Guanosine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
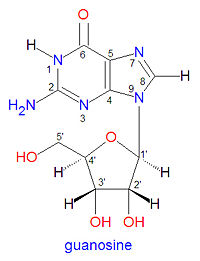
'''Guanosine''' (GUA) is a natural biomolecule found in [[DNA]] and [[RNA]] that is formed by the combination of two | '''Guanosine''' (GUA) is a natural biomolecule found in [[DNA]] and [[RNA]] that is formed by the combination of two ring systems, namely [[guanine]] (top) and [[ribose]] (bottom). In DNA the ribose ring is the 2'-deoxy form. It becomes incorporated into these nucleci acids via 5'-phosphorylated derivatives. In duplex DNA, guanosine is base-paired with a [[cytosine]] base (cytodine) on the opposite DNA strand. | ||
Revision as of 17:28, 8 April 2009
|
| |||||||
| guanosine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | DNA RNA biomolecules | ||||||
| Properties: | nucleotide | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Guanosine (GUA) is a natural biomolecule found in DNA and RNA that is formed by the combination of two ring systems, namely guanine (top) and ribose (bottom). In DNA the ribose ring is the 2'-deoxy form. It becomes incorporated into these nucleci acids via 5'-phosphorylated derivatives. In duplex DNA, guanosine is base-paired with a cytosine base (cytodine) on the opposite DNA strand.