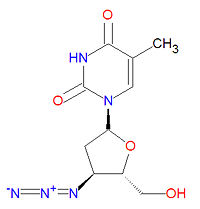
Zidovudine
|
| |||||||
| zidovudine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antiviral drug HIV | ||||||
| Properties: | reverse transcriptase inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Zidovudine is an antiviral drug used primarily for the treatment of HIV/AIDS.
Mechanism of action
Zidovudine is a nucleoside-based reverse transcriptase inhibitor that is structurally analogous to thymidine, a normal base in DNA. After phosphorylation, it becomes incorporated into viral DNA where it acts as a DNA chain terminator. The viral DNA chain is terminated because the 3'-hydroxy group needed for the formation of a phosphodiester bond is missing, having been replaced by an azido group. It also inhibits the HIV RT by binding with it and thus competing with natural substrates.
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for zidovudine is 1-[(2R,4S,5S)-4-azido-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4-dione and it has chemical formula C10H13N5O4, giving it a molecular mass of 267.2413 g/mol. It is dideoxynucleoside in which the usual 3'-hydroxy group has been replaced by an azido group, making incapable of forming normal phosphodiester bonds required for normal DNA.
Clinical uses
AZT can benefit patients with Human Immunodeficiency Virus .[1]
References
- ↑ Fischl MA, Richman DD, Grieco MH, et al. (July 1987). "The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial". N. Engl. J. Med. 317 (4): 185–91. PMID 3299089. [e]