Milankovitch cycles
Milankovitch cycles are cycles in the Earth's orbit that effect the amount of solar radiation striking the Earth at different times of the year. They are named after Milutin Milanković. These cycles include the precession, eccentricity, and obliquity of Earth's motions. All three processes occurring simultaneously produce 100,000 year ice age cycles. The cycles result with changes in high latitude insolation, which is the measurement of solar radiation absorbed on the surface area in an amount of time, expressed as W/m^2 or kilowatt-hours per square meter per day. Depending on the albedo of the surface area will determine how much light is reflected or absorbed (Snow has a very high albedo(.8-.9 on a 0-1 scale)). The solar radiation would lead to deglaciation, Earth's overall albedo will plummet exponentially as the ice melt's and more energy is absorbed. The Milankovich cycles are the cause that starts the initial warming. "It is concluded that changes in the earth's orbital geometry are the fundamental cause of the succession of Quaternary ice ages." [1]
This theory opens up a wide field of stratigraphic and sedimentological research.
Main Orbital Forces
- Precession is Earth's wobble caused by our daily rotation while orbiting the Sun. Hipparchus discovered the equinoxes were not static, but move west on the ecliptic when compared to distant stars that relatively seem fixed at this distance. He lived some 100-200 years BC.
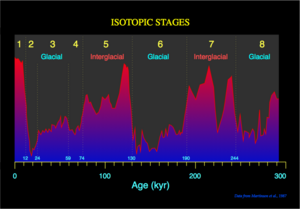
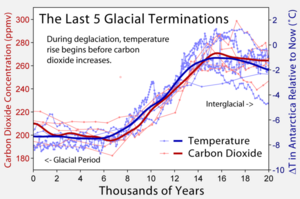
It is the same physics as a top's wobble: the Earth's axis will have a change in the direction, currently it points towards the star Polaris, but after 25,765 years (a Platonic year) our axis will have made a complete circle. At approximately 12,882.5 years our North will be 180 degrees away from where it points now, essentially South from the current perspective. The study of paleomagnetism has demonstrated that the Earth's magnetic field varies in both orientation and intensity through time. The positions of magnetic north and magnetic south become interchanged. "Evidence from high-sedimentation-rate South Atlantic deep-sea cores indicates that global and Southern Ocean carbon budget shifts preceded thermohaline circulation changes during the last ice age initiation and termination and that these were preceded by ice-sheet growth and retreat, respectively." [2] Magnetochronology is the study of geomagnetic reversals. When you make an observation of the direction of the geometric field, to calculate the pole position, and this is done from only one location, then it is called a VGP. Ten or more site-mean VGPs should be used to calculate a paleomagnetic pole, this number would provide a reasonable average.[3] "The last swing of the VGP (virtual geomagnetic pole) from the southern hemisphere to the northern hemisphere in the Brunhes-Matuyama geomagnetic reversal." [4] Ocean sediments are used for chronostratigraphy as well. This is time related to layers of rock, in this case ocean sediments. Global climate has been monitored and recorded covering the past 450,000 years from the Southern Hemisphere ocean-floor sediments. The oxygen isotopes from the rocks can be analyzed and correlated to the present temperature of Earth. Within the climatic variance of these records over 450,000 years there is a concentration of three spectral peaks recurring in periods of 23,000, 42,000, and approximately 100,000 years.
According to J. D. Hays, the 23,000-year portion of the variance on the 450,000 year record displays the same periods (about 23,000 and 19,000 years) as the quasi-periodic precession index.
Differential gravity is acting on Earth at all times. The Sun, moon, and other planets in our solar system all have a force of attraction. The equilateral bulge is proof of this, along with the precession of Earth's rotational axis.
- Eccentricityis the measure of how much the orbit shape deviates from a circle. The eccentricity of the Earth's orbit is currently about 0.0167. A circular orbit: e=0 so earth is not far from a circle being only .016 more eccentric.
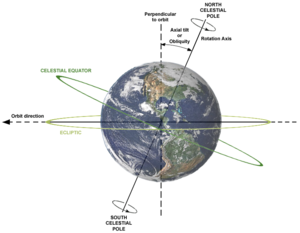
- Obliquityis earth's axial tilt. For the year 1980, the north geomagnetic pole was located at approximately 79°N, 289°E in the Canadian Arctic Islands. If earth's axis was perpendicular to it's orbit, there wouldn't be any precession. Eccentricity modulates the precessional signal as well. With these two forces occurring at the same time, we see a relationship of the 42,000-year peaks of climatic change on the 450,000 year records. This amount of time is the same period of variations in the obliquity.
Ice age cycles
Climate effects
Notes
- ↑ Hays, J. D., John Imbrie, and N. J. Shackleton (1976). "Variations in the Earth's Orbit: Pacemaker of the Ice Ages". Science 194 (4270): 1121 - 1132.
- ↑ Alexander M. Piotrowski, Steven L. Goldstein, Sidney R. Hemming, and Richard G. Fairbanks Science 25 March 2005 307: 1933-1938 [DOI: 10.1126/science.1104883]
- ↑ http://faculty.up.edu/butler/books/chap07.pdf
- ↑ Okada, M., Niitsuma, N., " Detailed paleomagnetic records during the Brunhes-Matuyama geomagnetic reversal, and a direct determination of depth lag for magnetization in marine sediments" Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, Volume 56, Issue 1-2, p. 133-150. 1989.
See also
- Precession(Wobble)
- Eccentricity(Earth's orbit)
- Obliquity(Axial tilt)