Chloroform: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Henry A. Padleckas m (footnote format) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
One of the first [[physician]]s to study and calculate dosages for the use of chloroform as surgical [[anesthesia]] was [[John Snow (physician)|John Snow]]. However, it was more [[toxic]] than [[diethyl ether]], another early anesthetic, and its use was discontinued. | One of the first [[physician]]s to study and calculate dosages for the use of chloroform as surgical [[anesthesia]] was [[John Snow (physician)|John Snow]]. However, it was more [[toxic]] than [[diethyl ether]], another early anesthetic, and its use was discontinued.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 28 July 2024
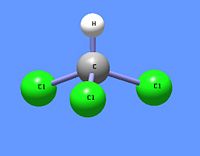
Chloroform (IUPAC name: trichloromethane) is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula CHCl3. It is a chlorinated methane with three chlorine substituents. At room temperature and pressure, chloroform is a clear, colorless, somewhat volatile liquid with an odor characteristic of chlorinated hydrocarbons.* It has been commonly used as a fairly non-polar solvent in laboratories.
* similar to the traditional old dry cleaners smell. That smell was perchloroethylene.
History
One of the first physicians to study and calculate dosages for the use of chloroform as surgical anesthesia was John Snow. However, it was more toxic than diethyl ether, another early anesthetic, and its use was discontinued.