Lactam: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (picture of lactam structurea) |
imported>David E. Volk (cephalosporin structure added) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
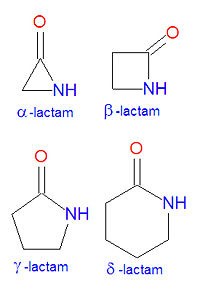
[[Image:Lactams.jpg|right|thumb|200px| | [[Image:Lactams.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small>Lactam structures.</small>]] | ||
In chemistry, a '''lactam''' is a cyclic [[amide]]. The name is derived from two chemical terms, [[lactone]], referring to a cyclic ketone, and [[amide]], a compound containing a [[nitrogen]] atom next to a [[carbonyl]] group. Lactams are named according to the size of the cyclic ring in the lactam: <math>\alpha</math>-lactams, <math>\beta</math>-lactams, <math>\gamma</math>-lactams and <math>\delta</math>-lactams contain rings made of three, four, five or six atoms, respectively. <math>\alpha</math>-lactams are also called aziridinones. Many widely used antibiotic drugs, including the[[penicillin]]s and [[cephalosporin]]s, owe their activity to the presence of a <math>\beta</math>-lactam structure. The lactams may have substitutions added to the nitrogen atom or any of the non-carbonyl carbon atoms in the base structure. | In chemistry, a '''lactam''' is a cyclic [[amide]]. The name is derived from two chemical terms, [[lactone]], referring to a cyclic ketone, and [[amide]], a compound containing a [[nitrogen]] atom next to a [[carbonyl]] group. Lactams are named according to the size of the cyclic ring in the lactam: <math>\alpha</math>-lactams, <math>\beta</math>-lactams, <math>\gamma</math>-lactams and <math>\delta</math>-lactams contain rings made of three, four, five or six atoms, respectively. <math>\alpha</math>-lactams are also called aziridinones. Many widely used antibiotic drugs, including the[[penicillin]]s and [[cephalosporin]]s, owe their activity to the presence of a <math>\beta</math>-lactam structure. The lactams may have substitutions added to the nitrogen atom or any of the non-carbonyl carbon atoms in the base structure. | ||
== Antibiotics == | |||
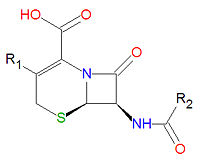
[[Image:Cephalosporin base.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small>Base structure of all cephalosporins.</small>]] | |||
The <math>\beta</math>-lactam forms the center structure of many antibiotic drugs, such as the [[cephalosporin]]s and the [[penicillin]]s, as shown above. | |||
Revision as of 14:38, 17 May 2008
In chemistry, a lactam is a cyclic amide. The name is derived from two chemical terms, lactone, referring to a cyclic ketone, and amide, a compound containing a nitrogen atom next to a carbonyl group. Lactams are named according to the size of the cyclic ring in the lactam: -lactams, -lactams, -lactams and -lactams contain rings made of three, four, five or six atoms, respectively. -lactams are also called aziridinones. Many widely used antibiotic drugs, including thepenicillins and cephalosporins, owe their activity to the presence of a -lactam structure. The lactams may have substitutions added to the nitrogen atom or any of the non-carbonyl carbon atoms in the base structure.
Antibiotics
The -lactam forms the center structure of many antibiotic drugs, such as the cephalosporins and the penicillins, as shown above.