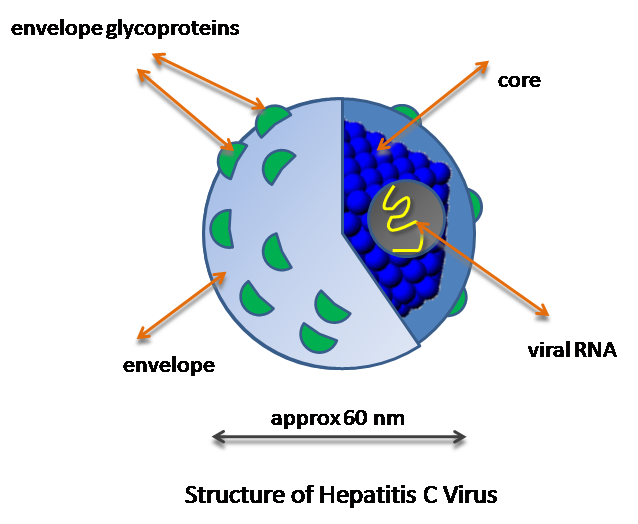
Hepatitis C virus
Articles that lack this notice, including many Eduzendium ones, welcome your collaboration! |
| x | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virus classification | ||||||||
|
Classification
Higher order taxa
Virus; ssRNA positive strand virus no DNA stage; Flaviviriade; hepacivirus
Species
Hepatitis C virus
Description and significance
The Hepatitis C virus (HCV) was discovered in 1989 at Chiron, Inc. The genome was located by using chimpanzees infected with a serum, that was from a patient with non-A, non-B Hepatitis. Through this screening they were able to discover what the virus was that was causing Hepatitis after blood transfusions that were not caused by Hepatitis A or Hepatitis B. This virus encodes a single polyprotein that is about 3,000 amino acids long. It is processed by host cells and viral proteases. This virus lives and infects the liver of its host. It reproduces in the hepatocytes of the liver. It is then spread throughout the body in the bloodstream where it can be transmitted to another host through direct blood to blood contact. It is important for its genome to be sequenced because of the lethal effects of HCV. This virus has been linked to cancer of the liver, cirrhosis, and has also been linked with many HIV patients. Also of importance because currently there are 6 different genotypes of HCV and through testing we have learned that different genotypes react differently to different methods of treatment.
Genome structure
The Genome of HCV is approximately 10,000 base pairs long. It contains single open reading frame (ORF) that encodes for a polyprotein of about 3000 amino acids. At both the 5’ and 3’ ends there are non coding regions. There are about 6 main types of genomic structure for HCV. There are thought to be many frameshift mutations during the replication of HCV, which help lead to its genetic variability. This enables the virus to become harder to track, and also leads to the difficulties in coming up with a cure for it, enhancing its life span as a virus.
Cell structure and metabolism
Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Describe any interactions with other organisms (included eukaryotes), contributions to the environment, effect on environment, etc.
Pathology
How does this organism cause disease? Human, animal, plant hosts? Virulence factors, as well as patient symptoms.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required