Midodrine: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
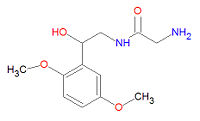
{{Image|Midodrine structure.jpg|right|200px|Midodrine.}} | |||
'''Midodrine''', or midodrina or midodrinum, is an ethanolamine derivative that is an alpha-1 [[adrenergic receptor]] agonist used as a vasoconstrictor agent in the treatment of [[hypotension]] (low blood pressure). Its chemical IUPAC name is 2-amino-N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]acetamide, and its chemical formula is C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>18</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>. It is sold under the brand name '''ProAmatine'''®. One of its major metabolites, desglymidodrine, formed by the desglycination of midodrine, is an alpha1-agonist and is the active substance associated with this drug. | '''Midodrine''', or midodrina or midodrinum, is an ethanolamine derivative that is an alpha-1 [[adrenergic receptor]] agonist used as a vasoconstrictor agent in the treatment of [[hypotension]] (low blood pressure). Its chemical IUPAC name is 2-amino-N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]acetamide, and its chemical formula is C<sub>12</sub>H<sub>18</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>4</sub>. It is sold under the brand name '''ProAmatine'''®. One of its major metabolites, desglymidodrine, formed by the desglycination of midodrine, is an alpha1-agonist and is the active substance associated with this drug. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 19 September 2024
Midodrine, or midodrina or midodrinum, is an ethanolamine derivative that is an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist used as a vasoconstrictor agent in the treatment of hypotension (low blood pressure). Its chemical IUPAC name is 2-amino-N-[2-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-hydroxyethyl]acetamide, and its chemical formula is C12H18N2O4. It is sold under the brand name ProAmatine®. One of its major metabolites, desglymidodrine, formed by the desglycination of midodrine, is an alpha1-agonist and is the active substance associated with this drug.
In patients with orthostatic hypotension, it raises the systolic and diastolic blood pressure in standing, sitting and supine positions. Activation of the alpha-1 adrenergic receptors in the arteriolar and venous vasculature increases vascular tone and elevates the blood pressure. It does not stimulate cardiac beta-adrenergic receptors.
Adverse effects
Symptoms of overdose include hypertension, goosebumps, urinary retention and a sensation of coldness.
Drug interactions
Although increased arterial pressure occurs when this drug is used in combination with many other drugs, possible hypertensive crisis can occur when taken with tranylcypromine, rasagiline, phenelzine and isocarboxazid. Less dangerous increases in arterial pressure may occur when taken in combination with:
- Betamethasone
- Cortisone acetate
- Dexamethasone
- Dobutamine
- Dopamine
- Ephedra
- Ephedrine
- Epinephrine
- Fenoterol
- Fludrocortisone
- Hydrocortisone
- Isoproterenol
- Mephentermine
- Methoxamine
- Metaraminol
- Methylprednisolone
- Norepinephrine
- Orciprenaline
- Paramethasone
- Phenylephrine
- Prednisolone
- Prednisone
- Pseudoephedrine
- Pirbuterol
- Phenylpropanolamine
- Procaterol
- Salbutamol
- Terbutaline
- Triamcinolone
External Links
The most up-to-date information about Midodrine and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Midodrine - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Midodrine - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Midodrine - Detailed information from DrugBank.