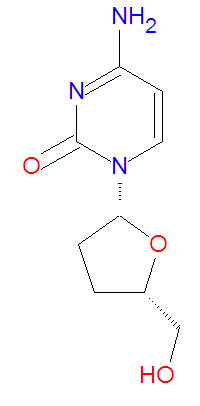
Zalcitabine
|
| |||||||
| zalcitabine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | HIV/AIDS | ||||||
| Properties: | RT inhibitor, cytosine analog, DNA terminator | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Zalcitabine, or dideoxycytidine (DDC or DDCYD), is a dideoxynucleoside antiviral drug that is an analog of the natural DNA base cytosine. The lack of 3'-hydroxyl group makes it a viral DNA chain terminator. It also inhibits HIV-1 reverse transcriptase by binding to it and competing with the natural substrate deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP). The related drug lamivudine, which has a sulfur atom in place of the 3'-carbon present in zalcitabine, supresses viruses in a similar manner.
Chemistry
Its IUPAC chemical name of zalcitabine is 4-amino-1-[(2R,5S)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one, but it is also called dideoxycytidine (ddC), and it has molecular formula C9H13N3O3 giving it a molecular mass of 211.2178 g/mol. It is a structural analog of the natural base deoxycytosine which used in DNA, but zalcitabine lacks the 3'-hydroxy group.
External links
- Zalcitabine - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank