Adenine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

John Leach (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
[[Category:Reviewed Passed]] | [[Category:Reviewed Passed]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Revision as of 11:00, 6 July 2024
|
| |||||||
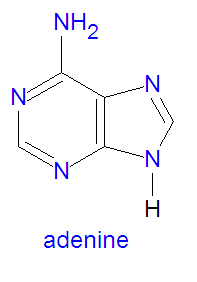
| adenine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | DNA RNA | ||||||
| Properties: | natural base | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Adenine is a naturally occurring base found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. When adenine is attached to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar, the complex is called adenosine. It is in this from that adenine is found in nucleic acids.
Adenine is also present in adenosine monophosphate (AMP), adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), NADH and NADPH, chemicals involved in the energy cycle and oxidation reduction steps within biology cells.