Comparative biology: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Daniel Mietchen (started as lemma) |
imported>Daniel Mietchen (+image) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
<!-- Text is transcluded from the BASEPAGENAME/Definition subpage--> | <!-- Text is transcluded from the BASEPAGENAME/Definition subpage--> | ||
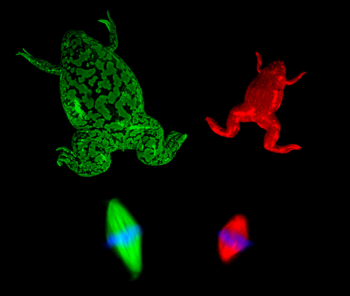
{{Image|Xenopus laevis and tropicalis with mitotic spindles JCB.png|right|350px|[[Mitotic spindle]]s (bottom) are about 30% longer in [[Xenopus laevis]] (green) than in its smaller, faster-breeding relative, [[Xenopus tropicalis|X. tropicalis]] (red).}} | |||
Revision as of 17:51, 19 May 2010

(CC) Image: CZ:Ref:Brown 2007 Xenopus tropicalis egg extracts provide insight into scaling of the mitotic spindle
Mitotic spindles (bottom) are about 30% longer in Xenopus laevis (green) than in its smaller, faster-breeding relative, X. tropicalis (red).
Mitotic spindles (bottom) are about 30% longer in Xenopus laevis (green) than in its smaller, faster-breeding relative, X. tropicalis (red).