Polyhedron
A polyhedron is a three-dimensional geometric closed figure bounded by a connected set of polygons. A polyhedron, in Euclidian geometry, must have at least four faces. A polyhedron of four sides is called a tetrahedron, six sides a hexahedron, eight sides an octahedron, ten sides a decahedron. Figures with more sides are typically named with the Greek name for the number of sides, followed by "-hedron".
The polygons bounding a polyhedron are known as faces; the line segments bounding the polygons are known as edges, and the points where the faces meet are vertices (singular vertex).
A convex polyhedron bounded by faces which are all the same-sized regular polygon is known as a Platonic solid. There are only five Platonic solids, shown in the table below:
| number of faces |
name | type of face | properties | image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | regular tetrahedron (or regular triangular pyramid) |
equilateral triangle | 4 vertices, 6 edges, self-dual | 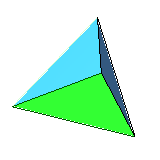
|
| 6 | cube | square | 8 vertices, 12 edges, dual to octahedron | 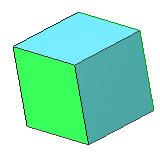
|
| 8 | regular octahedron | equilateral triangle | 6 vertices, 12 edges, dual to cube | 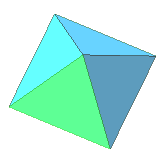
|
| 12 | regular dodecahedron | regular pentagon | 20 vertices, 30 edges, dual to icosahedron | 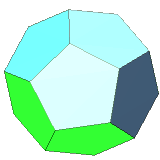
|
| 20 | regular icosahedron | equilateral triangle | 12 vertices, 30 edges, dual to dodecahedron | 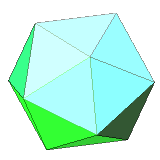
|