BTX: Difference between revisions
imported>Henry A. Padleckas (→Petrochemicals produced from BTX: mentioned re-isomerization for xylenes) |
imported>Milton Beychok m (→Petrochemicals produced from BTX: reseparation revised to re-separation.) |
||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
{{Image|BTX Derivatives.png|center|680px|Diagram of the chain of petrochemicals derived from the BTX aromatics.}} | {{Image|BTX Derivatives.png|center|680px|Diagram of the chain of petrochemicals derived from the BTX aromatics.}} | ||
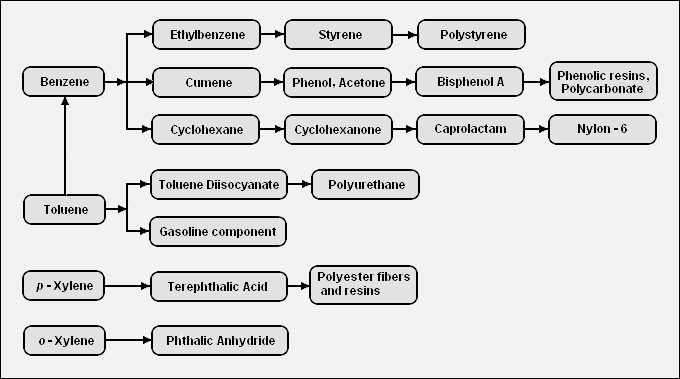
[[Polyethylene terephthalate]] (PET) is a reasonably economical plastic with excellent material properties and is recyclable. PET is produced in large quantities from [[terephthalic acid]] (or [[dimethyl terephthalate]]), which in turn is produced by oxidizing ''p-''xylene. This demand makes ''p''-xylene the most valuable of the xylene isomers, with ''o''-xylene second in demand, and ''m''-xylene the least in demand, although it is still used. The xylenes from BTX come in the 3-isomer mixture, and a couple of processes can be used to separate the xylene isomers, and re-isomerize the xylene stream least in demand for re-separation. Good separation of the xylenes by distillation is difficult because the [[boiling point]]s are close, especially the para and meta isomers. | |||
[[Polyethylene terephthalate]] (PET) is a reasonably economical plastic with excellent material properties and is recyclable. PET is produced in large quantities from [[terephthalic acid]] (or [[dimethyl terephthalate]]), which in turn is produced by oxidizing ''p-''xylene. This demand makes ''p''-xylene the most valuable of the xylene isomers, with ''o''-xylene second in demand, and ''m''-xylene the least in demand, although it is still used. The xylenes from BTX come in the 3-isomer mixture, and a couple of processes can be used to separate the xylene isomers, and re-isomerize the xylene stream least in demand for | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 17:19, 20 March 2012
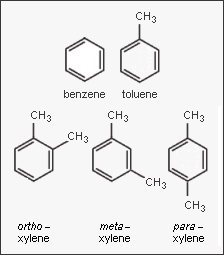
In the petroleum and petrochemical industries, the acronym BTX refers to mixtures of the aromatic hydrocarbons benzene, toluene, and the three xylene isomers. The xylene isomers are distinguished by the designations ortho – or o –, meta – or m –, and para – or p – as indicated in the adjacent diagram. If ethylbenzene is included, the mixture is sometimes referred to as BTEX.
The BTX aromatics are very important petrochemical materials. Global consumption of benzene, estimated at more than 40,000,000 tons in 2010, showed an unprecedented growth of more than 3,000,000 tons from the level seen in 2009. Likewise, the para-xylene consumption showed unprecedented growth in 2010, growing by 2,800,000 tons, a full ten percent growth from 2009.[1]
Toluene is also a valuable petrochemical for use as a solvent and intermediate in chemical manufacturing processes and as a high octane gasoline component.[2][3][4][5]
Properties of the BTX hydrocarbons
The table below lists some of the properties of the BTX aromatic hydrocarbons, all of which are liquids at typical room conditions:
| benzene | toluene | ethylbenzene | p - xylene | m - xylene | o - xylene | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H6 | C7H8 | C8H10 | C8H10 | C8H10 | C8H10 |
| Molecular mass, g · mol –1 | 78.12 | 92.15 | 106.17 | 106.17 | 106.17 | 106.17 |
| Boiling point, °C | 80.1 | 110.6 | 136.2 | 138.4 | 139.1 | 144.4 |
| Melting point, °C | 5.5 | – 95.0 | – 95.0 | 13.3 | – 47.9 | – 25.2 |
Production of BTX hydrocarbons
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Benzene, toluene, and xylenes can be made by various processes. However, most BTX production is based on the recovery of aromatics derived from the catalytic reforming of naphtha in a petroleum refinery.[4][7]
Catalytic reforming usually utilizes a feedstock naphtha that contains non-aromatic hydrocarbons with 6 to 11 or 12 carbon atoms and typically produces a reformate product containing C6 to C8 aromatics (benzene, toluene, xylenes) as well as paraffins and heavier aromatics containing 9 to 11 or 12 carbon atoms.
Another process for producing BTX aromatics involves the steam cracking of hydrocarbons which typically produces a cracked naphtha product commonly referred to as pyrolysis gasoline, pyrolysis gas or pygas. The pyrolysis gasoline typically consists of C6 to C8 aromatics, heavier aromatics containing 9 to 11 or 12 carbon atoms, and non-aromatic cyclic hydrocarbons (naphthenes) containing 6 or more carbon atoms.[4][7]
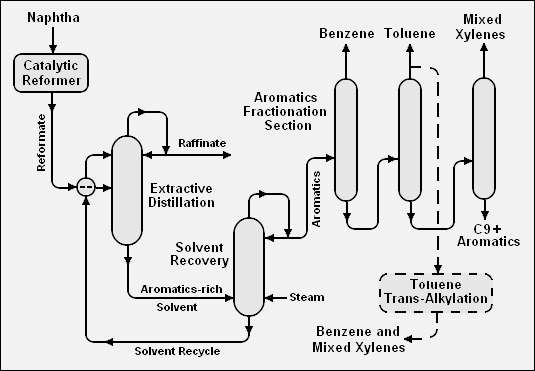
The adjacent table compares the BTX content of pyrolysis gasoline produced at standard cracking severity or at medium cracking severity with the BTX content of catalytic reformate produced by a either a continuous catalytic regenerative (CCR) reformer or by a semi-regenerative catalytic reformer. About 70 percent of the global production of benzene is by extraction from either reformate or pyrolysis gasoline.[4]
The BTX aromatics can be extracted from catalytic reformate or from pyrolysis gasoline by many different methods. Most of those methods, but not all, involve the use of a solvent either for liquid-liquid extraction or extractive distillation. Many different solvents are suitable, including sulfolane (C4H8O2S), furfural (C5H4O2), tetraethylene glycol (C8H18O5), dimethylsulfoxide (C2H6OS), and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (C5H9NO).
Below is a schematic flow diagram of one method, involving extractive distillation, for extraction of the BTX aromatics from a catalytic reformate:[2]
Petrochemicals produced from BTX
The BTX aromatics produced by catalytic reforming are used to raise the octane number in unleaded gasolines.
There are a very large number of petrochemicals produced from the BTX aromatics. The following diagram shows the chains leading from the BTX components to some of the petrochemicals that can be produced from those components:[2]
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) is a reasonably economical plastic with excellent material properties and is recyclable. PET is produced in large quantities from terephthalic acid (or dimethyl terephthalate), which in turn is produced by oxidizing p-xylene. This demand makes p-xylene the most valuable of the xylene isomers, with o-xylene second in demand, and m-xylene the least in demand, although it is still used. The xylenes from BTX come in the 3-isomer mixture, and a couple of processes can be used to separate the xylene isomers, and re-isomerize the xylene stream least in demand for re-separation. Good separation of the xylenes by distillation is difficult because the boiling points are close, especially the para and meta isomers.
References
- ↑ The Future of Benzene and Para-Xylene after Unprecedented Growth In 2010. From a ChemSystems report in 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 The BTX Chain: Benzene, Toluene, Xylene. Chapter 4 of the DOE's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) report entitled "Energy and Environmental Profile of the U.S. Chemical Industry" of May 2000.
- ↑ Use of Process Analytics in Aromatics (BTX and phenol) production plants. Case Study, August 2008. (scroll down to "Aromatics" section.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Benzene/Toluene. Introduction to a ChemSystems report, 2009.
- ↑ 10.6 Aromatics, Online Italian Encyclopedia of Hydrocarbons, Istituto della Enciclopedia Italiana, Volume II, 2006, pages 603-605.
- ↑ Robert C. Weast (Editor) (1975). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 56th Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 0-87819-455-X.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 International Energy Agency (2006).Energy Technology Perspectives. 1st Edition. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Page 414. ISBN 08070-1556-3.