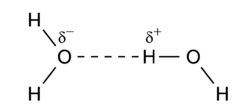Intermolecular forces
In physics, chemistry, and biology, intermolecular forces are forces that act between stable molecules or between functional groups of macromolecules. These non-covalent forces, which give rise to bonding energies of a few kcal/mol or less, are generally much weaker than chemical bonding forces. Nevertheless, intermolecular forces are responsible for a wide range of physical, chemical, and biological phenomena. For instance, they play a role in the deviation from the ideal gas law for real gases, the tertiary structure of macromolecules and signal induction in neurotransmitters.
In general one distinguishes short and long range intermolecular forces. The former are due to intermolecular exchange and charge penetration. They fall off exponentially as a function of intermolecular distance R and are repulsive for interacting closed-shell systems. In chemistry they are well known, because they give rise to steric hindrance, also known as Born or Pauli repulsion. Long range forces fall off with inverse powers of the distance, R −n, typically 3 ≤ n ≤ 10, and are mostly attractive.
The sum of long and short range forces gives rise to a minimum, referred to as Van der Waals minimum. The position and depth of the Van der Waals minimum depends on distance and mutual orientation of the molecules.
General theory
Before the advent of quantum mechanics the origin of intermolecular forces was not well understood. Especially the causes of hard sphere repulsion, postulated by Van der Waals, and the possibility of the liquefaction of noble gases were difficult to understand (see also Van der Waals equation). Soon after the formulation of quantum mechanics, however, all open questions regarding intermolecular forces were answered, first by S.C. Wang and then more completely and thoroughly by Fritz London.
The quantum mechanical basis for the majority of intermolecular effects is contained in a nonrelativistic energy operator, the molecular Hamiltonian. This operator consists only of kinetic energies and Coulomb interactions. Usually one applies the Born-Oppenheimer approximation and considers the electronic (clamped nuclei) Hamilton operator only. For very long intermolecular distances the retardation of the Coulomb force (first considered in 1948 for intermolecular forces by Hendrik Casimir and Dirk Polder) may have to be included. Sometimes, e.g., for interacting paramagnetic or electronically excited molecules, electronic spin and other magnetic effects may play a role. In this article, however, retardation and magnetic effects will not be considered. The books[1][2] may be consulted for modern and thorough expositions of the theory of intermolecular forces.
It is common to distinguish four fundamental interactions, see e.g., the books just mentioned and Refs.: [3][4]
- exchange
- electrostatic
- induction
- dispersion.
Perturbation theory
The last three of the fundamental interactions are most naturally accounted for by Rayleigh-Schrödinger perturbation theory (RS-PT). In this theory—applied to two monomers A and B—one uses as unperturbed Hamiltonian the sum of two monomer Hamiltonians,
while the perturbation is
where q i indicates the charge (in units e of elementary charge) of a particle of monomer A; q j belongs to monomer B. In the case of electrons q = −1, while a nucleus has q equal to its atomic number Z. The quantity r ij is the distance between particle i and particle j. In this equation and further in this article atomic units are used. Perturbation theory is based on expansions of perturbed states in terms of unperturbed states (eigenstates of H(0) ). In the present case the unperturbed states are products
Supermolecular approach
The early theoretical work on intermolecular forces was invariably based on RS-PT and its antisymmetrized variants. However, since the beginning of the 1990s it has become possible to apply standard quantum chemical methods to pairs of molecules. This approach is referred to as the supermolecule method. In order to obtain reliable results one must include electronic correlation in the supermolecule method (without it dispersion is not accounted for at all), and take care of the basis set superposition error. This is the effect that the atomic orbital basis of one molecule improves the basis of the other. Since this improvement is distance dependent, it gives easily rise to artifacts.
Supermolecule calculations must be performed with very high precision, because the problem, known as weighing the captain, arises here. First one weighs the ship with the captain aboard (total energy of molecules in interaction) and then the ship is weighed with the captain ashore (total energy of molecules at an infinite distance apart); the difference gives the captain's weight. This analogy is due to the late Charles Coulson. The analogy is based on the fact that the total energy of molecules is six to seven orders of magnitude larger than a typical intermolecular interaction. That is, the significant digits in the results of supermolecule calculations start to appear beyond the sixth or seventh decimal place.
A disadvantage of the supermolecule method is that it yields the interaction as a lump sum. It does not give an interaction energy separated in the four fundamental contributions mentioned above. Therefore, the supermolecule will not be discussed method any further in this article.
Exchange
The monomer functions ΦnA and ΦmB are antisymmetric under permutation of electron coordinates (i.e., they satisfy the Pauli principle), but the product states are not antisymmetric under intermolecular exchange of the electrons. An obvious way to proceed would be to introduce the intermolecular antisymmetrizer . But, as already noticed in 1930 by Eisenschitz and London,[5] this causes two major problems. In the first place the antisymmetrized unperturbed states are no longer eigenfunctions of H(0), which follows from the non-commutation
In the second place the projected excited states
become linearly dependent and there is no manifest choice of a physically meaningful linearly independent subset. In the late 1960s, the Eisenschitz-London approach was revived and different rigorous variants of symmetry adapted perturbation theory were developed. (The word symmetry refers here to the permutational symmetry of electrons, i.e., to the indistinguishability of electrons). The different approaches shared a major drawback: they were very difficult to apply in practice. Hence a somewhat less rigorous approach (weak symmetry forcing) was introduced: apply ordinary RS-PT (Rayleigh-Schrödinger perturbation theory) and introduce the intermolecular antisymmetrizer at appropriate places in the RS-PT equations. This approach leads to feasible equations, and, when electronically correlated monomer functions are used, weak symmetry forcing gives reliable results. [3] The first-order (most important) energy including exchange is in almost all symmetry-adapted perturbation theories given by the following expression
The main difference between covalent and non-covalent forces is the sign of this expression. In the case of chemical bonding this interaction is attractive (for certain electron-spin states, usually spin-singlet) and responsible for large bonding energies—on the order of a hundred kcal/mol. In the case of intermolecular forces between closed shell systems, the interaction is strongly repulsive and responsible for the "volume" of the molecule (see Van der Waals radius). Roughly speaking, the exchange interaction is proportional to the differential overlap between Φ0A and Φ0B. Since the wave functions decay exponentially as a function of distance, the exchange interaction does too. Hence the range of action is relatively short, which is why exchange interactions are referred to as short range interactions.
Electrostatic interactions
By definition the electrostatic interaction is given by the first-order Rayleigh-Schrödinger perturbation (RS-PT) energy (without exchange):
Remembering that we work within the clamped nuclei approximation, we let the clamped nucleus α on A have position vector Rα, then its charge times the Dirac delta function, Zα δ(r-Rα), is the charge density of nucleus α. The total charge density ρAtot of monomer A is is the sum of a nuclear contribution (sum of delta functions) and an electronic contribution (integral over electronic wave function squared):
with the electronic charge density given by an integral over nA − 1 primed electron coordinates:
An analogous definition holds for the charge density of monomer B. It can be shown that the first-order quantum mechanical expression can be written as
which is nothing but the classical expression for the electrostatic interaction between two charge distributions. This shows that the first-order RS-PT energy is indeed equal to the electrostatic interaction between A and B.
Multipole expansion
At present it is feasible to compute the electrostatic energy without any further approximations other than those applied in the computation of the monomer wave functions. In the past this was different and a further approximation was commonly introduced: VAB was expanded in a (truncated) series in inverse powers of the intermolecular distance R. This yields the multipole expansion of the electrostatic energy. Since its concepts still pervade the theory of intermolecular forces, we will present it here.
In this article the following expansion is proved
with the Clebsch-Gordan series defined by
and the irregular solid harmonic is defined by
The function YL,M is a normalized spherical harmonic, while and are spherical multipole moment operators. This expansion is manifestly in powers of 1/RAB.
Insertion of this expansion into the first-order (without exchange) expression gives a very similar expansion for the electrostatic energy, because the matrix element factorizes, Thus, the multipole-expansion of the electrostatic interaction (an expansion in powers of 1/R) is,
with the permanent multipole moments defined by
The series is of infinite length, and, indeed, most molecules have an infinite number of non-vanishing multipoles. In the past, when computer calculations for the permanent moments were not yet feasible, it was common to truncate this series after the first non-vanishing term.
It depends very much on the symmetry of the monomers which terms are non-vanishing,. For instance, molecules with an inversion center such as a homonuclear diatomic (e.g., molecular nitrogen N2), or an organic molecule like ethene (C2H4) do not posses a permanent dipole moment (l = 1), but do carry a quadrupole moment (l = 2). Molecules such a hydrogen chloride (HCl) and water (H2O) lack an inversion center and hence do have a permanent dipole. So, the first non-vanishing electrostatic term in, e.g., the N2—H2O dimer, is the lA = 2, lB = 1 term. From the formula above follows that this term contains the irregular solid harmonic of order L = lA + lB = 3, which has an R–4 dependence. Note, parenthetically, that in this dimer the quadrupole-quadrupole interaction (R–5) is not unimportant either, because the water molecule carries a non-vanishing quadrupole as well.
When computer calculations of permanent multipole moments of any order became possible, the matter of the convergence of the multipole series became urgent. It can be shown that, if the charge distributions of the two monomers overlap, the multipole expansion is formally divergent. It is an asymptotic series.
Ionic interactions
It is debatable whether ionic interactions are to be seen as intermolecular forces, as some workers consider them rather as special kind of chemical bonding. The forces occur between charged atoms or molecules (ions). Ionic bonds are formed when the difference between the electron affinity of one monomer and the ionization potential of the other is so large that electron transfer from the one monomer to the other is energetically favorable. Since a transfer of an electron is never complete there is always a degree of covalent bonding.
Once the ions (of opposite sign) are formed, the interaction between them can seen as a special case of multipolar attraction, with a 1/RAB distance dependence. Indeed, the ionic interaction is the electrostatic term with lA = 0 and lB = 0. Using that the irregular harmonics for L = 0 is simply
and that the monopole moments and their Clebsch-Gordan coupling are
(where qA and qB are the charges of the molecular ions) we recover—as to be expected—Coulomb's law
For shorter distances, where the charge distributions of the monomers overlap, the ions will repel each other because of intermonomer exchange of the electrons.
Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to the large amount of energy required to break the forces between the charged ions. When molten they are also good conductors of heat and electricity, due to the free or delocalised ions.
Numerical example
An example of a compound that is ionically bound is KCN. Due to the low ionization potential of potassium (4.339 eV) and the large electron affinity of CN (3.82 eV), the Coulomb attraction favors electron transfer from K to CN already at the large distance of 53 bohr (= 2.8 nm). For shorter distances the system can be regarded as to consist of two closed-shell monomers K+ and CN− that show the kind of intermolecular interactions discussed in this article. It can be estimated from numbers given in Ref.[6] that the dissociation energy of KCN → K + CN is about 75 kcal/mol (314 kJ/mol), which is the order of magnitude of a chemical binding energy. However, the motion of K+ around CN− is without appreciable energy barrier, whereas a covalent bond is characterized by a strong directionality. In that sense the K+ — CN− molecule indeed could be regarded as bound by intermolecular forces.
Dipole-dipole interactions
Dipole-dipole interactions, also called Keesom interactions or Keesom forces after Willem Hendrik Keesom, who produced the first mathematical description in 1921, are the forces that occur between two molecules with permanent dipoles. They result from the dipole-dipole interaction between two molecules. An example of this can be seen in hydrochloric acid:
The molecules are depicted here as two point dipoles in the energetically most unfavourable position. A point dipole is an idealization similar to a point charge (a finite charge in an infinitesimally small volume). A point dipole consists of two equal charges of opposite sign δ+ and δ– that are a distance d apart. The distance d is so small that at any distance R away from the point dipole, it holds that d/R >> (d/R)2. In this limit the electrostatic field outside the charge distribution consists of one (R−3) term only, see this article. The electrostatic interaction between two point dipoles is given by the single term lA = 1 and lB = 1 in the expansion above.
Obviously, no molecule is an ideal point dipole, and in the case of the HCl dimer, for instance, dipole-quadrupole, quadrupole-quadrupole, etc., interactions are by no means negligible (and neither induction nor dispersion interactions can be neglected).
Note that almost always the dipole-dipole interaction between two atoms is zero, because atoms rarely carry a permanent dipole, see atomic dipoles.
In order to obtain the mathematical equation for the dipole-dipole interaction, we must consider in the expansion of the electrostatic energy the term with lA = 1 and lB = 1. Because this expansion is termwise rotational invariant, we can choose a convenient system of axes to evaluate the term. We choose a coordinate system centered on A with its z-axis coinciding with the intermolecular vector RAB. Under this circumstance it holds for the irregular solid harmonic that
Hence, the dipole-dipole term becomes after substitution of two Clebsch-Gordan coefficients
where
Analogous relations hold for the permanent dipole moments on B. Then
Writing
and similarly for B, we get finally the well-known expression
Numerical example
As a numerical example we consider the HCl dimer depicted above. We assume that the left molecule is A and the right B, so that the z-axis is along the molecules and points to the right. Our convention of the dipole vector is such that it points from negative to positive charge. Note, parenthetically, that our convention, while common in physics, is opposite to the one used in organic chemistry. Since organic chemists hardly ever perform vector computations with dipoles, confusion hardly ever arises. In organic chemistry dipoles are mainly used in semi-quantitative discussions of charge separation in a molecule. So,
and it follows simply that
The value of μHCl is 0.43 (atomic units), so that at a distance of 10 bohr the dipole-dipole repulsion is 3.698 10–4 hartree (0.97 kJ/mol). If we rotate molecule B over 1800 degree, the negative chlorine atom comes close to the positive hydrogen atom of the other monomer and there is an attraction of 0.97 kJ/mol.
Thermal rotation
If one of the molecules is neutral and freely rotating, the total electrostatic interaction energy becomes zero, since all terms in the multipole expansion vanish upon free rotation, except the monopole-monopole interaction. (For the dipole-dipole interaction this is most easily proved by integrating over the spherical polar angles of the dipole vector, while using the volume element sinθ dθdφ). In gases and liquids the molecules are not rotating freely: for dipolar molecules the rotation is weighted by the Boltzmann factor exp(−Edip-dip/kT), where k is the Boltzmann constant and T the absolute temperature. It was first shown by Lennard-Jones[7] that the temperature-averaged dipole-dipole interaction is
Since the thermally averaged energy has an R−6 dependence, it is evidently much weaker than the unaveraged one, but it is not completely zero. It is attractive, because the Boltzmann weighting favors somewhat the attractive regions of space. In HCl–HCl we find for T = 300 K and RAB = 10 bohr (0.53 nm) the averaged attraction −62 J/mol, which shows a weakening, due to thermal rotational motion, of the interaction by a factor of about 16. In the literature there is much confusion about the size of the dipole-dipole interaction, because some workers quote unaveraged values, while others quote thermally averaged values—the two differ by more than an order of magnitude.
Hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonding is an intermolecular interaction with a hydrogen atom being present in the intermolecular bond. This hydrogen is covalently (chemically) bound in one molecule, which acts as the proton donor. The other molecule acts as the proton acceptor. In the following important example of the water dimer, the water molecule on the right is the proton donor, while the one on the left is the proton acceptor:
The donated proton in a hydrogen bond is usually bound to an electronegative atom of the donor molecule. Examples of electronegative atoms are nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. The electronegative atom is negatively charged (carries a charge δ-) and the hydrogen atom bound to it is positively charged. Consequently the proton donor is a polar molecule with a relatively large dipole moment. Often the positively charged hydrogen atom points towards an electron rich region in the acceptor molecule. The fact that an electron rich region exists in the acceptor molecule, implies already that the acceptor has a relatively large dipole moment as well. The result is a dimer that to a large extent is bound by the dipole-dipole force.
For quite some time it was believed that hydrogen bonding required an explanation that was different from the other intermolecular interactions. However, reliable computer calculations that became possible since the 1980s, have shown that only the four effects listed above play a role, with the dipole-dipole interaction being singularly important. Since the four effects account completely for the bonding in small dimers like the water dimer, for which highly accurate calculations are feasible, it is now generally believed that no other bonding effects are operative.
Hydrogen bonds are found throughout nature. They give water its unique properties that are so important to life on earth. Hydrogen bonds between hydrogen atoms and nitrogen atoms of adjacent base pairs provide the intermolecular force that bind together the two strands in a molecule of DNA.
To give an indication of the order of magnitude of a typical hydrogen-bonding energy, we quote the estimate De = −5.00 kcal/mol = −20.9 kJ/mol for the dissociation energy of the water dimer.[8]
Induction (polarization) forces
This type of interaction has a clear classical interpretation. Every molecule (except neutral S-state atom, such as the noble gases) offers an electric field to its surroundings. Every atom (including noble gas atoms) and every molecule is polarizable, that is, under influence of an electric field the charge distribution of the atom or molecule polarizes (positive charge shifts one way, negative charge the other, while the total charge is conserved). If we bring two molecules together, one molecule polarizes the other. This lowers the energy of the system and causes bonding. Generally speaking, induction energy is one of the less important components of the intermolecular force. It becomes important if one monomer has a monopole (charge) or large dipole, while the other is easily polarizable.
Quantum mechanically the induction interaction is described by second-order RS-PT (Rayleigh-Schrödinger perturbation theory). The RS-PT second-order energy is,
Here we assumed that both monomers have a discrete set of eigenstates. If not, the sums must be extended by integrals over the continuum part of the spectrum. Further we consider only the perturbation of the ground state, which we assume to be non-degenerate:
from which follows that the second-order energy E(2) is always negative. Finally, we restrict the double sum such that no "dangerous denominators" (i.e., zero denominators) appear. The double sum can be separated into three terms
In the first term on the right hand side A is in its ground state and polarizes B, in the second term B is in its ground state and polarizes A. The third term gives dispersion interaction and will be discussed in a later section.
It is possible to give general, non-multipole-expanded, expressions for the induction (without exchange). To this end we need to introduce a polarization propagator and to give an expression for the electric field generated by a molecule. [See, for instance, Eq. (19) in Ref.[3]]. It is also possible to use the multipole expansion and by an angular momentum recoupling procedure[9] to express the polarization energy in terms of monomer properties. Both approaches are outside the scope of this article.
A simple formula is obtained if both monomers are assumed to rotate freely. In contrast to the electrostatic energy, the rotationally averaged induction interaction is not zero, due to the negative definiteness of the second order RS-PT energy. We define
and the generalized isotropic polarizability
The rotationally averaged induction energy is[9]
The most important term for neutral subsystems is for lA = lB = 1. The usual dipole polarizability α0 is proportional to the generalized isotropic polarizability and (Q1)2 is proportional to the square of the length of the dipole μ:
Hence the first induction terms are
As a numeric example we consider HCl again. Its polarizability α0 is 17.5 au. Polarization of one monomer by the dipole of the other at R = 10 bohr gives an attraction of 3.2 10−6 hartree, which corresponds to −8.5 J/mol. Twice this number (−17 J/mol) may be compared with the thermally averaged electrostatic energy −62 J/mol mentioned above.
London (dispersion) forces
In 1908 Kamerling Onnes and his coworkers liquified helium, which experimentally proved that two helium atoms attract each other—so that a liquid can be formed—but also that they repel each other—so that the liquid does not implode. Earlier (1873) Van der Waals had already assumed on theoretical grounds that there must be attraction and repulsion between atoms. He made this assumption in the derivation of his equation of state.
Until the advent of quantum mechanics it was an enigma why two noble gas atoms would repel or attract each other. Shortly after the introduction of the Schrödinger equation, Wang (1927) solved this equation perturbatively for two ground-state hydrogen atoms at large interatomic distance R. Approximating the electronic interaction by a Taylor series in 1/R he found an attractive potential with as leading term −C6/R6. A few years later (1930) London[10] showed that so-called oscillator strengths appear in the equations for the intermolecular interactions. Oscillator strengths were known from the classical theory of the dispersion of light developed by Drude and Lorentz. Also later, in the quantum mechanical dispersion theory of Kramers and Heisenberg, these quantities played a central role. Because of the similarity of his perturbation theory with the older dispersion theory, London coined the name dispersion effect for the attraction between noble gas atoms. It is common today to refer to these attractive long-range forces as London or dispersion forces.
The dispersion force acts between any two molecules and is clearly the only long-range interaction between two noble gas atoms, as noble gases do not have non-vanishing multipoles. No long range electrostatic or induction interactions are operative between noble gas atoms. After London's quantum mechanical account of the dispersion attraction, many workers have tried to find a classical explanation. So far this has not led to any quantitative mathematical expressions, but only to handwaving arguments in which instantaneous dipoles (vectors of undetermined direction and magnitude) play an important role.
The dimers that interact mainly through dispersion forces are usually very weakly bound. In the CO-dimer the equilibrium dissociation energy De is about 1.5 kJ/mol, but this value is not due to dispersion alone. Recall that the carbon monoxide molecule has a small dipole and a reasonable quadrupole, which contribute to the interaction as well.
For noble gas pairs, dispersion is the only attracting force. For instance, He2 has the dissociation energy De = 0.091 kJ/mol. The dimer Ar2 has a dissociation energy of 1.1 kJ/mol, which is more than an order of magnitude larger than the value of the helium dimer. As we will see below, this is due to the fact that the polarizability of the argon atom (11.09 bohr3) is much larger than that of the helium atom (1.38 bohr3). A large factor (∼ 48.2) appears also in the ratio of the C6 values of Ar2 and He2, which are 70.8 and 1.47 au, respectively. The ratio between the dissociation energy of Ar2 and He2 (∼ 12.1) is less than would be expected from the ratio between their C6 values. This is because the equilibrium distance in He2 (5.6 bohr) is less than that in Ar2 (7.5 bohr), so that the C6/R6 term in the case of the helium dimer has a factor (7.5/5.6)6 = 5.8 more weight than in Ar2.
Quantum mechanical theory of dispersion forces
Above the quantum mechanical second-order RS-PT expression is given:
London developed the perturbation VAB in a series in R−1, where R is the distance between the nuclear centers of mass of the monomers. This series is the multipole expansion given above. When substituted into the second-order expression, Edisp is also obtained as series in R−1, with the first term being −C6/R6.
Much later (in the early 1980s) it was shown by several workers independently that the multipole expansion is not needed. It is possible to reformulate Edisp in terms of frequency-dependent polarization propagators. This work was a generalization of earlier work by Casimir and Polder (1948), who—using the multipole expansion—showed that the first term in the 1/R expansion can be written as the following integral
Here αA(iω) and αB(iω) are the frequency-dependent dipole polarizabilities of the respective atoms. The frequency ω is multiplied by the imaginary unit i. It is not difficult to give Casimir-Polder type expressions for the other terms in the expansion. In these higher terms one meets quadrupole, octupole, ... and mixed-pole (for example dipole-quadrupole) polarizabilities.
London obviously did not know the Casimir-Polder integral in 1930 and he made an additional approximation, named after Albrecht Unsöld. In this approximation one assumes that the excitation energies in the denominator of the second-order energies can be moved in front of the sum. In the summand remains an expression which is (almost) the unit operator—in its form of a resolution in terms of basis elements of Hilbert space (see closure relation). In this manner London obtained dispersion in terms of static (ω = 0) dipole polarizabilities and ionization potentials. He found the following approximation for the dispersion interaction Edisp between two atoms A and B. The quantities IA and IB are the first ionization potentials of the atoms,
Application of this London formula to the dispersion interaction between two hydrogen atoms [α(0) = 4 au, I = 0.5 hartree] gives C6 = 6 au. The generally assumed value is 6.499 au.
Note that the final London formula does not contain instantaneous dipoles. (The "explanation" of the dispersion force as the interaction between two such dipoles was invented after London gave the proper quantum mechanical theory. See the authoritative work[11] for a criticism of the instantaneous dipole model.)
Qualitatively the magnitude of a polarizability is a measure for the size of an atom or molecule. This is clearly demonstrated by the following dipole polarizabilities of the noble gases (in bohr3) from[12]
- He 1.383
- Ne 2.668
- Ar 11.09
- Kr 16.74
- Xe 27.0
Since the dispersion C6 values are proportional to dipole polarizabilities, the London dispersion forces are proportional to the sizes of the monomers as is shown by the following reasonably accurate upper bounds from Ref.[12] (C6 values in atomic units):
- He-He 1.47 Ne-Xe 46.5
- He-Ne 3.20 Ar-Ar 70.8
- He-Ar 10.1 Ar-Kr 100.
- He-Kr 14.2 Ar-Xe 151
- He-Xe 21.4 Kr-Kr 142
- Ne-Ne 7.27 Kr-Xe 215
- Ne-Ar 22.0 Xe-Xe 325
- Ne-Kr 30.9
Anisotropy and non-additivity of intermolecular forces
Consider the interaction between two electric point charges at position and . By Coulomb's law the interaction potential depends only on the distance between the particles. For molecules this is different. If we see a molecule as a rigid 3-D body, it has 6 degrees of freedom (3 degrees for its orientation and 3 degrees for its position in R3). The interaction energy of two molecules (a dimer) in isotropic and homogeneous space is in general a function of 2×6-6=6 degrees of freedom (by the homogeneity of space the interaction does not depend on the position of the center of mass of the dimer, and by the isotropy of space the interaction does not depend on the orientation of the dimer). The analytic description of the interaction of two arbitrarily shaped rigid molecules requires therefore 6 parameters. (One often uses two Euler angles per molecule, plus a dihedral angle, plus the distance.) The fact that the intermolecular interaction depends on the orientation of the molecules is expressed by stating that the potential is anisotropic. Since point charges are by definition spherical symmetric, their interaction is isotropic. Especially in the older literature, intermolecular interactions are regularly assumed to be isotropic (e.g., the potential is described in Lennard-Jones form, which depends only on distance).
Consider three arbitrary point charges at distances r12, r13, and r23 apart. The total interaction U is additive; i.e., it is the sum
Again for molecules this can be different. Pretending that the interaction depends on distances only—but see above—the interaction of three molecules takes in general the form
where is a non-additive three-body interaction. Such an interaction can be caused by exchange interactions, by induction, and by dispersion (the Axilrod-Teller triple dipole effect).
References
- ↑ A. J. Stone, The Theory of Intermolecular Forces, 1996, Clarendon Press, Oxford
- ↑ I. G. Kaplan, Intermolecular Interactions, Wiley, Hoboken NJ (2006)
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 B. Jeziorski, R. Moszynski, and K. Szalewicz, Perturbation Theory Approach to Intermolecular Potential Energy Surfaces of van der Waals complexes, Chemical Reviews, vol. 94, pp. 1887-1930 (1994).
- ↑ K. Szalewicz and B. Jeziorski, in: Molecular Interactions, editor S. Scheiner, Wiley, Chichester (1995). ISBN 0471 959219.
- ↑ R. Eisenschitz and F. London, Zeitschrift für Physik, vol. 60, p. 491 (1930). English translations in H. Hettema, Quantum Chemistry, Classic Scientific Papers, World Scientific, Singapore (2000), p. 336.
- ↑ P. E. S. Wormer and J. Tennyson, J. Chem. Phys. vol 75, pp. 1245-1253 (1981)
- ↑ J. E. Lennard-Jones, Cohesion, Proc. Physical Society (London), vol. 43, pp. 461-482 (1931).
- ↑ E. M. Mass, et al., J. Chem. Phys. vol 113, pp. 6687-6701 (2000).
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 P. E. S. Wormer, F. Mulder, and A. van der Avoird, Quantum Theoretical Calculations of Van der Waals Interaction between Molecules. Anisotropic Long Range Interactions, International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, vol. 11, pp. 959-970 (1977)
- ↑ F. London, Zeitschrift für Physik, vol. 60, p. 245 (1930) and Z. Physik. Chemie, vol. B11, p. 222 (1930). English translations in H. Hettema, Quantum Chemistry, Classic Scientific Papers, World Scientific, Singapore (2000).
- ↑ J. O. Hirschfelder, C. F. Curtiss, and R. B. Bird, Molecular Theory of Gases and Liquids, Wiley, New York, 1954
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 J. M. Standard and P. R. Certain, J. Chemical Physics, vol. 83, pp. 3002 - 3008 (1985)




![{\displaystyle {\big [}{\tilde {\mathcal {A}}}^{AB},H^{(0)}{\big ]}\neq 0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/55bd666acd3c73e212c9c448c04aec597ca20522)






![{\displaystyle V^{AB}=\sum _{\ell _{A}=0}^{\infty }\sum _{\ell _{B}=0}^{\infty }(-1)^{\ell _{B}}{\binom {2\ell _{A}+2\ell _{B}}{2\ell _{A}}}^{1/2}\sum _{M=-\ell _{A}-\ell _{B}}^{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B}}(-1)^{M}I_{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B},-M}(\mathbf {R} _{AB})\;\left[\mathbf {Q} ^{\ell _{A}}\otimes \mathbf {Q} ^{\ell _{B}}\right]_{M}^{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3e2a05f194d1384fe1078d8980259f87b8187f59)
![{\displaystyle \left[\mathbf {Q} ^{\ell _{A}}\otimes \mathbf {Q} ^{\ell _{B}}\right]_{M}^{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B}}\equiv \sum _{m_{A}=-\ell _{A}}^{\ell _{A}}\sum _{m_{B}=-\ell _{B}}^{\ell _{B}}\;Q_{m_{A}}^{\ell _{A}}Q_{m_{B}}^{\ell _{B}}\;\langle \ell _{A},m_{A};\ell _{B},m_{B}|\ell _{A}+\ell _{B},M\rangle .}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a695f5563a62a3dd78ff609eaf6580af2c6b4c8)
![{\displaystyle I_{L,M}(\mathbf {R} _{AB})\equiv \left[{\frac {4\pi }{2L+1}}\right]^{1/2}\;{\frac {Y_{L,M}({\widehat {\mathbf {R} }}_{AB})}{R_{AB}^{L+1}}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/67752416343d8f8d462256b129b1cd050fa195bc)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}E_{\mathrm {electrostatic} }^{(1)}=&\sum _{\ell _{A}=0}^{\infty }\sum _{\ell _{B}=0}^{\infty }(-1)^{\ell _{B}}{\binom {2\ell _{A}+2\ell _{B}}{2\ell _{A}}}^{1/2}\\&\sum _{M=-\ell _{A}-\ell _{B}}^{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B}}(-1)^{M}I_{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B},-M}(\mathbf {R} _{AB})\;\left[\mathbf {M} ^{\ell _{A}}\otimes \mathbf {M} ^{\ell _{B}}\right]_{M}^{\ell _{A}+\ell _{B}},\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7f6d30f5042c4dc6c58eabf510ae5dccb9ff0d69)


![{\displaystyle M_{0}^{0_{A}}=q_{A},\quad M_{0}^{0_{B}}=q_{B}\quad {\hbox{and}}\quad [\mathbf {M} ^{0_{A}}\otimes \mathbf {M} ^{0_{A}}]_{0}^{0}=q_{A}q_{B},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c8578235620d0c878c62a4121f8250ff0b27251f)

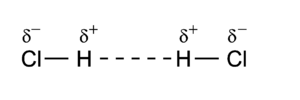

![{\displaystyle E_{\mathrm {dip-dip} }=-{\frac {1}{R_{AB}^{3}}}{\binom {4}{2}}^{1/2}\left[\mathbf {M} ^{1_{A}}\otimes \mathbf {M} ^{1_{B}}\right]_{0}^{2}=-{\frac {\sqrt {6}}{R_{AB}^{3}}}\left[{\frac {1}{\sqrt {6}}}(\mu _{1}^{A}\mu _{-1}^{B}+\mu _{-1}^{A}\mu _{1}^{B})+{\sqrt {\frac {2}{3}}}\mu _{0}^{A}\mu _{0}^{B}\right],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a0e8f3abfeefd0a505b73af915e37cf78d2a8147)

![{\displaystyle E_{\mathrm {dip-dip} }={\frac {1}{R_{AB}^{3}}}\left[\mu _{x}^{A}\mu _{x}^{B}+\mu _{y}^{A}\mu _{y}^{B}-2\mu _{z}^{A}\mu _{z}^{B}\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d45f09b37b3743bbcb4859d6b3b1cf6f158e4de0)

![{\displaystyle E_{\mathrm {dip-dip} }={\frac {1}{R_{AB}^{3}}}\left[{\boldsymbol {\mu }}^{A}\cdot {\boldsymbol {\mu }}^{B}-3({\boldsymbol {\mu }}^{A}\cdot {\hat {\mathbf {R} }}_{AB})({\hat {\mathbf {R} }}_{AB}\cdot {\boldsymbol {\mu }}^{B})\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1e3aee8bd3cff1ff3aed93416e7a8dcff52accdd)