percent OECD average, and the [[unemployment rate]] is 7.9 percent compared with an OECD average of 8.5 percent. | |||
==Armed Forces== | ==Armed Forces== | ||
The | The armed forces of the UK are known as the '''British Armed Forces''' or '''His Majesty's Armed Forces''', but officially '''Armed Forces of the Crown'''. Their Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, HM The King and they are managed by the [[Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom)|Ministry of Defence]]. The armed forces are controlled by the [[Defence Council]] currently headed by Air Chief Marshal Sir Jock Stirrup. | ||
The UK fields one of the most powerful and comprehensive armed forces in the World. Its global power projection capabilities are second only to those of the | The UK fields one of the most powerful and comprehensive armed forces in the World. Its global power projection capabilities are second only to those of the United States Military. The UK has the 2nd highest military expenditure in the world after the USA. | ||
The UK has a comprehensive nuclear arsenal, one of the few countries to do so, using the submarine-based [[Trident | The UK has a comprehensive nuclear arsenal, one of the few countries to do so, using the submarine-based [[UGM-133 Trident D5|Trident II]] ballistic missile system with nuclear warheads. These [[Vanguard-class|Vanguard class submarines]] were designed and built by [[Vickers Shipbuilding and Engineering Ltd|VSEL]] (now [[BAE Systems Submarines]]) at [[Barrow-in-Furness]]. | ||
The British Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK's wider security interests, and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in the [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation]] (NATO) and other coalition operations. | The British Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK's wider security interests, and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in the [[North Atlantic Treaty Organisation]] (NATO) and other coalition operations. | ||
[[Image:Trident II missile image.jpg|thumb|right|One of the [[Royal Navy]]'s Nuclear Submarines launches a [[Trident II]] Nuclear Missile.]] | [[Image:Trident II missile image.jpg|thumb|right|One of the [[Royal Navy]]'s Nuclear Submarines launches a [[Trident II]] Nuclear Missile.]] | ||
The [[British Army]] had a reported strength of 102,440 in 2005 <ref>"[http://www.mod.uk/NR/rdonlyres/6FBA7459-7407-4B85-AA47-7063F1F22461/0/modara_0405_s1_resources.pdf Annual Reports and Accounts 2004-05]", Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 14 May 2006. {{PDFlink}}</ref> and the [[Royal Air Force]] a strength of 49,210. The 36,320-member [[Royal Navy]] operates the UK | The [[British Army]] had a reported strength of 102,440 in 2005<ref>"[http://www.mod.uk/NR/rdonlyres/6FBA7459-7407-4B85-AA47-7063F1F22461/0/modara_0405_s1_resources.pdf Annual Reports and Accounts 2004-05]", Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 14 May 2006. {{PDFlink}}</ref> and the [[Royal Air Force]] a strength of 49,210. The 36,320-member [[Royal Navy]] operates the UK's nuclear deterrent, which consists of four Trident missile-armed submarines, while the [[Royal Marines]] are the Royal Navy's Light Infantry units for amphibious operations and for specialist reinforcement forces in and beyond the [[NATO]] area. This puts total active duty military troops in the 190,000 range, currently deployed in over eighty countries. | ||
There are also reserve forces supporting the regular military. These include an army reserve, the [[Territorial Army]] (TA); the Royal Naval Reserve (RNR), [[Royal Marines Reserve]] (RMR) and the [[Royal Auxiliary Air Force]] (RAuxAF). | There are also reserve forces supporting the regular military. These include an army reserve, the [[Territorial Army]] (TA); the Royal Naval Reserve (RNR), [[Royal Marines Reserve]] (RMR) and the [[Royal Auxiliary Air Force]] (RAuxAF). About 9% of the regular armed forces are comprised of women, a figure that is higher for the reserve forces. | ||
About 9% of the regular armed forces are comprised of women, a figure that is higher for the reserve forces. | |||
The [[United Kingdom Special Forces]], principally the [[Special Air Service]] (SAS) and | The [[United Kingdom Special Forces]], principally the [[Special Air Service]] (SAS) and Special Boat Service (SBS), but including others, provide troops trained for quick, mobile, military responses in Counter-Terrorism, land, maritime and amphibious operations; often where secrecy or covert operations are required. The Royal Navy is the second largest navy in the Western World in terms of gross tonnage. Despite the United Kingdom's wide-ranging capabilities, recent pragmatic defence policy has a stated assumption that "the most demanding operations" would be undertaken as part of a coalition.<ref>Office for National Statistics "UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" p. 89 </ref> Bosnia, Kosovo, Afghanistan, Iraq ''Granby'', no-fly zones, ''Desert Fox'', and ''Telic'') may all be taken as precedent; indeed the last war in which the British military fought alone was the [[Falklands War]] of 1982, with full-scale combat operations lasting almost three months. | ||
==Culture== | ==Culture== | ||
===Education and science=== | ===Education and science=== | ||
The UK has some of the world's leading universities <ref>"[http://ed.sjtu.edu.cn/rank/2005/ARWU2005_Top100.htm Top 500 World Universities (1-100)]", Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2005. Retrieved 15 May 2006</ref> | The UK has some of the world's leading universities,<ref>"[http://ed.sjtu.edu.cn/rank/2005/ARWU2005_Top100.htm Top 500 World Universities (1-100)]", Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2005. Retrieved 15 May 2006</ref> including the [[University of Oxford]] and the [[University of Cambridge]]. It has produced many great scholars, scientists and engineers including [[Isaac Newton]], [[Adam Smith]], The Lord [[Kelvin]], [[Humphry Davy]], [[Joseph John Thomson]], [[Michael Faraday]], [[Charles Darwin]], [[Alexander Fleming]], [[Francis Crick]], [[Joseph William Bazalgette]] and [[Isambard Kingdom Brunel]]; the nation is credited with numerous inventions including the steam [[locomotive]], [[vaccination]], [[television]], the modern [[railway]], the [[lawn mower]], [[electric lighting]], the [[electric motor]], the [[screw propeller]], the [[internal combustion engine]], the [[jet engine]], the modern [[bicycle]], the [[ejector seat]], the third mechanical and electronic [[computer]], along with the later development of the [[World Wide Web#Origins|World Wide Web]]. | ||
In 2006, it was reported that the UK was the most productive source of research after the USA, producing 9% of the world's scientific research papers and attracting 12% of all citations.<ref>"[http://education.guardian.co.uk/higher/research/story/0,,1736095,00.html Britain second in world research rankings]", ''Guardian'', 21 March 2006, retrieved 14 May 2006.</ref> | In 2006, it was reported that the UK was the most productive source of research after the USA, producing 9% of the world's scientific research papers and attracting 12% of all citations.<ref>"[http://education.guardian.co.uk/higher/research/story/0,,1736095,00.html Britain second in world research rankings]", ''Guardian'', 21 March 2006, retrieved 14 May 2006.</ref> | ||
=== Literature === | === Literature === | ||
The plays of [[William Shakespeare]] crowd the stage of English letters. Other major writers include [[Daniel Defoe]], [[Sir Walter Scott]], [[Jane Austen]], [[Charles Dickens]], the [[Brontë|Brontë sisters]], [[Thomas Hardy]], [[Joseph Conrad]], [[ | The plays of [[William Shakespeare]] crowd the stage of English letters. Other major writers include [[Daniel Defoe]], [[Sir Walter Scott]], [[Jane Austen]], [[Charles Dickens]], the [[Brontë|Brontë sisters]], [[Thomas Hardy]], [[Joseph Conrad]], Sir [[Arthur Conan Doyle]], [[Virginia Woolf]], [[D. H. Lawrence]], George Orwell and [[Graham Greene]] Contemporary British writers include [[Salman Rushdie]] and [[J. K. Rowling]]. | ||
Important playwrights include [[Christopher Marlowe]], [[Ben Jonson]] and, more recently [[Alan Ayckbourn]], [[Harold Pinter]] and [[Tom Stoppard]]. Important poets include [[Geoffrey Chaucer]], Shakespeare, [[John Milton]], [[William Blake]], [[Robert Burns]], [[William Wordsworth]], [[George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron|Lord Byron]], [[John Keats]], [[Alfred, Lord Tennyson|Lord Tennyson | Important playwrights include [[Christopher Marlowe]], [[Ben Jonson]] and, more recently [[Alan Ayckbourn]], [[Harold Pinter]] and [[Tom Stoppard]]. Important poets include [[Geoffrey Chaucer]], Shakespeare, [[John Milton]], [[William Blake]], [[Robert Burns]], [[William Wordsworth]], [[George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron|Lord Byron]], [[John Keats]], [[Alfred, Lord Tennyson|Lord Tennyson]], [[R. S. Thomas]], [[Wilfred Owen]], [[John Betjeman]], [[W. H. Auden]], [[Dylan Thomas]] and [[Ted Hughes]]. | ||
=== Design and architecture === | === Design and architecture === | ||
| Line 215: | Line 135: | ||
=== Music === | === Music === | ||
George Frideric Handel, especially with his English oratorios (notably "Messiah"), is the most performed British composer. Others include [[Henry Purcell]], [[Edward Elgar]], [[Arthur Sullivan]] (most famous for working with librettist [[W. S. Gilbert]]), [[Ralph Vaughan Williams]], and [[Benjamin Britten]]. | George Frideric Handel, especially with his English oratorios (notably "Messiah"), is the most performed British composer (he was naturalized by Act of Parliament in 1727). Others include [[Henry Purcell]], [[Edward Elgar]], [[Arthur Sullivan]] (most famous for working with librettist [[W. S. Gilbert]] as "[[Gilbert and Sullivan]]"), [[Ralph Vaughan Williams]], and [[Benjamin Britten]]. | ||
The UK was, with the USA, one of the two main contributors in the development of [[rock and roll]], and the UK has provided some of the world's most famous rock bands including [[the Beatles]], [[Led Zeppelin]], [[Pink Floyd]] and [[the Rolling Stones]]. The UK was at the forefront of [[punk rock]] with bands like [[the Sex Pistols]] and [[the Clash]], music in the 1970s as well as the subsequent rebirth of [[Heavy metal (music)|heavy metal]]. The late-1970s and 1980s saw the rise of [[New Wave music|New Wave]]. The so-called 'Second British Invasion' into the US popular music scene took place from 1982 to 1984 when UK bands flooded the US Billboard charts. In the mid to late-1990s, the [[Britpop]] phenomenon saw bands such as [[Oasis (band)|Oasis]] and [[Blur]] attain considerable national and international success. The 1990s also saw the rise of major Welsh bands such as [[the Stereophonics]] and [[Manic Street Preachers]]. The UK is also at the forefront of [[electronica]], with British artists such as [[the Prodigy]] and [[the Chemical Brothers]] helping this mainly underground genre to cross over into the mainstream (having originated in the early-90's with techno bands such as [[Orbital (techno)|Orbital]]). Also British pop producers [[Stock Aitken Waterman]] - dominated the charts in the late-80's and early-90's with their instantly recognisable brand of pop. The 1990s charts were also dominated by the [[boy band]] phenomenon, with groups such as [[Take That]] thriving amongst countless others. Girl groups such as the [[Spice Girls ]] also found considerable success. From 1997 onwards, so-called 'soft rock' bands have dominated the serious popular music scene including [[Coldplay]], although after 2003 a high number of 'indie rock' bands emerged and have found considerable success. | |||
=== Media === | === Media === | ||
The UK has a large and diverse media, and the prominence of the English language gives it an international dimension. | The UK has a large and diverse media, and the prominence of the English language gives it an international dimension. | ||
The [[BBC]] is the UK's publicly-funded [[radio]] and [[television]] broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest broadcaster in the world. Funded by the compulsory [[television licence]], the BBC operates several [[BBC Television|television]] channels and [[BBC Radio|radio]] stations both in the UK and abroad. The [[BBC World Service]] radio channel is broadcast in 33 languages around the world. [[BBC News]] is also broadcast around the world. The main, free-to-air television channels in the UK are [[BBC1]], [[BBC2]], [[ITV]]1 (STV in | The [[BBC]] is the UK's publicly-funded [[radio]] and [[television]] broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest broadcaster in the world. Funded by the compulsory [[television licence]], the BBC operates several [[BBC Television|television]] channels and [[BBC Radio|radio]] stations both in the UK and abroad. The [[BBC World Service]] radio channel is broadcast in 33 languages around the world. [[BBC News]] is also broadcast around the world. The main, free-to-air television channels in the UK are [[BBC1]], [[BBC2]], [[ITV]]1 (STV in Scotland), [[Channel 4]] and [[Five (TV)|Five]]. The main satellite broadcaster is [[Sky Digital (UK)|British Sky Broadcasting]], and digital [[Cable television|cable]] services are provided by Virgin Media (created by the merger of NTL and Telewest ), and [[free-to-air]] digital terrestrial television by [[Freeview]]. | ||
Radio in the UK is dominated by [[BBC Radio]], which operates | Radio in the UK is dominated by [[BBC Radio]], which operates ten national and forty regional radio stations. The most popular radio station, by number of listeners, is [[BBC Radio 2]] which specialises in popular music aimed at the '[[middle aged]]' age bracket; it is closely followed by [[BBC Radio 1]], aimed at the 15-24 aged bracket and the previous market leader. Commercial radio tends to be regionalized, although [[Virgin Radio]], [[Classic FM (UK)|Classic FM]] and [[talkSPORT]] are broadcast nationally. Popular regional stations include [[Capital Radio]] in London; [[Heart FM|Heart]] in London and Midlands; [[Galaxy FM|Galaxy]] in Birmingham and the north of England; [[Magic Radio|Magic]] in London and the north of England; and [[Radio Clyde]] in [[Glasgow]]. | ||
Traditionally, British newspapers could be split into "quality", serious-minded newspapers (usually referred to as ''[[broadsheets]]'' because of their large size) and ''[[tabloid]]'', popular newspapers. However, because of considerations of convenience of reading, many traditional broadsheets have both switched to a '[[Compact (newspaper)|compact]]'-sized format, traditionally used by [[tabloid]]s. [[The Sun (newspaper)|''The Sun'']] has the highest circulation of any daily newspaper in the UK, with approximately a quarter of the market; its sister paper, ''[[The News of The World]]'' similarly leads the Sunday newspaper market <ref> [http://www.timesonline.co.uk/section/0,,1782,00.html ABC Newspaper Circulation Figures] ''[[The Times]]'', May 12 2006, accessed May 16 2006.</ref> | Traditionally, British newspapers could be split into "quality", serious-minded newspapers (usually referred to as ''[[broadsheets]]'' because of their large size) and ''[[tabloid]]'', popular newspapers. However, because of considerations of convenience of reading, many traditional broadsheets have both switched to a '[[Compact (newspaper)|compact]]'-sized format, traditionally used by [[tabloid]]s. [[The Sun (newspaper)|''The Sun'']] has the highest circulation of any daily newspaper in the UK, with approximately a quarter of the market; its sister paper, ''[[The News of The World]]'' similarly leads the Sunday newspaper market,<ref> [http://www.timesonline.co.uk/section/0,,1782,00.html ABC Newspaper Circulation Figures] ''[[The Times]]'', May 12 2006, accessed May 16 2006.</ref> and traditionally focuses on celebrity-led stories. ''[[The Daily Telegraph]]'', a [[Right-wing politics|right-of-centre]] paper, is the highest selling of the ''qualities'' (former broadsheets), having overtaken ''[[The Times]]'' in circulation figures.<ref>{{cite web | ||
<ref>{{cite web | |||
| url = http://www.abc.org.uk/ | | url = http://www.abc.org.uk/ | ||
| title = Audit Bureau of Circulation ''Interactive Analysis National Newspaper Selection - Average Net Circulation (UK) 03-Jul-2006 to 30-Jul-2006'' | | title = Audit Bureau of Circulation ''Interactive Analysis National Newspaper Selection - Average Net Circulation (UK) 03-Jul-2006 to 30-Jul-2006'' | ||
| accessdate = 2006-09-04 | | accessdate = 2006-09-04 | ||
}} Lists ''Daily Telegraph'' as 844,929 and ''The Times'' as 620,456.</ref> | }} Lists ''Daily Telegraph'' as 844,929 and ''The Times'' as 620,456.</ref> ''[[The Guardian]]'' is a more [[Liberalism_in_the_United_Kingdom|liberal]] or left-wing former broadsheet. The ''[[Financial Times]]'' is the main business paper, printed on distinctive salmon-pink broadsheet paper. | ||
''[[The Guardian]]'' is a more [[Liberalism_in_the_United_Kingdom|liberal]] or left-wing former broadsheet. The ''[[Financial Times]]'' is the main business paper, printed on distinctive salmon-pink broadsheet paper. | |||
===Sport=== | ===Sport=== | ||
A number of major sports originated in the United Kingdom including [[association football]] and [[cricket]], which are the world's most popular team sports in terms of both spectators and participants. Other sports which originated in Britain are [[golf]] and rugby football ([[rugby union]] and [[rugby league]]), while sports like [[boxing]], [[horse racing]], [[motor racing]], and [[tennis]] owe their modern popularity to British development and promotion. London has hosted the [[Olympic Games]] three times — in 1908, 1948, and 2012. | |||
A number of major | |||
The most popular sport in the | ====Football==== | ||
The most popular sport in the country is association football, commonly known just as "football". The UK never competes as a nation in football tournaments. Instead, the home nations compete individually as [[England national football team|England]], [[Northern Ireland national football team|Northern Ireland]], [[Scotland national football team|Scotland]], and [[Wales national football team|Wales]]. It is because of this unique four-team arrangement that the British Olympic squad does not include a football team. | |||
Domestically, British football clubs compete in [[Football in the United Kingdom|national leagues and competitions]] from which the top teams may qualify to compete in European competitions. English clubs are generally successful in Europe and several have won continental titles. The most prestigious title is the European Cup, now called the UEFA Champions League. [[Celtic F.C.|Celtic]] were the first British winners of the European Cup in 1967, but that remains the only one won by a Scottish club. [[Liverpool F.C.|Liverpool]] with six European Cup wins to 2024 are the most successful British club; [[Manchester United F.C.|Manchester United]] were the first English winners in 1968 and have three titles. | |||
====Cricket==== | |||
Football superseded cricket as the country's national sport around the end of the 19th century. Cricket is still the most popular summer sport with clubs in almost every town and village, especially throughout England. The highest level of domestic competition is the [[County Cricket Championship]], which involves eighteen county clubs as far afield as [[Durham (cricket)|Durham]], [[Kent (cricket)|Kent]], and [[Somerset (cricket)|Somerset]]. Seventeen of the [[First-class cricket|first-class counties]] are in England; the exception is [[Glamorgan (cricket)|Glamorgan]] in South Wales. The most successful county teams tend to be those with international stadiums such as [[Yorkshire (cricket)|Yorkshire]], [[Lancashire (cricket)|Lancashire]], [[Nottinghamshire (cricket)|Nottinghamshire]], [[Surrey (cricket)|Surrey]], and [[Middlesex (cricket)|Middlesex]] whose home ground is the famous [[Lord's Cricket Ground|Lord's]], owned by [[Marylebone Cricket Club]] (MCC) in north London. | |||
Internationally, the [[England (cricket)|England]] team is an amalgam of England and Wales, reflecting the structure of the County Championship. England is a full member of the [[International Cricket Council]] (ICC) and so plays [[Test cricket]]. Northern Ireland and the [[Republic of Ireland]] play cricket together and the combined [[Ireland (cricket)|Ireland]] team is also a full ICC member. [[Scotland (cricket)|Scotland]] has been independent in cricket since 1992 and is an associate member of the ICC, meaning they can play in [[limited over international]] matches but not Test matches. | |||
====Other sports==== | |||
[[Horse racing]] has been very popular in England ever since the time of [[Charles II]] when it became known as the "Sport of Kings". It remains a royal pastime to this day and [[Elizabeth II]] was an acknowleged expert. World-famous races include the [[Grand National]] and the [[Epsom Derby]]. | |||
The ancient sport of boxing became popular in 18th century England in the form of bareknuckle prizefighting for large purses. A set of rules was drafted in 1743 by the champion fighter Jack Broughton and these formed the basis of the London Prize Ring Rules in 1838. Modern boxing is based on the Queensberry Rules which were written by John Graham Chambers, a Welshman, in 1865. Heavyweight boxing is very popular in Britain and the country has produced several famous fighters including Bob Fitzsimmons, Tommy Farr, Henry Cooper, Lennox Lewis, and Tyson Fury. | |||
Golf | Golf, which originated in Scotland, remains one of the UK's most popular participation sports. The Royal and Ancient Golf Club, which organises the Open Championship every July, is based in St Andrews, Fife. The Open is one of golf's four Major Tournaments. In [[tennis]], the [[Wimbledon Championships]] are held in June each year and this is one of the four Grand Slam tournaments. | ||
[[Shinty|Shinty or camanachd]] (a sport derived from the same root as the | [[Shinty|Shinty or camanachd]] (a sport derived from the same root as the Irish [[hurling]] and similar to [[bandy]]) is popular in the Scottish Highlands, sometimes attracting crowds numbering thousands in the most sparsely populated region of the UK. | ||
The country is closely associated with [[motorsport]]. Many teams and drivers in [[Formula One]] and | The country is closely associated with [[motor racing|motorsport]] of all kinds. Many teams and drivers in [[Formula One]] and other events are based in Britain and the British Grand Prix, held every summer at the Silverstone race track in [[Northamptonshire]], is an event in the Formula One World Championship. British world champions in Formula One include Jim Clark, Jackie Stewart and Lewis Hamilton. | ||
Legend has it that a schoolboy called William Webb Ellis invented rugby football when he picked up the ball during a football match and ran with it in his hands into his opponents' goal. The story is apocryphal but the sport does get its name from the school in [[Rugby, Warwickshire]], where Webb was a pupil in the 1820s (the same place is the setting for ''[[Tom Brown's Schooldays]]''). Rugby league originated in the North of England in 1895, following a split with union on the issue of professionalism. League is still a predominately northern sport, whereas union is very popular in Wales and has many clubs throughout the South of England. Union is considered the national sport of Wales. League has a single international team called Great Britain; union has England, Scotland, and Wales. As in cricket, Northern Ireland is part of a combined Ireland team. Union also has the British and Irish Lions team for summer tours of Australia, New Zealand or South Africa. | |||
==Symbols== | ==Symbols== | ||
* The '''flag''' of the UK is the Union Flag (commonly known as the "Union Jack"), which is a superimposition of the flags of England (St George's Cross) and Scotland (Saint Andrew's Cross); the Saint Patrick's cross, representing Ireland, was added in 1801. | |||
* The ''' | * The '''national anthem''' is ''God Save the King'', or ''God Save the Queen'', as appropriate.<ref> It is sometimes asserted by those used to a legislative tradition that ''God Save the King/Queen'' is not the actual national anthem of the UK, (or sometimes that it is the ''de facto'' national anthem) because no law has ever been passed to say so. In Britain, however, codification of the law is usually unnecessary; custom, practice and proclamation are sufficient to establish it as the official national anthem.</ref> | ||
* [[Britannia]] is a personification of | * [[Britannia]] is a personification of Great Britain, originating from the Roman occupation of the southern and central parts of the island, which they called Britannia.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.24carat.co.uk/britanniaframe.html |title=Britannia on British Coins |publisher=Chard |accessdate=2006-06-25}}</ref> Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag. Sometimes she is depicted as riding the back of a lion. In modern usage, Britannia is often associated with maritime dominance, as in the patriotic song ''[[Rule Britannia]]''. | ||
* The [[lion]] has also been used as a symbol of the UK; one is depicted behind Britannia on the 50 pence piece and one is shown crowned on the back of the 10 pence piece, it is also used as a symbol on the non-ceremonial flag of the [[British Army]]. Lions have been used as | * The [[lion]] has also been used as a symbol of the UK; one is depicted behind Britannia on the 50 pence piece and one is shown crowned on the back of the 10 pence piece, it is also used as a symbol on the non-ceremonial flag of the [[British Army]]. Lions have been used as heraldic devices many times, including in the royal arms of the kingdoms of England, Scotland, Kingdom of Gwynedd in Wales and of Northern Ireland. The lion is featured on the emblem of the England national football team, and the England Women's team is known as the Lionesses. | ||
* The | * The bulldog, or "British Bulldog", is sometimes used as a symbol of the United Kingdom. | ||
*Britain (especially England) is also personified as the character [[John Bull]]. | * Britain (especially England) is also personified as the character [[John Bull]]. | ||
==Miscellaneous data== | ==Miscellaneous data== | ||
* Cellular | * Cellular frequency: GSM 900, GSM 1800, UMTS 2100 | ||
* Cellular | * Cellular technology: [[Global System for Mobile Communications|GSM]]/[[General Packet Radio Service|GPRS]]/[[Enhanced Data Rates for Global Evolution|EDGE]]/[[Universal Mobile Telecommunications System|UMTS]]/[[HSDPA|HSDPA]] | ||
* | * Date format: DD/MM/YY (example: 22/12/05) or 22 December 2005 | ||
* [[Time]] format: Generally 12-hour format when spoken or in writing (example: 5.15 pm), 24-hour format is used in some official documentation and in timetables (example: 17:15 or 1715). | * [[Time]] format: Generally 12-hour format when spoken or in writing (example: 5.15 pm), 24-hour format is used in some official documentation and in timetables (example: 17:15 or 1715). | ||
* | * Decimal separator is a [[full stop]]: 123.45 | ||
* Thousands are separated (formal) by a comma: 10,000. (To avoid confusion with continental countries which use the comma as the decimal separator, a space may be used, e.g. 10 000.) | * Thousands are separated (formal) by a comma: 10,000. (To avoid confusion with continental countries which use the comma as the decimal separator, a space may be used, e.g. 10 000.) | ||
* [[Voltage]]: 230V (+10% / -6%), 50 Hz; | * [[Voltage]]: 230V (+10% / -6%), 50 Hz; Power connector: 3 rectangle pins | ||
== | ==Footnotes== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
[[Category: | [[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:00, 3 November 2024
The United Kingdom is a political union of the countries of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Its formal title is "The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland". It is often referred to as "Britain", including by the government. Its principal language is English, but the Welsh language is also officially recognised. Other indigenous languages include Scots, Scottish Gaelic and British Sign Language. Its citizens are called Britons (or, informally, "Brits"), and their nationality is referred to as "British". It is located off the north-western coast of Europe, and it is geographically and politically a part of the continent. It is a member of the British Commonwealth and the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation and is a founder member of the United Nations with a permanent seat on the United Nations Security Council. In 2016, a majority of British voters opted to leave the European Union, and this was implemented in 2020.
History
The British people have acquired a genetic inheritance from immigrants including Celts, Romans, Saxons, Danes, Normans, and many others. An early cultural inheritance came from the Celts of central Europe and a further contribution came when missionaries established monasteries in the British Isles. Little cultural progress was made during the five centuries of Anglo-Saxon rule in England, however, and the technological knowledge that was lost when the Romans left was only slowly regained. Intellectual thought was dominated for several centuries by a religious establishment concerned mainly with the preservation of orthodoxy, and it was not until the Renaissance that inductive modes of reasoning became acceptable. The British constitutional inheritance has been the outcome of an intermittent progression from an unruly conglomeration of uncoordinated kingships into an orderly democratic nation. A transition from autocracy to constitutional monarchy happened by the transfer of power to deliberative assemblies in a succession of discrete steps that included the Magna Carta of 1215, the Bill of Rights of 1688, the Reform Act of 1867, and the Representation of the People Act of 1928. The dissolution of the rigid hierarchical structure of rights and obligations of the feudal system happened at an earlier stage in Britain than in other European countries and the resulting increase in labour mobility made possible the earlier development of the Industrial Revolution -and gave it a decisive, although temporary, economic advantage. As a result it was for a time, the world's richest and most powerful country. It acquired - and then lost - responsibility for managing the world's financial system, and for ruling an Empire of almost a quarter of the world's population, covering a larger area than any other empire in history. In the course of the 20th century, it suffered major losses of its economic resources in two world wars and it gave independence to nearly all the former members its empire, and devolved a degree of legislative independence to Northern Ireland, Wales and Scotland. It joined the European Union but did not adopt its common currency. It joined with the United States of America in the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, and supported it in wars in Korea, Afghanistan and Iraq, but not Vietnam.
Government and politics
The Constitution
Parliamentary sovereignty is the ruling principle of the constitution[1] of the United Kingdom. Parliament is the country's supreme legal authority, and it can create or end any law. It has from time to time passed laws that limit the application of its sovereignty, but it is not bound by those laws. nor by any other of its past decisions [2].
The UK parliament is bicameral, consisting of a wholly-elected House of Commons and a mainly-appointed House of Lords, of which the House of Commons is its primary legislative assembly, and the functions of the House of Lords are mainly deliberative. Once elected, the House of Commons serves for a fixed term of five years unless the government loses a vote of no confidence, and unless a new government does not receive a vote of confidence within a fortnight, or two thirds of its members vote for its dissolution[3].
The political head of the UK government is its Prime Minister who is a member of one of the Houses of Parliament, appointed by the Monarch on the presumption that he or she would able to command the support of a majority of the members of the House of Commons. (The appointee is expected to submit his or her resignation if he or she is unable to win the of confidence of the House of Commons). It is nowadays understood that the Prime Minister must be in the House of Commons. (Apart from a very short period in 1963,[4] this has always been the case since 1902.) The person chosen to be Prime Minister is normally the elected leader of one of the country's political parties.
The British monarch is the country's Head of State. The functions of the monarchy are mainly ceremonial, but the Sovereign, as its embodiment, has the right to advise the Prime Minister in private. The Sovereign has the personal power to resolve an otherwise intractable constitutional crisis but is bound, in all other circumstances, to give way to ministerial advice. In other respects, the royal prerogative, which includes the power to declare war, is effectively exercised by ministers. The ancient feudal functions of the monarchy continue to be reflected in constitutional and legal terminology and usage. For those purposes, the term "The Crown", refers to a legal fiction that makes the state a legal entity that can be a party to a legal transaction or a legal action[5].
The conduct of government
It is the Prime Minister's responsibility to select those members of the Houses of Parliament who are to become Ministers and serve as political managers of government departments, and to decide who among them are to serve in the top decision-making body known as "the Cabinet". With rare exceptions, a government's business is conducted in accordance with the "doctrine of collective responsibility"[6], under which ministers are bound to defend Cabinet decisions, whether or not they agree with them. The conduct of ministers is governed by a ministerial code[7] covering their personal conduct, the presentation of policy, and their relations with Parliament and the civil service. Ministers receive political advice from "special advisers", and impartial advice from permanent civil servants. Permanent civil servants are recruited by open competition under the supervision of an independent Commission[8], and their appointment does not change with changes of government; whereas special advisers are temporary civil servants who are appointed by ministers, and whose tenure ends when there is a change of government[9]. In 2010/11 there were 68 special advisors[10] within a total of about 440,000 civil servants. Legislation is normally initiated by government departments and piloted through the legislative process by the party Whips. Legislative proposals by a Government with a substantial majority in the House of Commons are usually enacted. Government Whips warn members who rebel against its motions that they are damaging their prospects of promotion.
Political parties
Nearly all MPs belong to political parties; often all do. Currently, 10 parties are represented in the Commons, of which the only two that have been in power alone recently are the Conservative Party and the Labour Party. The Liberal Democrats were in a coalition government from 2010 to 2015. Among the others, the Scottish National Party and Plaid Cymru campaign for the independence of Scotland and Wales respectively; the Democratic Unionist Party(DUP) represent unionist, and Sinn Féin and the Social Democratic an Labour Party represent nationalist interests in Northern Ireland, while the Alliance Party tries to bridge the divide. The Green Party is also represented in the Commons. Many other parties are represented in other elected positions, or were formerly represented in Parliament. Analysts have remarked upon the apparent lack of ideological differences among the three major national parties[11], an impression that is supported by a comparison of their 2010 election manifestoes[12].
The current administration
The 2019 United Kingdom general election resulted in a majority for the Conservative Party led by Boris Johnson. He was succeeded as Prime Minister by Liz Truss on 6th September 2022, and she in turn was succeeded by Rishi Sunak on 25th October.
Regional Structure
Devolution
Following devolution referendums in Scotland and Wales in 1997, and in both parts of Ireland in 1998, the United Kingdom Parliament transferred a range of powers to national parliaments or assemblies[13]. The arrangements are different in the three parts of the country, reflecting their history and administrative structures. The Scottish Government develops and implements policy on matters that include health, education, justice, rural affairs and transport[14], and is accountable to the Scottish Parliament[15]. The Welsh Assembly Government[16] has responsibilities which include health, education, economic development, culture, the environment and transport, and is accountable to the National Assembly for Wales[17]. The Northern Ireland Executive[18] is responsible for economic and social matters, agriculture and rural development, culture, arts, education, health, social services and public safety, and is accountable to the Northern Ireland Assembly[19]. The United Kingdom Parliament is still able to pass legislation for any part of the United Kingdom, though in practice it only deals with devolved matters with the agreement of the devolved governments.
Local Government
The United Kingdom is divided, for the purposes of government, into a set of further administrative subdivisions. In most of England there are two levels of local government: a county council and a district council. County councils cover large areas and provide public services that include schools, social services, and public transportation. District councils cover smaller areas and provide more local services, including council housing, gyms and leisure facilities, local planning, recycling and trash collection. In most large towns and cities, and in some small counties, there is only one level of local government responsible for all local services. In London, each borough is a unitary authority, but the Greater London Authority provides London-wide services including transport and police. In Scotland there is a unitary system with one level of local government. In Northern Ireland there are local councils, but most services are carried out by other organisations. In some parts of England and Wales there are also town and parish councils that are responsible for services like allotments, public toilets, parks and ponds, war memorials, and local halls and community centres. In Wales, they are called community councils. In Scotland there are community councils with fewer powers. There is no equivalent in Northern Ireland.
Law
The United Kingdom has three systems of law: one for England and Wales, one for Northern Ireland and one for Scotland. In England and Wales and Northern Ireland they are "common law systems", under which decisions are determined by precedent, except where precedent is overruled by legislation (as distinct from "civil law systems" under which decisions are determined exclusively by legislative enactment). Scotland has a "mixed jurisdiction system" which is a mixture of common law and civil law. Each system has a hierarchy of courts, and each permits appeal to a higher court against a decision of a lower court. In England and Wales, the court system includes the Court of Appeal, the High Court of Justice (for civil cases) and the Crown Court (for criminal cases). In Scotland, the principal courts are the Court of Session, for civil cases, and the High Court of Justiciary, for criminal cases, and the sheriff court is the Scottish equivalent of the English county court. The United Kingdom's highest court is the Supreme Court,[20] roughly speaking. The provisions of the European Communities Act 1972 require United Kingdom courts to apply European law, and to give it preference when it conflicts with previous parliamentary legislation[21]. The Human Rights Act 1998[22] embodies the provisions of the European Convention on Human Rights.
Geography
The United Kingdom comprises the island of Great Britain, Northern Ireland, and numerous smaller islands in the surrounding seas. It is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean and its ancillary bodies of water, including the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, and the Irish Sea. On the island of Ireland, Northern Ireland has a land border with the Republic of Ireland to the south and west. There are several islands which are not part of the United Kingdom, including the Isle of Man, Jersey, Guernsey and Alderney). They are all British Crown Dependencies, which means that they are effectively self-governing with their own legislature and tax systems: the UK remains responsible for foreign policy and in certain circumstances has legal authority superior to the parliaments.
Most of England consists of rolling lowland, divided east from west by mountains in the Northwest (Cumbrian Mountains of the Lake District) and north (the upland moors of the Pennines) and limestone hills of the Peak District by the Tees-Exe line. The lower limestone hills of the Isle of Purbeck, Cotswolds, Lincolnshire and chalk downs of the Southern England Chalk Formation. The main rivers and estuaries are the Thames, Severn and the Humber Estuary. The largest urban area is Greater London. Near Dover, the Channel Tunnel links the UK to France.[23] The highest mountain in England is Scafell Pike in the Lake District, at 978m (3,208 ft).
Scotland's geography is varied, with lowlands in the south and east and highlands in the north and west, including Ben Nevis, the highest mountain in the British Isles at 1,343m (4,406 ft). There are many long and deep-sea arms, firths, and lochs. Scotland has nearly 800 islands, mainly west and north of the mainland, notably the Hebrides, Orkney Islands and Shetland Islands. The capital city is Edinburgh, the centre of which is a World Heritage site. The largest city is Glasgow.[24] The UK has about 1,000 islands, with 700 in Scotland alone.[25]
Wales (Cymru in Welsh) is mostly mountainous, the highest peak being Snowdon (Yr Wyddfa) at 1,085m (3,560 ft) above sea level. North of the mainland is the island of Anglesey (Ynys Môn). The largest city, Cardiff (Caerdydd), has been the Welsh capital since 1955.[26] The greatest concentration of people live in the south, in the cities of Swansea and Newport, as well as Cardiff, and the South Wales Valleys. The largest town in North Wales is Wrexham.
Northern Ireland, making up the north-eastern part of Ireland, is mostly hilly. The capital is Belfast ('Béal Feirste' in Irish), with other major cities being Londonderry/Derry ('Doire' in Irish) and Armagh. The province includes one of the UK’s World Heritage sites, the Giant's Causeway, which consists of more than 40,000 hexagonal basalt columns up to 40 feet (12 m) high. Lough Neagh, the largest body of water in the British Isles (388 km² / 150 mi²), can be found in Northern Ireland.[27] The highest peak is Slieve Donard at 849m (2,786 ft) in the Mourne Mountains.
Climate
England has a temperate climate, with plentiful rainfall all year round. The seasons are quite variable in temperature, but temperatures rarely fall below −5°C (23°F) or rise above 30°C (86°F). The prevailing wind is from the south-west, bringing mild and wet weather regularly from the Atlantic Ocean. It is driest in the east and warmest in the south-east. Snowfall can occur in Winter and early Spring, though it is uncommon away from high ground. The highest temperature recorded in England is 38.5 °C (101.3 °F) on 10 August 2003 at Brogdale, near Faversham, in Kent. [1]. The lowest temperature recorded is −26.1 °C (−15.0 °F) on 10 January 1982 at Edgmond, near Newport, in Shropshire. [2]
Wales' climate is similar, with the highest temperature recorded at 35.2°C (95.4°F) in Hawarden Bridge, Flintshire on 2 August 1990, and the lowest temperature at -23.3°C (-10°F) in Rhayader, Radnorshire on 21 January 1940. [1]
The climate of Scotland is temperate and oceanic, and tends to be very changeable. It is warmed by the Gulf Stream from the Atlantic, and is much warmer than areas on similar latitudes, for example Oslo, Norway. However, temperatures are generally lower than in the rest of the UK, with the coldest ever UK temperature of -27.2°C (-16.96°F) recorded at Braemar in the Grampian Mountains, on 11 February 1895 and 10 January 1982 and also at Altnaharra, Highland, on 30 December 1995. Winter maximums average 6°C (42.8°F) in the lowlands, with summer maximums averaging 18°C (64.4°F). The highest temperature recorded was 32.9°C (91.22°F) at Greycrook, Scottish Borders on 9 August 2003.
Generally, western Scotland is warmer than the east because of the influence of the Atlantic ocean currents and the colder surface temperatures of the North Sea. Tiree, in the Inner Hebrides, is the sunniest place in Scotland: it had 300 days with sunshine in 1975. Rainfall varies widely across Scotland. The western highlands of Scotland are the wettest place, with annual rainfall exceeding 3,000 mm (120 inches),while much of lowland Scotland receives less than 800 mm (31 inches) annually. Heavy snowfall is not common in the lowlands, but becomes more common with altitude. Braemar has an average of 59 snow days per year, while coastal areas have an average of fewer than 10 days.
Northern Ireland has a temperate maritime climate, wetter in the west than the east, although cloud cover is persistent across the region. The weather is unpredictable at all times of the year, and the seasons are less pronounced than in interior Europe or the eastern seaboard of North America. Average daytime maximums in Belfast are 6.5°C (43.7°F) in January and 17.5°C (63.5°F) in July. The damp climate and extensive deforestation in the 16th and 17th centuries resulted in much of the region being covered in rich green grassland. The highest maximum temperature was set at 30.8°C (87.4°F) at Knockarevan, near Belleek, County Fermanagh on 30 June 1976 and at Belfast on 12 July 1983, whilst the lowest minimum temperature recorded at -17.5°C (0.5°F) in Magherally, near Banbridge, County Down on 1 January 1979. [16]
The UK, like the rest of Europe, has been in recent years, hit by many freak heatwaves during the summer. The heatwaves have been the reason for many deaths in the past years when temperatures easily soar past 30°C (86°F), nearing the 40°C (104°F) mark.
Cities
Due to differences between the administrative boundaries and metropolitan areas of cities, and because of merging of settlements into conurbations, there are many different statistics and debates on which cities are the UK's largest. The capitals of the UK's constituent countries are London (England), Edinburgh (Scotland), Cardiff (Wales) and Belfast (Northern Ireland). London is by far the UK's largest city,[28] whilst Birmingham is considered, population-wise, the 'second city'.
Demography
The UK population according to the 2011 census was 63,181,775.[29] In 2007 birth per woman were 1.84 (up from 1.74 in 2005); the net annual migration was 190,000 (up from 145,000 in 2005), and the life expectancy at birth for females was 86.2 years (up from 85.0).
Its overall population density is one of the highest in the world. About a quarter of the population lives in the south-east[30] and is predominantly urban and suburban, with an estimated 7,517,700 in the capital of London.[31] The United Kingdom's high literacy rate (99%)[32] is attributable to universal public education established by law for the primary level in 1870 (though in fact nearly all children of primary age were already attending school) and secondary level in 1900 (except in Scotland where it was introduced in 1696). Education is mandatory from ages four or five (dependent on birth date) to sixteen.
Population history
The lands now constituting the UK have been subject to many invasions and migrations, especially from Scandinavia and the continent of Europe, including Roman occupation for several centuries. The Romans, however, left a minimal long-term impact on the culture. The Celtic, Anglo-Saxon, and Norse cultural traditions were blended under the Normans after that French-speaking group invaded and conquered England in 1066.
Immigration
Immigration has come through interaction with continental Europe and ties forged by the British Empire. Continuous waves of immigration have brought people to the UK, with Europe, Africa and South-East Asia being the biggest areas from where people emigrate. The UK has amongst the highest immigration rates in Europe, along with Italy and Spain[33] In the Greater London area the 2011 census found only 45% of the population identifying themselves as "White British"[34] and only about 43% identifying as English. The latest wave of immigration began in May 2004 when the European Union was expanded. From May 2004 to June 2006, around 600,000 people from Central and Eastern Europe emigrated to the UK to work; this figure is for arrivals only and does not take account of people leaving, so net migration will be lower.[35] In 2004 net migration from EU states stood at 74,000.[36]
Language
English is understood and used everyday by the vast majority of British people. Its continued use is therefore of some cultural importance; the British enjoy the prestige and status of being a major English-speaking nation whose language acts as a common lingua franca for millions worldwide.
Various laws and procedures award some degree of recognition to other indigenous languages of the UK: for example, in 2011, Welsh became an official language of Wales through legislation passed by the Welsh Assembly[37], and Scottish law promotes Scots Gaelic with a view to making it official. In Northern Ireland, Irish and Ulster Scots are officially-recognised minority varieties. European Union legislation designed to protect minority languages has also granted some legislative protection to such languages as Scots, Cornish and British Sign Language (BSL). In contrast, though English is recognised in Scotland and Wales, no legal document explicitly defines it as an official language of the whole UK, meaning that the tongue of the overwhelming majority is protected by its sheer number of speakers rather than any act of parliament (though all acts of the British Parliament are in English).
The UK's native languages, aside from BSL, can be divided into two families: English and Scots are two closely-related Germanic languages, while Welsh, Scots Gaelic, Irish and Cornish are Celtic.[38]
Romani is a language brought to the UK's shores through immigration, but in the UK the term immigrant languages is generally reserved for more recent arrivals. The open passport system in the Commonwealth enabled immigration from former colonies. The UK includes the largest groups of Hindi and Punjabi speakers outside Asia. Such groups may maintain ties with historic homelands while playing an active part in all aspects of British life.
Even more recently, the expansion of the European Union in 2004 to accommodate ten mainly Eastern European countries has led to increased, although predominantly temporary, immigration. In a typical British urban area, therefore, languages such as Polish may be heard alongside Urdu and Bengali; likewise, English as a first or second language will be common to most of these speakers. Polish is currently the UKs second most spoken language, though this may cease to be true after the UK leaves the EU.
Religion
The United Kingdom is an increasingly secular society. Numbers saying they have no religion vary substantially with the exact form of the question, but time series indicate a substantial increase, and some surveys now give a majority. However, this overall decline masks increases, sometimes substantial, in non-Christian religions.[39] Similarly, the decline in Christianity masks growth in some forms, particularly some Evangelical/Pentecostal churches.
In terms of actual religious practice, 62 percent of those surveyed say that they never attend a religious service[40] The Church of England is the officially established church in England, and is the senior branch of the worldwide Anglican Communion[41]. The Presbyterian Church of Scotland (known as "The Kirk") is the official national church of Scotland. In Wales, the Church in Wales is disestablished from the Church of England, but remains a member of the Anglican communion. The Roman Catholic Church is the country's second largest Christian denomination and is the largest denomination in Northern Ireland. The Presbyterian Church in Ireland is closely linked to the Church of Scotland, and is the province's largest Protestant denomination. The United Kingdom's Christian denominations also include the Methodists and Baptists, and there are substantial numbers of Muslims, Hindus and Sikhs with Judaism, Buddhism and other religions occurring in smaller numbers.
Economy
(the numbers quoted in this paragraph come from the OECD 2010 factbook[3], unless otherwise stated)
The United Kingdom has an open market economy with limited natural resources and a proficient workforce. It is an industrialised economy with a small agricultural sector. In more precise terms, trade in goods and services amounts to around 30 percent of GDP, and there are no trade restrictions except for agricultural products. Seventy percent of the working age population is in employment, with proficiency levels in reading, mathematics and science that are close to the OECD average. Agricultural products account for less than one percent of the value of domestic output, as compared with 39 percent for production and distribution, 17 percent for government, health and education, and 8 per cent for finance and insurance[42]. It is a heavily indebted economy with a household debt burden among the highest in the world at about 160 percent of disposable income, and government debt in line with the OECD average at about 100 percent of GDP; and the debt burden is expected to rise[43]. As percentages of GDP, total tax revenue, and taxation on corporate income are about the same as the OECD average, and the revenue from taxation on personal income is about 10 per cent higher. The economy is currently running at below capacity with an output gap of 4.4 percent, compared with a 3.4 percent OECD average, and the unemployment rate is 7.9 percent compared with an OECD average of 8.5 percent.
Armed Forces
The armed forces of the UK are known as the British Armed Forces or His Majesty's Armed Forces, but officially Armed Forces of the Crown. Their Commander-in-Chief is the British monarch, HM The King and they are managed by the Ministry of Defence. The armed forces are controlled by the Defence Council currently headed by Air Chief Marshal Sir Jock Stirrup.
The UK fields one of the most powerful and comprehensive armed forces in the World. Its global power projection capabilities are second only to those of the United States Military. The UK has the 2nd highest military expenditure in the world after the USA.
The UK has a comprehensive nuclear arsenal, one of the few countries to do so, using the submarine-based Trident II ballistic missile system with nuclear warheads. These Vanguard class submarines were designed and built by VSEL (now BAE Systems Submarines) at Barrow-in-Furness.
The British Armed Forces are charged with protecting the UK and its overseas territories, promoting the UK's wider security interests, and supporting international peacekeeping efforts. They are active and regular participants in the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) and other coalition operations.
The British Army had a reported strength of 102,440 in 2005[44] and the Royal Air Force a strength of 49,210. The 36,320-member Royal Navy operates the UK's nuclear deterrent, which consists of four Trident missile-armed submarines, while the Royal Marines are the Royal Navy's Light Infantry units for amphibious operations and for specialist reinforcement forces in and beyond the NATO area. This puts total active duty military troops in the 190,000 range, currently deployed in over eighty countries.
There are also reserve forces supporting the regular military. These include an army reserve, the Territorial Army (TA); the Royal Naval Reserve (RNR), Royal Marines Reserve (RMR) and the Royal Auxiliary Air Force (RAuxAF). About 9% of the regular armed forces are comprised of women, a figure that is higher for the reserve forces.
The United Kingdom Special Forces, principally the Special Air Service (SAS) and Special Boat Service (SBS), but including others, provide troops trained for quick, mobile, military responses in Counter-Terrorism, land, maritime and amphibious operations; often where secrecy or covert operations are required. The Royal Navy is the second largest navy in the Western World in terms of gross tonnage. Despite the United Kingdom's wide-ranging capabilities, recent pragmatic defence policy has a stated assumption that "the most demanding operations" would be undertaken as part of a coalition.[45] Bosnia, Kosovo, Afghanistan, Iraq Granby, no-fly zones, Desert Fox, and Telic) may all be taken as precedent; indeed the last war in which the British military fought alone was the Falklands War of 1982, with full-scale combat operations lasting almost three months.
Culture
Education and science
The UK has some of the world's leading universities,[46] including the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge. It has produced many great scholars, scientists and engineers including Isaac Newton, Adam Smith, The Lord Kelvin, Humphry Davy, Joseph John Thomson, Michael Faraday, Charles Darwin, Alexander Fleming, Francis Crick, Joseph William Bazalgette and Isambard Kingdom Brunel; the nation is credited with numerous inventions including the steam locomotive, vaccination, television, the modern railway, the lawn mower, electric lighting, the electric motor, the screw propeller, the internal combustion engine, the jet engine, the modern bicycle, the ejector seat, the third mechanical and electronic computer, along with the later development of the World Wide Web.
In 2006, it was reported that the UK was the most productive source of research after the USA, producing 9% of the world's scientific research papers and attracting 12% of all citations.[47]
Literature
The plays of William Shakespeare crowd the stage of English letters. Other major writers include Daniel Defoe, Sir Walter Scott, Jane Austen, Charles Dickens, the Brontë sisters, Thomas Hardy, Joseph Conrad, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, Virginia Woolf, D. H. Lawrence, George Orwell and Graham Greene Contemporary British writers include Salman Rushdie and J. K. Rowling.
Important playwrights include Christopher Marlowe, Ben Jonson and, more recently Alan Ayckbourn, Harold Pinter and Tom Stoppard. Important poets include Geoffrey Chaucer, Shakespeare, John Milton, William Blake, Robert Burns, William Wordsworth, Lord Byron, John Keats, Lord Tennyson, R. S. Thomas, Wilfred Owen, John Betjeman, W. H. Auden, Dylan Thomas and Ted Hughes.
Design and architecture
The UK has produced a number of important architects, including Sir Christopher Wren, and Sir Norman Foster along with designers Charles Rennie Mackintosh and Jonathan Ive.
Music
George Frideric Handel, especially with his English oratorios (notably "Messiah"), is the most performed British composer (he was naturalized by Act of Parliament in 1727). Others include Henry Purcell, Edward Elgar, Arthur Sullivan (most famous for working with librettist W. S. Gilbert as "Gilbert and Sullivan"), Ralph Vaughan Williams, and Benjamin Britten.
The UK was, with the USA, one of the two main contributors in the development of rock and roll, and the UK has provided some of the world's most famous rock bands including the Beatles, Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd and the Rolling Stones. The UK was at the forefront of punk rock with bands like the Sex Pistols and the Clash, music in the 1970s as well as the subsequent rebirth of heavy metal. The late-1970s and 1980s saw the rise of New Wave. The so-called 'Second British Invasion' into the US popular music scene took place from 1982 to 1984 when UK bands flooded the US Billboard charts. In the mid to late-1990s, the Britpop phenomenon saw bands such as Oasis and Blur attain considerable national and international success. The 1990s also saw the rise of major Welsh bands such as the Stereophonics and Manic Street Preachers. The UK is also at the forefront of electronica, with British artists such as the Prodigy and the Chemical Brothers helping this mainly underground genre to cross over into the mainstream (having originated in the early-90's with techno bands such as Orbital). Also British pop producers Stock Aitken Waterman - dominated the charts in the late-80's and early-90's with their instantly recognisable brand of pop. The 1990s charts were also dominated by the boy band phenomenon, with groups such as Take That thriving amongst countless others. Girl groups such as the Spice Girls also found considerable success. From 1997 onwards, so-called 'soft rock' bands have dominated the serious popular music scene including Coldplay, although after 2003 a high number of 'indie rock' bands emerged and have found considerable success.
Media
The UK has a large and diverse media, and the prominence of the English language gives it an international dimension.
The BBC is the UK's publicly-funded radio and television broadcasting corporation, and is the oldest broadcaster in the world. Funded by the compulsory television licence, the BBC operates several television channels and radio stations both in the UK and abroad. The BBC World Service radio channel is broadcast in 33 languages around the world. BBC News is also broadcast around the world. The main, free-to-air television channels in the UK are BBC1, BBC2, ITV1 (STV in Scotland), Channel 4 and Five. The main satellite broadcaster is British Sky Broadcasting, and digital cable services are provided by Virgin Media (created by the merger of NTL and Telewest ), and free-to-air digital terrestrial television by Freeview.
Radio in the UK is dominated by BBC Radio, which operates ten national and forty regional radio stations. The most popular radio station, by number of listeners, is BBC Radio 2 which specialises in popular music aimed at the 'middle aged' age bracket; it is closely followed by BBC Radio 1, aimed at the 15-24 aged bracket and the previous market leader. Commercial radio tends to be regionalized, although Virgin Radio, Classic FM and talkSPORT are broadcast nationally. Popular regional stations include Capital Radio in London; Heart in London and Midlands; Galaxy in Birmingham and the north of England; Magic in London and the north of England; and Radio Clyde in Glasgow.
Traditionally, British newspapers could be split into "quality", serious-minded newspapers (usually referred to as broadsheets because of their large size) and tabloid, popular newspapers. However, because of considerations of convenience of reading, many traditional broadsheets have both switched to a 'compact'-sized format, traditionally used by tabloids. The Sun has the highest circulation of any daily newspaper in the UK, with approximately a quarter of the market; its sister paper, The News of The World similarly leads the Sunday newspaper market,[48] and traditionally focuses on celebrity-led stories. The Daily Telegraph, a right-of-centre paper, is the highest selling of the qualities (former broadsheets), having overtaken The Times in circulation figures.[49] The Guardian is a more liberal or left-wing former broadsheet. The Financial Times is the main business paper, printed on distinctive salmon-pink broadsheet paper.
Sport
A number of major sports originated in the United Kingdom including association football and cricket, which are the world's most popular team sports in terms of both spectators and participants. Other sports which originated in Britain are golf and rugby football (rugby union and rugby league), while sports like boxing, horse racing, motor racing, and tennis owe their modern popularity to British development and promotion. London has hosted the Olympic Games three times — in 1908, 1948, and 2012.
Football
The most popular sport in the country is association football, commonly known just as "football". The UK never competes as a nation in football tournaments. Instead, the home nations compete individually as England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. It is because of this unique four-team arrangement that the British Olympic squad does not include a football team.
Domestically, British football clubs compete in national leagues and competitions from which the top teams may qualify to compete in European competitions. English clubs are generally successful in Europe and several have won continental titles. The most prestigious title is the European Cup, now called the UEFA Champions League. Celtic were the first British winners of the European Cup in 1967, but that remains the only one won by a Scottish club. Liverpool with six European Cup wins to 2024 are the most successful British club; Manchester United were the first English winners in 1968 and have three titles.
Cricket
Football superseded cricket as the country's national sport around the end of the 19th century. Cricket is still the most popular summer sport with clubs in almost every town and village, especially throughout England. The highest level of domestic competition is the County Cricket Championship, which involves eighteen county clubs as far afield as Durham, Kent, and Somerset. Seventeen of the first-class counties are in England; the exception is Glamorgan in South Wales. The most successful county teams tend to be those with international stadiums such as Yorkshire, Lancashire, Nottinghamshire, Surrey, and Middlesex whose home ground is the famous Lord's, owned by Marylebone Cricket Club (MCC) in north London.
Internationally, the England team is an amalgam of England and Wales, reflecting the structure of the County Championship. England is a full member of the International Cricket Council (ICC) and so plays Test cricket. Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland play cricket together and the combined Ireland team is also a full ICC member. Scotland has been independent in cricket since 1992 and is an associate member of the ICC, meaning they can play in limited over international matches but not Test matches.
Other sports
Horse racing has been very popular in England ever since the time of Charles II when it became known as the "Sport of Kings". It remains a royal pastime to this day and Elizabeth II was an acknowleged expert. World-famous races include the Grand National and the Epsom Derby.
The ancient sport of boxing became popular in 18th century England in the form of bareknuckle prizefighting for large purses. A set of rules was drafted in 1743 by the champion fighter Jack Broughton and these formed the basis of the London Prize Ring Rules in 1838. Modern boxing is based on the Queensberry Rules which were written by John Graham Chambers, a Welshman, in 1865. Heavyweight boxing is very popular in Britain and the country has produced several famous fighters including Bob Fitzsimmons, Tommy Farr, Henry Cooper, Lennox Lewis, and Tyson Fury.
Golf, which originated in Scotland, remains one of the UK's most popular participation sports. The Royal and Ancient Golf Club, which organises the Open Championship every July, is based in St Andrews, Fife. The Open is one of golf's four Major Tournaments. In tennis, the Wimbledon Championships are held in June each year and this is one of the four Grand Slam tournaments.
Shinty or camanachd (a sport derived from the same root as the Irish hurling and similar to bandy) is popular in the Scottish Highlands, sometimes attracting crowds numbering thousands in the most sparsely populated region of the UK.
The country is closely associated with motorsport of all kinds. Many teams and drivers in Formula One and other events are based in Britain and the British Grand Prix, held every summer at the Silverstone race track in Northamptonshire, is an event in the Formula One World Championship. British world champions in Formula One include Jim Clark, Jackie Stewart and Lewis Hamilton.
Legend has it that a schoolboy called William Webb Ellis invented rugby football when he picked up the ball during a football match and ran with it in his hands into his opponents' goal. The story is apocryphal but the sport does get its name from the school in Rugby, Warwickshire, where Webb was a pupil in the 1820s (the same place is the setting for Tom Brown's Schooldays). Rugby league originated in the North of England in 1895, following a split with union on the issue of professionalism. League is still a predominately northern sport, whereas union is very popular in Wales and has many clubs throughout the South of England. Union is considered the national sport of Wales. League has a single international team called Great Britain; union has England, Scotland, and Wales. As in cricket, Northern Ireland is part of a combined Ireland team. Union also has the British and Irish Lions team for summer tours of Australia, New Zealand or South Africa.
Symbols
- The flag of the UK is the Union Flag (commonly known as the "Union Jack"), which is a superimposition of the flags of England (St George's Cross) and Scotland (Saint Andrew's Cross); the Saint Patrick's cross, representing Ireland, was added in 1801.
- The national anthem is God Save the King, or God Save the Queen, as appropriate.[50]
- Britannia is a personification of Great Britain, originating from the Roman occupation of the southern and central parts of the island, which they called Britannia.[51] Britannia is symbolised as a young woman with brown or golden hair, wearing a Corinthian helmet and white robes. She holds Poseidon's three-pronged trident and a shield, bearing the Union Flag. Sometimes she is depicted as riding the back of a lion. In modern usage, Britannia is often associated with maritime dominance, as in the patriotic song Rule Britannia.
- The lion has also been used as a symbol of the UK; one is depicted behind Britannia on the 50 pence piece and one is shown crowned on the back of the 10 pence piece, it is also used as a symbol on the non-ceremonial flag of the British Army. Lions have been used as heraldic devices many times, including in the royal arms of the kingdoms of England, Scotland, Kingdom of Gwynedd in Wales and of Northern Ireland. The lion is featured on the emblem of the England national football team, and the England Women's team is known as the Lionesses.
- The bulldog, or "British Bulldog", is sometimes used as a symbol of the United Kingdom.
- Britain (especially England) is also personified as the character John Bull.
Miscellaneous data
- Cellular frequency: GSM 900, GSM 1800, UMTS 2100
- Cellular technology: GSM/GPRS/EDGE/UMTS/HSDPA
- Date format: DD/MM/YY (example: 22/12/05) or 22 December 2005
- Time format: Generally 12-hour format when spoken or in writing (example: 5.15 pm), 24-hour format is used in some official documentation and in timetables (example: 17:15 or 1715).
- Decimal separator is a full stop: 123.45
- Thousands are separated (formal) by a comma: 10,000. (To avoid confusion with continental countries which use the comma as the decimal separator, a space may be used, e.g. 10 000.)
- Voltage: 230V (+10% / -6%), 50 Hz; Power connector: 3 rectangle pins
Footnotes
- ↑ The British constitution is not codified into a single document but is recorded in the form of an extensive a body of common-and state law.
- ↑ Parliamentary sovereignty, www.parliament.uk
- ↑ Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011
- ↑ The Earl of Home completed the legal formalities of disclaiming his peerage four days after being appointed Prime Minister, and was elected to the Commons in a by-election shortly after.
- ↑ Crown Definition, Duhaime's Legal Dictionary
- ↑ Oonagh Gay and Thomas Powell: The collective responsibility of Ministers - an outline of the issues, House of Commons Research Paper, 15 November 2004
- ↑ Ministerial Code, Cabinet Office, May 2010
- ↑ The Civil Service Commission
- ↑ Constitutional Reform and Governance Act 2010
- ↑ Oonagh Gay Special Advisers, House of Commons Library, November 2010
- ↑ Bob Tyrrell: Is British politics ideology-free?, BBC News, 13 April 2006
- ↑ Where They Stand: Guide to party election policies, Election 2010, BBC News
- ↑ Devolved government in the UK, DirectGov, 2012
- ↑ The Scottish Government
- ↑ The Scottish Parliament, 2012
- ↑ Welsh Government, 2012
- ↑ National Assembly for Wales, 2012
- ↑ Northern Ireland Executive, 2012
- ↑ Northern Ireland Assembly, 2012
- ↑ The Supreme Court, 2012
- ↑ European Law as a source of UK Law, UK Law online, 2012
- ↑ Human Rights Act 1998, Legislation.gov.uk
- ↑ Geography of the United Kingdom CIA, Accessed May 22 2006
- ↑ Geography of Scotland Heritage of Scotland, Accessed May 22 2006
- ↑ Dialysis Scotland Accessed May 22, 2006
- ↑ Geography of Wales BBC Wales, Accessed May 22 2006
- ↑ Geography of Northern Ireland University of Ulster Accessed May 22 2006]]
- ↑ using the term in an objective sense; officially, Greater London is not a city, the population of the official "City" of London is in four figures, and Birmingham is the largest city
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ Census 2001: South East, Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 14 May 2006.
- ↑ All people population: City of London. Office for National Statistics. Retrieved on 2006-08-31.
- ↑ United Kingdom. Humana. Retrieved on 2006-05-18.
- ↑ Immigration fails to stem European population loss. The Guardian (2006-08-17). Retrieved on 2006-08-20.
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ 'Nearly 600,000' new EU migrants, BBC, 22 August 2006. Retrieved 22 August 2006.
- ↑ International migration: Net inflow rose in 2004, ONS, 15 December 2005. Retrieved 24 August 2006.
- ↑ BBC News: ''Historic' assembly vote for new Welsh language law'. 7th December 2010.
- ↑ The Indo-Aryan language Romani, which is spoken by the Roma minority, is not native to the UK, though its speakers are mostly British.
- ↑ 2011 census data give the following percentage increases in absolute numbers over the 2001 census: Muslims 75, Buddhists 72, Hindus 49, Sikhs 29, Jews 1, total other religions 47; for comparison, the total for no religion or not stated (in 2001, these were not separated in all parts of the country) increased by 52%, while the figure for Christians decreased by 11%. What would have been the 2021 census for Scotland was postponed for a year because of the Covid-19 pandemic, but the rest of the country went ahead. As a result, there are no UK-wide figures for any one date. However, the figures for England and Wales, which include most of the population, clearly show even nominal Christians now a minority. Other religions have continued to grow (religions added together still include the majority of the population), with the highest proportionate growth being for Shamanism, though it still has small absolute numbers.
- ↑ The British Social Attitudes Survey, data.gv.uk 2011
- ↑ The Anglican Community
- ↑ Blue book par 2.1
- ↑ Household debt forecast. Office of Budget Responsibility, April 2011
- ↑ "Annual Reports and Accounts 2004-05", Ministry of Defence. Retrieved 14 May 2006. Template:PDFlink
- ↑ Office for National Statistics "UK 2005: The Official Yearbook of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland" p. 89
- ↑ "Top 500 World Universities (1-100)", Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2005. Retrieved 15 May 2006
- ↑ "Britain second in world research rankings", Guardian, 21 March 2006, retrieved 14 May 2006.
- ↑ ABC Newspaper Circulation Figures The Times, May 12 2006, accessed May 16 2006.
- ↑ Audit Bureau of Circulation Interactive Analysis National Newspaper Selection - Average Net Circulation (UK) 03-Jul-2006 to 30-Jul-2006. Retrieved on 2006-09-04. Lists Daily Telegraph as 844,929 and The Times as 620,456.
- ↑ It is sometimes asserted by those used to a legislative tradition that God Save the King/Queen is not the actual national anthem of the UK, (or sometimes that it is the de facto national anthem) because no law has ever been passed to say so. In Britain, however, codification of the law is usually unnecessary; custom, practice and proclamation are sufficient to establish it as the official national anthem.
- ↑ Britannia on British Coins. Chard. Retrieved on 2006-06-25.