Methionine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

John Leach (talk | contribs) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
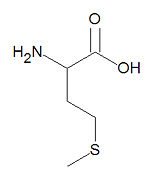
{{Image|Methionine stick figure.jpg|right|150px|'''Methionine''', a common amino acid.}} | {{Image|Methionine stick figure.jpg|right|150px|'''Methionine''', a common amino acid.}} | ||
'''Methionine''', abbreviated '''Met''' or '''M''', is one of the twenty common <math>\alpha</math>-[[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[proteins]]. Methionine and [[cysteine]] are the only amino acids that contain [[sulphur]]. The DNA codon for methionine is the "start" codon for protein synthesis, so all protein synthesis starts with a methionine on the N-terminus of proteins. Methionine also plays a role in the transfer of methyl groups within cells. | '''Methionine''', abbreviated '''Met''' or '''M''', is one of the twenty common <math>\alpha</math>-[[amino acid]]s used by living organisms to build [[proteins]]. Methionine and [[cysteine]] are the only amino acids that contain [[sulphur]]. The DNA codon for methionine is the "start" codon for protein synthesis, so all protein synthesis starts with a methionine on the N-terminus of proteins. Methionine also plays a role in the transfer of methyl groups within cells.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 18 September 2024
Methionine, abbreviated Met or M, is one of the twenty common -amino acids used by living organisms to build proteins. Methionine and cysteine are the only amino acids that contain sulphur. The DNA codon for methionine is the "start" codon for protein synthesis, so all protein synthesis starts with a methionine on the N-terminus of proteins. Methionine also plays a role in the transfer of methyl groups within cells.