Glucose-6-phosphate: Difference between revisions
imported>Aleksander Stos m (WP credit, template cleanup) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "glycogenolysis" to "glycogenolysis") |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{ | {{subpages}} | ||
| | {{Image|Glucose-6-phosphate structures.jpg|right|350px|Glucose-6-phosphate}} | ||
'''Glucose-6-phosphate''', often abbreviated as '''G6P''', is [[glucose]] that has been [[phosphorylated]] on carbon 6. The conversion from glucose to G6P is the first step of [[glycolysis]] for energy production in [[cell (biology)|cells]]. This compound is very common in cells as the vast majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way. Like glucose, it exists in linear and cyclic forms. | |||
| | |||
Because if its prominent position in cellular chemistry, glucose-6-phosphate has many possible fates within the cell. It lies at the start of two major [[metabolic pathway]]s, namely glycolysis and the [[pentose phosphate pathway]]. In addition to these metabolic pathways, glucose-6-phosphate may also be converted to [[glycogen]] or [[starch]] for storage. This storage is in the [[liver]] in the form of glycogen for most multicellular [[animals]], and in [[intracellular]] starch or glycogen granules for most other organisms. | |||
==Production of glucose-6-phosphate== | |||
The major reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent diffusion out of the cell. The phosphorylation adds a charged [[phosphate]] group so that the [[glucose-6-phosphate]] cannot easily cross the [[cell membrane]], in contrast to free [[glucose]]. | |||
Within a cell, glucose-6-phosphate is produced by phosphorylation of glucose on the sixth carbon. This is catalyzed by the [[enzyme]] [[hexokinase]] in most cells, and [[glucokinase]] in certain cells, most notably liver cells. One [[adenosine triphosphate|ATP]] is consumed in this reaction. | |||
Within a cell, glucose 6-phosphate is produced by phosphorylation of | |||
<!--{{Enzymatic Reaction | <!--{{Enzymatic Reaction | ||
| Line 176: | Line 15: | ||
|reverse_enzyme= | |reverse_enzyme= | ||
|substrate=α-<small>D</small>-[[Glucose]] | |substrate=α-<small>D</small>-[[Glucose]] | ||
|product=α-<small>D</small>-[[Glucose 6-phosphate]] | |product=α-<small>D</small>-[[Glucose-6-phosphate]] | ||
|reaction_direction_(foward/reversible/reverse)=foward | |reaction_direction_(foward/reversible/reverse)=foward | ||
|minor_foward_substrate(s)=[[ATP]] | |minor_foward_substrate(s)=[[ATP]] | ||
| Line 187: | Line 26: | ||
{{KEGG compound|C00031}} {{KEGG enzyme|2.7.1.1}} {{KEGG compound|C00668}} {{KEGG reaction|R01786}}--> | {{KEGG compound|C00031}} {{KEGG enzyme|2.7.1.1}} {{KEGG compound|C00668}} {{KEGG reaction|R01786}}--> | ||
Glucose-6-phosphate is also produced during [[ | Glucose-6-phosphate is also produced during glycogenolysis from [[glucose-1-phosphate]], the first product of the breakdown of [[glycogen]] polymers. | ||
== Fate 1: Pentose | == Fate 1: Pentose phosphate pathway == | ||
When the ratio of NADP<sup>+</sup> : NADPH increases, the body realizes it needs to produce more NADPH (a reducing agent for several reactions like fatty acid synthesis). This will cause the G6P to be dehydrogenated by glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This reversible reaction is the initial step of the [[pentose phosphate pathway]], which generates the useful cofactor NADPH as well as ribulose 5-phosphate, a carbon source for the synthesis of other molecules . Also, if the body needs nucleotide precursors of DNA for growth and synthesis, G6P will also be dehydrogenated and enter the pentose phosphate pathway. | When the ratio of NADP<sup>+</sup> : [[NADPH]] increases, the body realizes it needs to produce more NADPH (a reducing agent for several reactions like fatty acid synthesis). This will cause the G6P to be dehydrogenated by [[glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase]]. This reversible reaction is the initial step of the [[pentose phosphate pathway]], which generates the useful cofactor NADPH as well as [[ribulose-5-phosphate]], a carbon source for the synthesis of other molecules . Also, if the body needs nucleotide precursors of DNA for growth and synthesis, G6P will also be dehydrogenated and enter the pentose phosphate pathway. | ||
== Fate 2: Glycolysis == | == Fate 2: Glycolysis == | ||
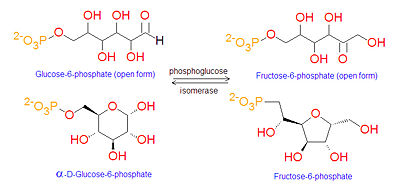
If the cell needs energy or carbon skeletons for synthesis then glucose 6-phosphate is targeted for [[glycolysis]]. | {{Image|G6P to F6P reaction.jpg|right|400px|Conversion of G6P to F6P}} | ||
If the cell needs energy or carbon skeletons for synthesis then glucose-6-phosphate is targeted for [[glycolysis]]. G6P (an [[aldose]]) is first isomerized to [[fructose-6-phosphate]] (F6P, a [[ketose]]) by the enzyme [[phosphoglucose isomerase]] F6P exists in both the open chain form and cyclic forms. | |||
This reaction converts glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate in preparation for phosphorylation to [[fructose-1,6-bisphosphate]] by the enzyme [[phosphofructokinase]]. The addition of the second phosphate group to produce fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is an irreversible step, and so is used to irreversibly target the glucose-6-phosphate breakdown to provide energy for ATP production via glycolysis. | |||
== Fate 3: Storage as glycogen == | |||
Whenever cellular glucose-6-phosphate levels are high the [[osmotic pressure]] inside the cell increases, and this may lead water to diffuse into the cell, causing it to become turgid and (eventually) lyse. Since osmotic pressure is proportional to the concentration of solutes, rather than to the total mass of solutes, this problem can be overcome by storing G6P in a polymeric form. In plant cells, this polymeric form of glucose is [[starch]], whereas animals store [[glycogen]]. | |||
== Fate 4: Dephosphorylation and release into the bloodstream == | |||
Liver cells possess [[glucose-6-phosphatase]], which removes the phosphate group from glucose-6-phosphate produced during glycogenolysis or [[gluconeogenesis]]. The free glucose is sent into the bloodstream for uptake by other cells. | |||
== Fate 4: Dephosphorylation and | |||
Liver cells possess [[glucose-6-phosphatase]], which removes the phosphate group from glucose-6-phosphate produced during | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
* {{cite book |last=Berg |first=Jeremy M. |coauthors=Tymoczko, Stryer |title=Biochemistry |year=2002 |edition=5th |publisher=[[W.H. Freeman and Company]] |location=New York |id=ISBN 0-7167-3051-0 | url =http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=stryer.TOC&depth=10}} | * {{cite book |last=Berg |first=Jeremy M. |coauthors=Tymoczko, Stryer |title=Biochemistry |year=2002 |edition=5th |publisher=[[W.H. Freeman and Company]] |location=New York |id=ISBN 0-7167-3051-0 | url =http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?call=bv.View..ShowTOC&rid=stryer.TOC&depth=10}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 08:11, 19 September 2024
Glucose-6-phosphate, often abbreviated as G6P, is glucose that has been phosphorylated on carbon 6. The conversion from glucose to G6P is the first step of glycolysis for energy production in cells. This compound is very common in cells as the vast majority of glucose entering a cell will become phosphorylated in this way. Like glucose, it exists in linear and cyclic forms.
Because if its prominent position in cellular chemistry, glucose-6-phosphate has many possible fates within the cell. It lies at the start of two major metabolic pathways, namely glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. In addition to these metabolic pathways, glucose-6-phosphate may also be converted to glycogen or starch for storage. This storage is in the liver in the form of glycogen for most multicellular animals, and in intracellular starch or glycogen granules for most other organisms.
Production of glucose-6-phosphate
The major reason for the immediate phosphorylation of glucose is to prevent diffusion out of the cell. The phosphorylation adds a charged phosphate group so that the glucose-6-phosphate cannot easily cross the cell membrane, in contrast to free glucose.
Within a cell, glucose-6-phosphate is produced by phosphorylation of glucose on the sixth carbon. This is catalyzed by the enzyme hexokinase in most cells, and glucokinase in certain cells, most notably liver cells. One ATP is consumed in this reaction.
Glucose-6-phosphate is also produced during glycogenolysis from glucose-1-phosphate, the first product of the breakdown of glycogen polymers.
Fate 1: Pentose phosphate pathway
When the ratio of NADP+ : NADPH increases, the body realizes it needs to produce more NADPH (a reducing agent for several reactions like fatty acid synthesis). This will cause the G6P to be dehydrogenated by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. This reversible reaction is the initial step of the pentose phosphate pathway, which generates the useful cofactor NADPH as well as ribulose-5-phosphate, a carbon source for the synthesis of other molecules . Also, if the body needs nucleotide precursors of DNA for growth and synthesis, G6P will also be dehydrogenated and enter the pentose phosphate pathway.
Fate 2: Glycolysis
If the cell needs energy or carbon skeletons for synthesis then glucose-6-phosphate is targeted for glycolysis. G6P (an aldose) is first isomerized to fructose-6-phosphate (F6P, a ketose) by the enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase F6P exists in both the open chain form and cyclic forms.
This reaction converts glucose-6-phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate in preparation for phosphorylation to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate by the enzyme phosphofructokinase. The addition of the second phosphate group to produce fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is an irreversible step, and so is used to irreversibly target the glucose-6-phosphate breakdown to provide energy for ATP production via glycolysis.
Fate 3: Storage as glycogen
Whenever cellular glucose-6-phosphate levels are high the osmotic pressure inside the cell increases, and this may lead water to diffuse into the cell, causing it to become turgid and (eventually) lyse. Since osmotic pressure is proportional to the concentration of solutes, rather than to the total mass of solutes, this problem can be overcome by storing G6P in a polymeric form. In plant cells, this polymeric form of glucose is starch, whereas animals store glycogen.
Fate 4: Dephosphorylation and release into the bloodstream
Liver cells possess glucose-6-phosphatase, which removes the phosphate group from glucose-6-phosphate produced during glycogenolysis or gluconeogenesis. The free glucose is sent into the bloodstream for uptake by other cells.
References
- Berg, Jeremy M.; Tymoczko, Stryer (2002). Biochemistry, 5th. New York: W.H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 0-7167-3051-0.