Natural pentation: Difference between revisions
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov (Load the draft) |
imported>Dmitrii Kouznetsov m (→Properties of the natural pentation: wording) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Ackerplot400.jpg|300px|thumb| [[Natural pentation]] compared to other [[ackermanns]] ]] | [[File:Ackerplot400.jpg|300px|thumb| [[Natural pentation]] compared to other [[ackermanns]] ]] | ||
[[File:Penplot.jpg|300px|thumb|< | [[File:Penplot.jpg|300px|thumb|<math>y\!=\!\mathrm{pen}(x)</math> and its approximations]] | ||
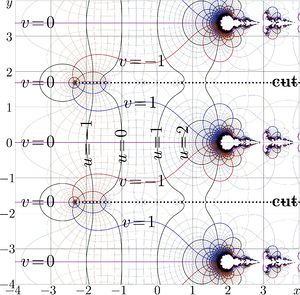
[[File:Penmap.jpg|300px|thumb| < | [[File:Penmap.jpg|300px|thumb| <math>u\!+\!\mathrm i v=\mathrm{pen}(x\!+\!\mathrm i y)</math> in the <math>x,y</math> plane]] | ||
Pentation appears as 5th [[ackermann]]. | Pentation appears as 5th [[ackermann]]. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
where | where | ||
<math>A_{b,5}</math> is Fifth ackermann to base <math>b</math>. | <math>A_{b,5}</math> is Fifth [[ackermann]] to base <math>b</math>. | ||
<ref name="book"> | |||
https://www.morebooks.de/store/ru/book/Суперфункции/isbn/978-3-659-56202-0 | |||
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/BOOK/202.pdf | |||
http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/BOOK/202.pdf | |||
Д.Кузнецов. Суперфункции. Lambert Academic Publishing, 2014, in Russian. | |||
</ref><ref name="2014acker"> | |||
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf <br> | |||
http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf | |||
D.Kouznetsov. Holomorphic ackermanns. 2014, under consideration. | |||
</ref>. | |||
If the base of tetration <math>b\!=\!\mathrm e\!=\!\exp(1)\!\approx\! 2.71</math>, then the tetration is called [[natural tetration]] and the corresponding pentation is called [[Natural pentation]]. | If the base of tetration <math>b\!=\!\mathrm e\!=\!\exp(1)\!\approx\! 2.71</math>, then the tetration is called [[natural tetration]] and the corresponding pentation is called [[Natural pentation]]. | ||
Namely this case is considered on this article. | Namely this case is considered on this article. | ||
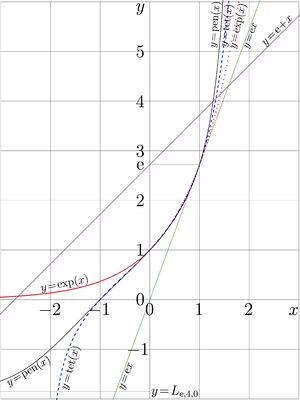
The first 5 [[ackermann]]s (addition of e, multiplication by e, exponent, tetration, | The first 5 [[ackermann]]s (addition of e, multiplication by e, exponent, tetration, pentation) are shown in the top figure at right. | ||
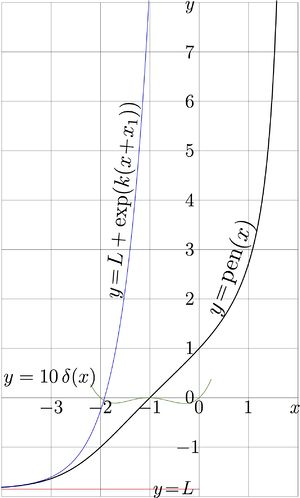
Natural pentation is compared to its asymptotics at the second figure. | Natural pentation is compared to its asymptotics at the second figure. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 36: | ||
Pentation satisfies the transfer equation | Pentation satisfies the transfer equation | ||
<math>\mathrm{pen}_b(z\!+\!1) = \mathrm{tet}_b\Big( \mathrm{pen}_b(z)\Big)<math> | <math>\mathrm{pen}_b(z\!+\!1) = \mathrm{tet}_b\Big( \mathrm{pen}_b(z)\Big)</math> | ||
where <math>\mathrm{tet}_b</math> is [[tetration]] to base < | where <math>\mathrm{tet}_b</math> is [[tetration]] to base <math>b</math>. | ||
The additional condition, common for all [[ackermanns]] is assumed, | The additional condition, common for all [[ackermanns]] is assumed, | ||
<math>\mathrm{pen}_b(0)=1</math> | <math>\mathrm{pen}_b(0)=1</math> | ||
Pentation is holomorphic at least in the part of the complex plane, while the real part of the argument does not exceed some constant. For < | Pentation is holomorphic at least in the part of the complex plane, while the real part of the argument does not exceed some constant. For <math>b\!=\!\mathrm e</math>, | ||
this constant is about < | this constant is about <math>-2.5</math> | ||
The range of holomorphism of pentation includes alto the real axis. | The range of holomorphism of pentation includes alto the real axis. | ||
For the real base < | For the real base <math>b>1</math>, pentation <math>\mathrm{pen}_b</math> is real–holomorphic, | ||
<math>\mathrm{pen}_b(z^*)=\mathrm{pen}_b(z)^*</math> | <math>\mathrm{pen}_b(z^*)=\mathrm{pen}_b(z)^*</math> | ||
| Line 50: | Line 60: | ||
<math>\varepsilon=\exp(k (z-X))</math>, | <math>\varepsilon=\exp(k (z-X))</math>, | ||
parameters <math>k</math> and <math>X</math> depend on the base < | parameters <math>k</math> and <math>X</math> depend on the base <math>b</math>. | ||
For base <math>b\!>\!1</math>, the increment < | For base <math>b\!>\!1</math>, the increment <math>k</math> is positive. This increment is determined by the derivative of [[tetration]] at its lowest real [[fixed point]], and pentation is periodic function; the period <math>P=2 \pi \mathrm i /k</math>. For real base <math>b\!>\!1</math>, | ||
the increment is positive. | the increment is positive. | ||
==Properties of the natural pentation== | ==Properties of the natural pentation== | ||
The base < | The base <math>b</math> of pentation is indicated as subscript, but it it is e, the subsctipt can be omitted, as in the case of tetration, arctetration, exponential and logarithm. The [[natural pentation]] is | ||
[[superfunction]] of [[natural tetration]] tet <ref name="analuxp"> | [[superfunction]] of [[natural tetration]] tet <ref name="analuxp"> | ||
http://www.ams.org/mcom/2009-78-267/S0025-5718-09-02188-7/home.html <br> | http://www.ams.org/mcom/2009-78-267/S0025-5718-09-02188-7/home.html <br> | ||
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2009analuxpRepri.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Analytic solution of F(z+1)=exp(F(z)) in complex z-plane. Mathematics of Computation, v.78 (2009), 1647-1670. | http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2009analuxpRepri.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Analytic solution of F(z+1)=exp(F(z)) in complex z-plane. Mathematics of Computation, v.78 (2009), 1647-1670. | ||
</ref>< | </ref><ref name="vladie"> | ||
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2010vladie.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Superexponential as special function. [[Vladikavkaz Mathematical Journal]], 2010, v.12, issue 2, p.31-45. | http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2010vladie.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Superexponential as special function. [[Vladikavkaz Mathematical Journal]], 2010, v.12, issue 2, p.31-45. | ||
</ref>. | </ref>. | ||
| Line 75: | Line 85: | ||
A little bit more than two periods are covered by the range of the [[complex map]] at right. | A little bit more than two periods are covered by the range of the [[complex map]] at right. | ||
[[Natural pentation]] has the countable set of logarithmic singularities. The cut lines divide the right hand side of the complex plane to the set of "independent" strips of width < | [[Natural pentation]] has the countable set of logarithmic singularities. The cut lines divide the right hand side of the complex plane to the set of "independent" strips of width <math>P</math>. | ||
In addition, there are many branch points at the right hand side of the map in vicinity of the real axis; | In addition, there are many branch points at the right hand side of the map in vicinity of the real axis; | ||
and these branch points also reproduce at the translations for period <math>P</math>. | and these branch points also reproduce at the translations for period <math>P</math>. | ||
| Line 91: | Line 101: | ||
In vicinity of the range <math> -2.1 < z <1.1</math>, natural pentation can be approximated with linear function, <math> \mathrm{pen}(z)\approx 1\!+\!z</math>; this approximation gives of order of 2 correct decimal digits. Error of this approximation can be characterised with function | In vicinity of the range <math> -2.1 < z <1.1</math>, natural pentation can be approximated with linear function, <math> \mathrm{pen}(z)\approx 1\!+\!z</math>; this approximation gives of order of 2 correct decimal digits. Error of this approximation can be characterised with function | ||
<math>\delta(z)=\mathrm{pen}(z)-(1\!+\!z)</math>. In order to make it visible, it is scaled with factor 10, | <math>\delta(z)=\mathrm{pen}(z)-(1\!+\!z)</math>. In order to make it visible, it is scaled with factor 10, | ||
id est, | id est, <math>y\!=\!10\delta(x)</math> is plotted with thin curve in the intermediate figure. | ||
At larger positive values of the argument, pentation shows very fast growth, much faster than that of [[superfactorial]] or that of natural [[tetration]]. | At larger positive values of the argument, pentation shows very fast growth, much faster than that of [[superfactorial]] or that of natural [[tetration]]. | ||
Visually, <math>\mathrm{pen}(2)</math> looks as infinity, and, perhaps, <math>\ | Visually, <math>\mathrm{pen}(2)</math> looks as infinity, and, perhaps, <math>\mathrm{pen}(3)</math> can be considered a "numerical approximation" of the fake [[Mizugadro number]]. [[Tetration]] has singularity and the branch point <math>-2</math>, and this singularity determines the set of singularities in vicinity of the real axis. | ||
Construction and evaluation of [[tetration]], [[pentation]] and highest [[ackermann]]s may be good excersice for testing and debugging of the automatic procedure for calculation of [[superfuncion]]s and non-integer iterates of holomorphic functions. Up to year 2014, such an automatic procedure is not yet implemented, and the superfunctions are built-up semi-manually; with human control of the overlapping of various representations and manual check of the residual at the substitution of various approximations into the transfer equation. | Construction and evaluation of [[tetration]], [[pentation]] and highest [[ackermann]]s may be good excersice for testing and debugging of the automatic procedure for calculation of [[superfuncion]]s and non-integer iterates of holomorphic functions. Up to year 2014, such an automatic procedure is not yet implemented, and the superfunctions are built-up semi-manually; with human control of the overlapping of various representations and manual check of the residual at the substitution of various approximations into the transfer equation. | ||
| Line 103: | Line 113: | ||
http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/BOOK/202.pdf | http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/BOOK/202.pdf | ||
Д.Кузнецов. Суперфункции. Lambert Academic Publishing, 2014, in Russian. | Д.Кузнецов. Суперфункции. Lambert Academic Publishing, 2014, in Russian. | ||
</ref><ref> | </ref><ref name="2014acker"> | ||
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf <br> | http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf <br> | ||
http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf | http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf | ||
D.Kouznetsov. Holomorphic ackermanns. 2014, under consideration. | D.Kouznetsov. Holomorphic ackermanns. 2014, under consideration. | ||
</ref> | </ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:26, 9 September 2014
Pentation appears as 5th ackermann.
For , Pentation specific superfunction of tetration , constructed with regular iteration at its lowest real fixed point. Pentation is denoted with symbol pen;
where is Fifth ackermann to base . [1][2].
If the base of tetration , then the tetration is called natural tetration and the corresponding pentation is called Natural pentation. Namely this case is considered on this article.
The first 5 ackermanns (addition of e, multiplication by e, exponent, tetration, pentation) are shown in the top figure at right.
Natural pentation is compared to its asymptotics at the second figure.
The complex map of the natural pentation is shown in the last figure.
General properties
Pentation satisfies the transfer equation
where is tetration to base . The additional condition, common for all ackermanns is assumed,
Pentation is holomorphic at least in the part of the complex plane, while the real part of the argument does not exceed some constant. For , this constant is about
The range of holomorphism of pentation includes alto the real axis.
For the real base , pentation is real–holomorphic,
Pentation has the exponential asymptotic at large negative values of the real part of the argument,
where is fixed point of tetration, it is solution of equation
,
parameters and depend on the base . For base , the increment is positive. This increment is determined by the derivative of tetration at its lowest real fixed point, and pentation is periodic function; the period . For real base , the increment is positive.
Properties of the natural pentation
The base of pentation is indicated as subscript, but it it is e, the subsctipt can be omitted, as in the case of tetration, arctetration, exponential and logarithm. The natural pentation is superfunction of natural tetration tet [3][4].
Natural pentation has the following properties:
The limiting value at minus infinity is fuxed point of the natural tetration,
Increment at negative values of the real part is
Period
The period is pure imaginary, so, the map shown in the figure reproduces at the translations along the imaginary axis. A little bit more than two periods are covered by the range of the complex map at right.
Natural pentation has the countable set of logarithmic singularities. The cut lines divide the right hand side of the complex plane to the set of "independent" strips of width . In addition, there are many branch points at the right hand side of the map in vicinity of the real axis; and these branch points also reproduce at the translations for period . There is no way to direct these cut lines to the left, because infinite amount of singularities are in the right hand side of the complex map.
Along the real axis, at minus infinity, the function pen grows exponentially from its asymptotic value
The graphic passes through points with coordinates , , , .
In vicinity of the range , natural pentation can be approximated with linear function, ; this approximation gives of order of 2 correct decimal digits. Error of this approximation can be characterised with function . In order to make it visible, it is scaled with factor 10, id est, is plotted with thin curve in the intermediate figure.
At larger positive values of the argument, pentation shows very fast growth, much faster than that of superfactorial or that of natural tetration.
Visually, looks as infinity, and, perhaps, can be considered a "numerical approximation" of the fake Mizugadro number. Tetration has singularity and the branch point , and this singularity determines the set of singularities in vicinity of the real axis.
Construction and evaluation of tetration, pentation and highest ackermanns may be good excersice for testing and debugging of the automatic procedure for calculation of superfuncions and non-integer iterates of holomorphic functions. Up to year 2014, such an automatic procedure is not yet implemented, and the superfunctions are built-up semi-manually; with human control of the overlapping of various representations and manual check of the residual at the substitution of various approximations into the transfer equation. [1][2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 https://www.morebooks.de/store/ru/book/Суперфункции/isbn/978-3-659-56202-0 http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/BOOK/202.pdf http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/BOOK/202.pdf Д.Кузнецов. Суперфункции. Lambert Academic Publishing, 2014, in Russian.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf
http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/PAPERS/2014acker.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Holomorphic ackermanns. 2014, under consideration. - ↑
http://www.ams.org/mcom/2009-78-267/S0025-5718-09-02188-7/home.html
http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2009analuxpRepri.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Analytic solution of F(z+1)=exp(F(z)) in complex z-plane. Mathematics of Computation, v.78 (2009), 1647-1670. - ↑ http://www.ils.uec.ac.jp/~dima/PAPERS/2010vladie.pdf D.Kouznetsov. Superexponential as special function. Vladikavkaz Mathematical Journal, 2010, v.12, issue 2, p.31-45.
The first version of this article is adopted from TORI, http://mizugadro.mydns.jp/t/index.php/Pentation
Keywords
Ackermann, Pentation, Superfunction, Tetration, Transfer equation