Network topology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Eric M Gearhart (Changed pics to be to the right of the text) |
imported>Eric M Gearhart (Well that didn't really work out :/) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
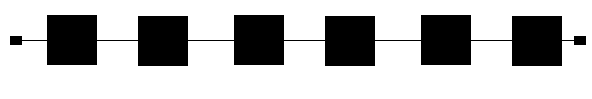
A "bus network" is hooked together like stops on a Public Bus route, one after the other. | A "bus network" is hooked together like stops on a Public Bus route, one after the other. | ||
[[Image:Bus_Network.png | [[Image:Bus_Network.png|Bus network]] | ||
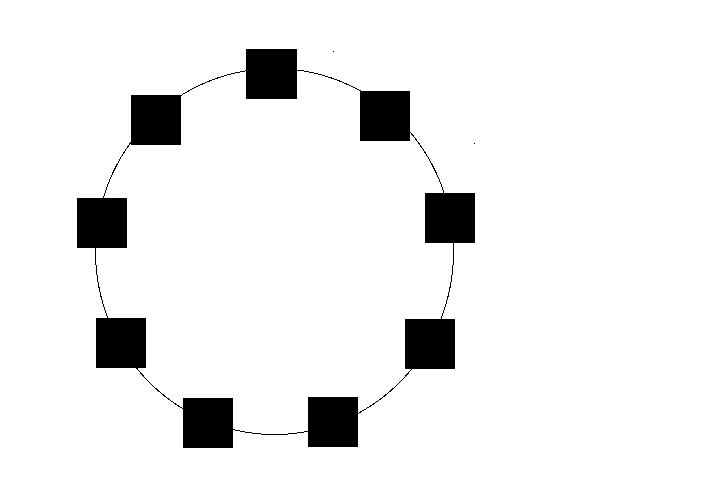
A ring topology | A ring topology | ||
A "ring network" is literally in the shape of a ring; devices reach each other by passing data around in a ring. | A "ring network" is literally in the shape of a ring; devices reach each other by passing data around in a ring. | ||
[[Image:Ring_Network.png | [[Image:Ring_Network.png|Ring network]] | ||
[[Category:CZ Live]] | [[Category:CZ Live]] | ||
[[Category:Computers Workgroup]] | [[Category:Computers Workgroup]] | ||
Revision as of 09:32, 2 April 2007
There are several different topologies of Computer networks. Here are several, with diagrams:
A bus topology
A "bus network" is hooked together like stops on a Public Bus route, one after the other.
A ring topology
A "ring network" is literally in the shape of a ring; devices reach each other by passing data around in a ring.