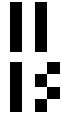Postscript: Difference between revisions
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov m (→The coordinate system: gramar) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''PostScript (PS)''' is a programming language designed for description of two- | {{subpages}} | ||
'''PostScript (PS)''' is a programming language designed for description of two-dimensional objects for visual observation by humans, characterized in that, that, in order to avoid the use of the group operation (parenthesis), the command (operator), in general, appears after the operands. | |||
PostScript is standard format for presentation of illustrations at the electronic submission of figures for the publication is the [[scientific journal]]s. | PostScript is standard format for presentation of illustrations at the electronic submission of figures for the publication is the [[scientific journal]]s. | ||
==The coordinate system== | ==The coordinate system== | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
The extension of the postscript allows the change the size of the image, at least, while each size of the image does not exceed the default size. | The extension of the postscript allows the change the size of the image, at least, while each size of the image does not exceed the default size. | ||
The corresponding format is called EPS, which means ''' | The corresponding format is called EPS, which means '''Encapsulated Post Script'''. | ||
In particular the EPS format is used in the small examples below, which has no need to occupy the whole page. | In particular the EPS format is used in the small examples below, which has no need to occupy the whole page. | ||
Usually, the image encoded in the EPS format, has name *.eps or *.EPS . | |||
Usually, the EPS format and the size of the image are indicated with two lines at the beginning of the file: | Usually, the EPS format and the size of the image are indicated with two lines at the beginning of the file: | ||
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | %!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | ||
%%BoundingBox: <math>a</math> <math>b</math> <math>C</math> <math>D</math> | %%BoundingBox: <math>a</math> <math>b</math> <math>C</math> <math>D</math> | ||
The first line indicates, that the default frame is | The first line indicates, that the default frame is suspect to change.<br> | ||
The second line indicates that the region with coordinates <math>(x,y)</math> satisfying | The second line indicates that the region with coordinates <math>(x,y)</math> satisfying | ||
<math>a\le x \le C</math>, | <math>a\le x \le C</math>, | ||
<math>b\le y \le D</math> should be displayed. | <math>b\le y \le D</math> should be displayed. | ||
Values should be substituted instead of variables<math>a,b,C,D</math> for the execution. | Values should be substituted instead of variables<math>a,b,C,D</math> for the execution. | ||
Usually, <math>a=b=0</math>, but some advanced software recognizes also | Usually, <math>a=b=0</math>, but some advanced software recognizes also positive and sometimes even negative values of these parameters. At <math>a\ne</math> or <math>b\ne 0</math>, view of the image depends on the software used to interpret the EPS file; this can be used to reduce the portability of the image, allowing the viewing only with some specific software. | ||
==Vector representation of figures== | ==Vector representation of figures== | ||
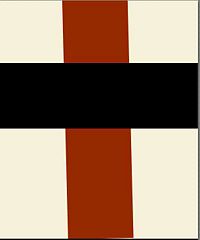
[[Image:BlackSquareReproduction.jpg|200px|thumb|The EPS-reproduction of the [[Black Square]] by [[Kazimir Malevich|K.Malevich]] ]] | [[Image:BlackSquareReproduction.jpg|200px|thumb|The EPS-reproduction of the [[Black Square]] by [[Kazimir Malevich|K.Malevich]] ]] | ||
Typically, the postscript uses the analytical description of | Typically, the postscript uses the analytical description of figure with simple objects | ||
(straight lines, circles and arcs of circles and ellipses, | (straight lines, circles and arcs of circles and ellipses, polygons); similar representation is used also for letters. This allows the compact description of data and the strong (sometimes, orders of magnitude) | ||
zooming-in, keeping the [[camera-ready]] quality of the figure. | zooming-in, keeping the [[camera-ready]] quality of the figure. | ||
Some images allow efficient representation through the EPS format. For example, the code below reproduces the famous painting | Some images allow efficient representation through the EPS format. For example, the code below reproduces the famous painting | ||
[[Black Square]] by [[Kazimir Malevich]] (originally implemented with oil on canvas): | [[Black Square]] | ||
<ref name="ka">Kazimir Malevich. Black Square. Russian Paintings, | |||
http://www.russianpaintings.net/doc.vphp?id=126 | |||
</ref><ref name="famousBlack"> | |||
AP Worldstream. | |||
Russian government to buy famous "Black Square" for 1 million dollars. | |||
High Beam Research, April 26, 2002; http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-52631971.html | |||
</ref> by [[Kazimir Malevich]] (originally implemented with oil on canvas): | |||
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | %!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | ||
| Line 40: | Line 48: | ||
==Roster representation of data== | ==Roster representation of data== | ||
[[Image:BitmapPostscriptExample00.png|right|Example of a roster image]] | [[Image:BitmapPostscriptExample00.png|right|Example of a roster image]] | ||
The bitmap representation of data is also supported, although for the roster representation, the advantages of the postscript are not so obvious. The | The bitmap representation of data is also supported, although for the roster representation, the advantages of the postscript are not so obvious. The syntax of postscript allows to generate the simple images with few lines, for example, the code | ||
!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | !PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | ||
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 62 122 | %%BoundingBox: 0 0 62 122 | ||
| Line 47: | Line 55: | ||
.0 .6 translate 4 4 1 [8 0 0 8 0 0] {<5a5a>} image | .0 .6 translate 4 4 1 [8 0 0 8 0 0] {<5a5a>} image | ||
showpage | showpage | ||
%Trailer | %%Trailer | ||
generates the figure shown at right. In the code above, the line with sequence "5a5a" produces the two vertical sticks at the top of the image. | generates the figure shown at right. In the code above, the line with sequence "5a5a" produces the two vertical sticks at the top of the image. | ||
The more complicated example with description can be found at | The more complicated example with description can be found at | ||
<ref name="rosterSmile"> | <ref name="rosterSmile">Example of the roster image of smile made in postscript, http://www.tailrecursive.org/postscript/image.html</ref>. | ||
==Basic elements of the image== | ==Basic elements of the image== | ||
| Line 58: | Line 66: | ||
In Postscripts, the basic elements are lines and arcs. | In Postscripts, the basic elements are lines and arcs. | ||
===Painting of circles=== | ===Painting of circles=== | ||
The painting [[Black Circle]] can be generated with code | |||
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | %!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 | ||
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 100 104 | %%BoundingBox: 0 0 100 104 | ||
| Line 70: | Line 78: | ||
0 0 M 100 0 L 100 104 L 0 104 L C F | 0 0 M 100 0 L 100 104 L 0 104 L C F | ||
0 0 0 RGB 60 64 40 0 360 arc C F | 0 0 0 RGB 60 64 40 0 360 arc C F | ||
showpage | showpage | ||
%%Trailer | %%Trailer | ||
This code uses the command '''arc''', that has following parameters: | This code uses the command '''arc''', that has following parameters: | ||
two | two coordinates of the center, radius, initial polar angle measured in degrees and final polar angle, measured in degrees. | ||
In this notation, one degree | In this notation, one degree corresponds to <math>\pi/180</math>; In particular, the pair of polar angles 0,360 produces the circle. | ||
As usually in Postscript, the [[operands]] of the operator are separated with spacebars, and the name of the operator is typed after the operands. | |||
===Drawing of lines=== | ===Drawing of lines=== | ||
[[Image:Supermatizm1921-1927.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Eps version of the painting [[Supermatizm]] by [[Kazimir Malevich|K.Malevich]] ]] | [[Image:Supermatizm1921-1927.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Eps version of the painting [[Supermatizm]] by [[Kazimir Malevich|K.Malevich]] ]] | ||
| Line 95: | Line 105: | ||
==Use of postscript== | ==Use of postscript== | ||
Several manuals on the postscript are available online; they allows to use the | The postscript figures can be included in to the [[LaTeX]] texts. | ||
One writes the command | |||
\usepackage{graphicz} | |||
at the top of the latex soure; then, the command | |||
\includegraphic{filename} | |||
includes postscript (or PDF) version of the image into the printed version of the document. | |||
Several manuals on the postscript are available online; they allows to use the postscript without any preliminary learning. | |||
<ref name="tail"> http://www.tailrecursive.org/postscript/postscript.html</ref> | <ref name="tail"> http://www.tailrecursive.org/postscript/postscript.html</ref> | ||
In some cases, (for example, at work with Latex and [[DVI]] files) the postscript figures can be used directly; | |||
for other applications, for example, to include an image to a [[webpage]], the postscript file should be converted to | |||
[[jpg]] or other acceptable format. In particular, the reproductions of the paintings by Malevich above were converted from EPS to jpg before the uploading. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 6 October 2024
PostScript (PS) is a programming language designed for description of two-dimensional objects for visual observation by humans, characterized in that, that, in order to avoid the use of the group operation (parenthesis), the command (operator), in general, appears after the operands. PostScript is standard format for presentation of illustrations at the electronic submission of figures for the publication is the scientific journals.
The coordinate system
Originally, the postscript uses the default Cartesian coordinate system. The image is supposed to occupy the rectangle 8.5 inch by 11 inch, called also letter size. The left lower corner has coordinates (0,0). The upper right corner has coordinates (612, 792).
The extension of the postscript allows the change the size of the image, at least, while each size of the image does not exceed the default size. The corresponding format is called EPS, which means Encapsulated Post Script. In particular the EPS format is used in the small examples below, which has no need to occupy the whole page. Usually, the image encoded in the EPS format, has name *.eps or *.EPS . Usually, the EPS format and the size of the image are indicated with two lines at the beginning of the file:
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0 %%BoundingBox:
The first line indicates, that the default frame is suspect to change.
The second line indicates that the region with coordinates satisfying
,
should be displayed.
Values should be substituted instead of variables for the execution.
Usually, , but some advanced software recognizes also positive and sometimes even negative values of these parameters. At or , view of the image depends on the software used to interpret the EPS file; this can be used to reduce the portability of the image, allowing the viewing only with some specific software.
Vector representation of figures
Typically, the postscript uses the analytical description of figure with simple objects (straight lines, circles and arcs of circles and ellipses, polygons); similar representation is used also for letters. This allows the compact description of data and the strong (sometimes, orders of magnitude) zooming-in, keeping the camera-ready quality of the figure. Some images allow efficient representation through the EPS format. For example, the code below reproduces the famous painting Black Square [1][2] by Kazimir Malevich (originally implemented with oil on canvas):
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 100 100
/M {moveto} bind def
/L {lineto} bind def
/C {closepath} bind def
/F {fill} bind def
/RGB {setrgbcolor} bind def
.96 .94 .85 RGB 0 0 M 100 0 L 100 100 L 0 100 L C F
0 0 0 RGB 10 10 M 90 10 L 90 90 L 10 90 L C F
showpage
%%Trailer
Roster representation of data
The bitmap representation of data is also supported, although for the roster representation, the advantages of the postscript are not so obvious. The syntax of postscript allows to generate the simple images with few lines, for example, the code
!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 62 122
100 100 scale
.1 .1 translate 4 4 1 [8 0 0 8 0 0] {<5a6a>} image
.0 .6 translate 4 4 1 [8 0 0 8 0 0] {<5a5a>} image
showpage
%%Trailer
generates the figure shown at right. In the code above, the line with sequence "5a5a" produces the two vertical sticks at the top of the image.
The more complicated example with description can be found at [3].
Basic elements of the image
In Postscripts, the basic elements are lines and arcs.
Painting of circles
The painting Black Circle can be generated with code
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 100 104
/M {moveto} bind def
/L {lineto} bind def
/S {stroke} bind def
/C {closepath} bind def
/F {fill} bind def
/RGB {setrgbcolor} bind def
.95 .9 .8 RGB
0 0 M 100 0 L 100 104 L 0 104 L C F
0 0 0 RGB 60 64 40 0 360 arc C F
showpage
%%Trailer
This code uses the command arc, that has following parameters: two coordinates of the center, radius, initial polar angle measured in degrees and final polar angle, measured in degrees. In this notation, one degree corresponds to ; In particular, the pair of polar angles 0,360 produces the circle. As usually in Postscript, the operands of the operator are separated with spacebars, and the name of the operator is typed after the operands.
Drawing of lines
Even few lines can produce a product of art. For example, the reproduction (see the figure) of the painting Supermatizm by K.Malevich can be generated with the EPS code below:
%!PS-Adobe-2.0 EPSF-2.0
%%BoundingBox: 0 0 100 120
/M {moveto} bind def
/L {lineto} bind def
/S {stroke} bind def
/C {closepath} bind def
/F {fill} bind def
/RGB {setrgbcolor} bind def
.96 .94 .85 RGB 0 0 M 120 0 L 100 120 L 0 120 L C F
33 setlinewidth
.6 .16 0 RGB 51 0 M 48 121 L S
0 0 0 RGB .01 72 M 100 72 L S
showpage
%%Trailer
Use of postscript
The postscript figures can be included in to the LaTeX texts. One writes the command
\usepackage{graphicz}
at the top of the latex soure; then, the command
\includegraphic{filename}
includes postscript (or PDF) version of the image into the printed version of the document.
Several manuals on the postscript are available online; they allows to use the postscript without any preliminary learning. [4]
In some cases, (for example, at work with Latex and DVI files) the postscript figures can be used directly; for other applications, for example, to include an image to a webpage, the postscript file should be converted to jpg or other acceptable format. In particular, the reproductions of the paintings by Malevich above were converted from EPS to jpg before the uploading.
References
- ↑ Kazimir Malevich. Black Square. Russian Paintings, http://www.russianpaintings.net/doc.vphp?id=126
- ↑ AP Worldstream. Russian government to buy famous "Black Square" for 1 million dollars. High Beam Research, April 26, 2002; http://www.highbeam.com/doc/1P1-52631971.html
- ↑ Example of the roster image of smile made in postscript, http://www.tailrecursive.org/postscript/image.html
- ↑ http://www.tailrecursive.org/postscript/postscript.html