B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett (Started theray) |
imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In [[medicine]], '''B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia''' is a "chronic leukemia characterized by abnormal B-lymphocytes and often generalized lymphadenopathy. In patients presenting predominately with blood and bone marrow involvement it is called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); in those predominately with enlarged lymph nodes it is called small lymphocytic lymphoma. These terms represent spectrums of the same disease."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref><ref name="pmid16983131">{{cite journal |author=Shanafelt TD, Byrd JC, Call TG, Zent CS, Kay NE |title=Narrative review: initial management of newly diagnosed, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=145 |issue=6 |pages=435–47 |year=2006 |month=September |pmid=16983131 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/content/full/145/6/435 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15728813">{{cite journal |author=Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M |title=Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=352 |issue=8 |pages=804–15 |year=2005 |month=February |pmid=15728813 |doi=10.1056/NEJMra041720 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/352/8/804 |issn=}}</ref> | In [[medicine]], '''B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia''' is a "chronic leukemia characterized by abnormal B-lymphocytes and often generalized lymphadenopathy. In patients presenting predominately with blood and bone marrow involvement it is called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); in those predominately with enlarged lymph nodes it is called small lymphocytic lymphoma. These terms represent spectrums of the same disease."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref><ref name="pmid16983131">{{cite journal |author=Shanafelt TD, Byrd JC, Call TG, Zent CS, Kay NE |title=Narrative review: initial management of newly diagnosed, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=145 |issue=6 |pages=435–47 |year=2006 |month=September |pmid=16983131 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/content/full/145/6/435 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid15728813">{{cite journal |author=Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M |title=Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=352 |issue=8 |pages=804–15 |year=2005 |month=February |pmid=15728813 |doi=10.1056/NEJMra041720 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/352/8/804 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
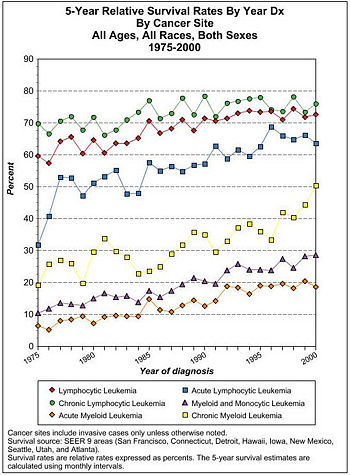
==Prognosis== | |||
{{Image|5-Year Relative Survival Rates By Year Dx By Leukemia type All Ages, All Races, Both Sexes 1975-2000.jpg|right|350px|5-Year Relative Survival Rates By Year Dx By Leukemia type All Ages, All Races, Both Sexes 1975-2000.}} | |||
===Staging information=== | |||
{{PDQ-staging|http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/CLL/HealthProfessional/page3}} | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
{{PDQ-treatment|http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/CLL/HealthProfessional/page4}} | |||
As a primary [[antineoplastic agent]], [[fludarabine]] may be more effective than [[chlorambucil]].<ref name="pmid11114313">{{cite journal |author=Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, ''et al'' |title=Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=343 |issue=24 |pages=1750–7 |year=2000 |month=December |pmid=11114313 |doi= |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/343/24/1750 |issn=}}</ref> | As a primary [[antineoplastic agent]], [[fludarabine]] may be more effective than [[chlorambucil]].<ref name="pmid11114313">{{cite journal |author=Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, ''et al'' |title=Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=343 |issue=24 |pages=1750–7 |year=2000 |month=December |pmid=11114313 |doi= |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/343/24/1750 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 1 March 2009
In medicine, B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a "chronic leukemia characterized by abnormal B-lymphocytes and often generalized lymphadenopathy. In patients presenting predominately with blood and bone marrow involvement it is called chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL); in those predominately with enlarged lymph nodes it is called small lymphocytic lymphoma. These terms represent spectrums of the same disease."[1][2][3]
Prognosis
Staging information
B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia staging information from the National Cancer Institute's Physician Data Query
Treatment
B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia treatment information from the National Cancer Institute's Physician Data Query
As a primary antineoplastic agent, fludarabine may be more effective than chlorambucil.[4]
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), B-Cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Shanafelt TD, Byrd JC, Call TG, Zent CS, Kay NE (September 2006). "Narrative review: initial management of newly diagnosed, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Ann. Intern. Med. 145 (6): 435–47. PMID 16983131. [e]
- ↑ Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M (February 2005). "Chronic lymphocytic leukemia". N. Engl. J. Med. 352 (8): 804–15. DOI:10.1056/NEJMra041720. PMID 15728813. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Rai KR, Peterson BL, Appelbaum FR, et al (December 2000). "Fludarabine compared with chlorambucil as primary therapy for chronic lymphocytic leukemia". N. Engl. J. Med. 343 (24): 1750–7. PMID 11114313. [e]