Cefalexin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 125: | Line 125: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
{{CZMed}} | {{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 25 July 2024
|
| |||||||
| cefalexin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefalexin (cephalexin) is one of the most widely used antibiotic medications. It is a first-generation cephalosporin type of antibiotic drug, that is sold under nearly 100 brand names.
Chemistry
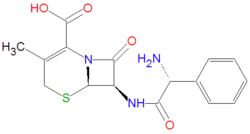
An IUPAC chemical name of cefalexin is (6R,7R)-7-[[(2R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula, C16H17N3O4S, gives it an average molecule mass of 347.3890 gram/mole. Its antibacterial activity is due to the core beta-lactam structure, which bind with penicillin-binding proteins within bacteria, thereby inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis, by an acylation reaction of the lactam with the bacterial proteins.
Brand Names
|
|
|
|
|
References
The most up-to-date information about Cefalexin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cefalexin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefalexin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefalexin - Detailed information from DrugBank.