Developmental biology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Daniel Mietchen (image) |
imported>Daniel Mietchen (image legend) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
<!-- Text is transcluded from the BASEPAGENAME/Definition subpage--> | <!-- Text is transcluded from the BASEPAGENAME/Definition subpage--> | ||
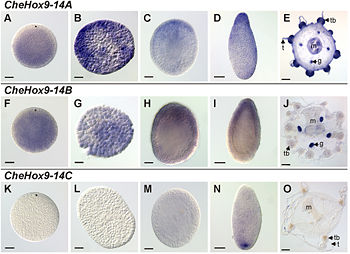
{{Image|Developmental and medusa-specific expression of Hox genes in Clytia hemisphaerica (part).jpg|right|350px|A typical study in developmental biology, targeting the [[gene expression|expression]] of several [[gene]]s ([[CheHox9-14A]], [[CheHox9-14B]] and [[CheHox9-14C]]) in the [[hydroid]] [[Clytia hemisphaerica]] at different [[stage (biology)|stages]] of [[embryogenesis|development]] (non-[[fertilization|fertilised]] [[oocyte|egg]], [[blastula]], [[gastrula]], [[planula]] and [[medusa]]; from left to right). [[Scale bar]]s: E, J, O: 100 µm; A–D, F–I, K–N: 50 µm.}} | {{Image|Developmental and medusa-specific expression of Hox genes in Clytia hemisphaerica (part).jpg|right|350px|A typical study in developmental biology, targeting the [[gene expression|expression]] of several [[gene]]s ([[CheHox9-14A]], [[CheHox9-14B]] and [[CheHox9-14C]]) in the [[hydroid]] [[Clytia hemisphaerica]] at different [[stage (biology)|stages]] of [[embryogenesis|development]] (non-[[fertilization|fertilised]] [[oocyte|egg]], [[blastula]], [[gastrula]], [[planula]] and [[medusa]]; from left to right). [[Scale bar]]s: E, J, O: 100 µm; A–D, F–I, K–N: 50 µm. Legends: g: [[gonad]]; m: [[manubrium]]; t: [[tentacle]]; tb: [[tentacle bulb]].}} | ||
Revision as of 05:53, 22 May 2010
Developmental biology [r]: The study of how cells grow and interact to form an organism. [e]
This article contains just a definition and optionally other subpages (such as a list of related articles), but no metadata. Create the metadata page if you want to expand this into a full article.

(CC) Image: Chiori et al., 2009
A typical study in developmental biology, targeting the expression of several genes (CheHox9-14A, CheHox9-14B and CheHox9-14C) in the hydroid Clytia hemisphaerica at different stages of development (non-fertilised egg, blastula, gastrula, planula and medusa; from left to right). Scale bars: E, J, O: 100 µm; A–D, F–I, K–N: 50 µm. Legends: g: gonad; m: manubrium; t: tentacle; tb: tentacle bulb.
A typical study in developmental biology, targeting the expression of several genes (CheHox9-14A, CheHox9-14B and CheHox9-14C) in the hydroid Clytia hemisphaerica at different stages of development (non-fertilised egg, blastula, gastrula, planula and medusa; from left to right). Scale bars: E, J, O: 100 µm; A–D, F–I, K–N: 50 µm. Legends: g: gonad; m: manubrium; t: tentacle; tb: tentacle bulb.