Lisinopril: Difference between revisions
imported>Meg Taylor m (spelling: suppliments -> supplements) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<div class="references-small"> | <div class="references-small"> | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
</div> | </div>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 12 September 2024
|
| |||||||
| Lisinopril | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | ACE inhibitor. | ||||||
| Properties: | synthetic peptide | ||||||
| Hazards: | see side effects & drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
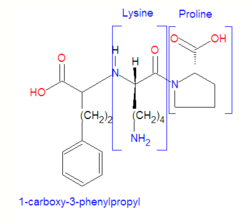
Lisinopril[1] is an oral long-acting medication primarily used to treat congestive heart failure and high blood pressure (hypertension), and to improve survival after heart a attack. It is a synthetic peptide derivative, (S)-1-[N2-(1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)-L-lysyl]-L-proline dihydrate, that acts as an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (ACE inhibitor).
Precautions
Lisinopril could cause birth defects if taken during pregnancy. The use of alcohol with lisinopril may cause additional lowering of blood pressure to a dangerous level. Drink plenty of fluids when taking this medication and avoid salt substitutes and potassium supplements. Patients with any of the following conditions should discuss them with their doctor before taking lisinopril: kidney disease, liver disease, heart disease, congestive heart failure, diabetes, or connective tissue disease.
Major Drug Interactions
Lisinopril is known to have major interactions with the following drugs[2]:
- allopurinol
- amiloride, (and amiloride/hydrochlorothiazide), a potassium-sparing diuretic
- bisacodyl (sodium biphosphate/sodium phosphate), may cause phosphate nephropathy.
- hydrochlorothiazide/spironolactone, a potassium-sparing diuretic.
- hydrochlorothiazide/triamterene
- methenamine/sodium biphosphate may cause phosphate nephropathy.
- sodium phosphate/sodium biphosphate may cause phosphate nephropathy.
- tizanidine
- triamterene