Cysteine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
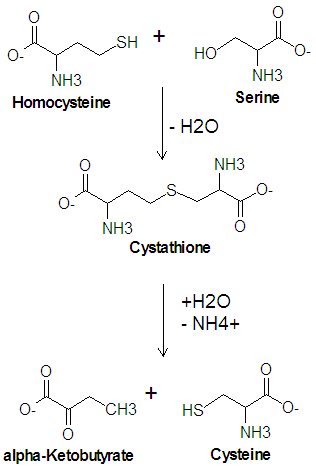
'''Cysteine''' is one of the twenty common [[amino acid|amino acids]]. It is one of two amino acids which contain a sulfur atom, the other being [[methionine]], and is one of the two amino acids which contain a hydroxyl group, the other being [[threonine]]. Cysteine is a precursor of methionine in the [[activated methyl cycle]], and it is synthesized from a condensation reaction between the amino acid [[serine]] and [[homocysteine]]. | '''Cysteine''' is one of the twenty common [[amino acid|amino acids]]. It is one of two amino acids which contain a sulfur atom, the other being [[methionine]], and is one of the two amino acids which contain a hydroxyl group, the other being [[threonine]]. Cysteine is a precursor of methionine in the [[activated methyl cycle]], and it is synthesized from a condensation reaction between the amino acid [[serine]] and [[homocysteine]]. | ||
Revision as of 16:44, 5 April 2009
Cysteine is one of the twenty common amino acids. It is one of two amino acids which contain a sulfur atom, the other being methionine, and is one of the two amino acids which contain a hydroxyl group, the other being threonine. Cysteine is a precursor of methionine in the activated methyl cycle, and it is synthesized from a condensation reaction between the amino acid serine and homocysteine.