Quorum sensing
Quorum sensing is the ability of populations of bacteria to communicate and coordinate behavior via signaling molecules which are often small peptides or homoserine lactones. An early name for the general clas of signalling compounds is autoinducer, refering to their ability to trigger gene expression in the cells (autoinduction) of the same species that produce the compound. In Gram negative bacteria, two main classes of autoinducer have been defined, namely AI-1 and AI-2.
Purpose of quorum sensing
A major function of quorum sensing is to coordinate certain behaviour or actions between bacteria of the same kind, depending on their number. The use of the word quorum is an allusion to the attendance numbers required for valid business meetings that legally require a "quorum".
An example of bacterial coordination is when opportunistic bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa can grow within a host without harming it, until they reach a certain concentration. Then at a certain cell density (the quorum) they can channel their activities into activities (such as specialised biofilm formation and immune system suppression where the presence of large number of cooperating bacteria may overwhelm the large host.
It is hoped that the therapeutic useful enzymatic degradation of the signalling molecules might be used prevent the formation of bacterial biofilms and possibly weaken established biofilms. Disrupting the signalling process in this way is called quorum quenching.
Role of quorum sensing in specific organisms
Quorum sensing has been implicated in many different microorganisms as a mechanism for triggering of a wide range of complex or highly evolved responses whose effectiveness depends on large numbers of cells of the sane type being peesent in a particular location. These include [1] [2]:
- Bioluminescence by Vibrio bacteria, discovered in the 1970s
- Mating ability of the Gram positive coccus Enterococcus faecalis, Clewell, 1975,
- Cytolysin (virulence factor) production by Enterococcus
- Antibiotic production by variuos Streptomyces and Erwinia bacteria
- Fruiting body production by Myxococcus bacteria
- Virulence, biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Biofilm ability coded by F factor in Escherichia coli
- Virulence in Vibrio cholerae
- DNA injection into plants by Agrobacterium tumefaciens]
- Erwinia bacteria's virulence for plants
- DNA uptake (transformation) competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Competence for DNA transformation , spore formation in Bacillus
- Staphylococcus aureus virulence
The first organisms in which quorum sensing was observed were Myxobacteria and Streptomyces species. However, the most well known (and beautiful) example is the regulation of light production in Vibrio fischeri, a bioluminiscent bacterium that lives as a symbiont in the light-producing organ of the Hawaiian bobtail squid. When V. fischeri cells are free-living, the autoinducer is at low concentration and thus cells do not luminesce. In the light organ of the squid (photophore), they are highly concentrated (about 1011 cells/ml) and transcription of luciferase is induced, leading to bioluminescence.
Processes possibly regulated or partially regulated by AI-2-mediated quorum sensing in E. coli include cell division. In other species such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-related processes include biofilm development, exopolysaccharide production, and cell aggregation. AI-2 was found to increase expression of sdiA, a transcriptional regulator of promoters which promote ftsQ, part of the ftsQAZ operon essential for cell division.
Streptococcus pneumoniae uses quorum sensing to become competent for DNA uptake natural gene transformation.
Overview of quorum sensing provided by Wingren and Levin 2006
Ned Wingreen and Simon A. Levin have provided an excellant up-to-date review of quorum sensing through PLoS:
Cooperation among Microorganisms
Ned S. Wingreen, Simon A. Levin*
One of the organizing principles of life on Earth is that cells cooperate. This is evident in the case of multicellular organisms, from nematodes to humans, but it also appears to apply widely among single-celled organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and amoeba. In many cases, the label “single-celled” applies to only part of the life cycle of these organisms. For example, the model amoeba Dictyostelium discodium is single-celled under conditions of nutritional abundance, but upon starvation, it communicates to form aggregates that subsequently pass through multicellular stages of slug and fruiting body. Indeed, in light of recent discoveries of communication among bacteria and the importance and prevalence of bacterial biofilms, “single-celled” may turn out to be a misnomer even for these organisms. Here we highlight some of the better-studied examples of cooperation among microorganisms and attempt to identify some of the important questions in this emerging field. Understanding cooperation among microorganisms presents conceptual and mathematical challenges at the interface of evolutionary biology and the theory of emergent properties of independent agents, two of the most exciting areas in modern mathematical biology.
Most of the best-studied cases of cooperation among microorganisms concern intraspecies cooperation. An example of this is quorum sensing among bacteria, in which cells produce, secrete, and detect small molecules, called autoinducers. At high enough autoinducer concentrations (high cell densities), the bacteria enter a new mode of existence characterized by expression of genes associated with collective behaviors that are best carried out in concerted fashion by many cells [1]. These behaviors include the formation of protective biofilms, the expression of virulence factors to attack a host, the production of light, the establishment of competence to exchange DNA (a bacterial form of sexual recombination), and many others. The signaling pathway for one of the better- studied quorum-sensing circuits, that of Vibrio cholerae, the human pathogen, is shown in Figure 1.
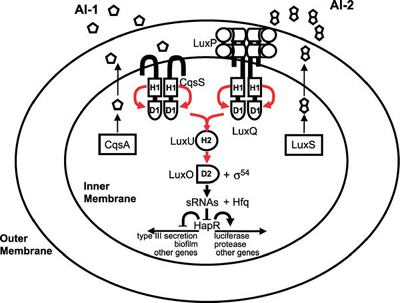 Figure 1. Quorum-Sensing Circuit of the Bacterial Pathogen Vibrio cholerae Red arrows indicate phosphoryl-group transfer [1]. (Figure: Matthew B. Neiditch, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, United States). Cooperation among Microorganisms Ned S. Wingreen, Simon A. Levin PLoS Biol 4(9): e299. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040299 Published: September 12, 2006
Figure 1. Quorum-Sensing Circuit of the Bacterial Pathogen Vibrio cholerae Red arrows indicate phosphoryl-group transfer [1]. (Figure: Matthew B. Neiditch, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, United States). Cooperation among Microorganisms Ned S. Wingreen, Simon A. Levin PLoS Biol 4(9): e299. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040299 Published: September 12, 2006Another well-studied example of intraspecies cooperation concerns the cyanobacterium Anabaena, which grows in long chains, in which approximately one cell out of ten differentiates into a heterocyst that provides fixed nitrogen for the neighboring cells (Figure 2) [2]. Dictyostelium is probably the most-studied model for cooperation among eukaryotic microorganisms, but even in the nonmotile eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae, hyphal growth (that is, filamentous growth) can be viewed as a cooperative mechanism for foraging.
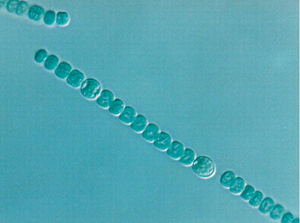 Figure 2. Heterocyst Differentiation in Anabaena sp. UTCC-426 (Photograph: Mary Olaveson, University of Toronto Scarborough, Toronto, Ontario, Canada). Cooperation among Microorganisms Ned S. Wingreen, Simon A. Levin PLoS Biol 4(9): e299. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040299 Published: September 12, 2006
Figure 2. Heterocyst Differentiation in Anabaena sp. UTCC-426 (Photograph: Mary Olaveson, University of Toronto Scarborough, Toronto, Ontario, Canada). Cooperation among Microorganisms Ned S. Wingreen, Simon A. Levin PLoS Biol 4(9): e299. DOI:10.1371/journal.pbio.0040299 Published: September 12, 2006Cooperation between different microorganism species is much less understood, or studied, partially for practical reasons, but also because the ubiquity of communication among microorganisms has only recently been appreciated. Nevertheless, it has been clear for many years that bacteria form biofilms on many surfaces (including human teeth, artificial joints, and organs, as well as on the surfaces and in the roots of plants, including crops) that consist of large consortia of different organisms. Moreover, it is clear that, far from being a case of pure Darwinian competition, interactions among these species and with eukaryotic hosts may be mutually beneficial. A recent case in point is the discovery of a mutualistic interaction of four bacterial species with the tomato plant (M. del Gallo, personal communication). Rather than competing, the four species coexist and strongly promote plant growth by fixing nitrogen, providing growth hormones, and preventing hostile bacterial species from growing. Tooth biofilms have been shown to consist of stable consortia of hundreds of distinct species, and bacterial mats are believed to consist of even larger numbers of species, in dynamic equilibrium among themselves, and with multiple bacterial viruses. Interest in bacterial cooperation has been spurred by the discovery that one of the autoinducers, named AI-2 (a furanone), is produced by a wide variety of bacteria, including most known human pathogens, and it may be one of a class of universal interspecies communication molecules [3,4].
These examples highlight the range of behaviors that could be termed “cooperation.” Cooperative behaviors include complex social interactions such as division of labor and mutualism in providing shelter, foraging, reproduction, and dispersal [5]. The examples also highlight the importance of communication in adjusting group behavior to environmental circumstances and population density. Cooperation also has its discontents, and there is growing interest in the role and fate of “cheaters” among microorganisms. There is some evidence as well for “police,” particularly in the context of bacterial-host interactions, in which host systems favor the growth of symbiotic bacteria but discourage growth of noncooperative, but otherwise identical, cells [6,7]. For a recent review of communication in bacteria that highlights these issues, see [8].
Understanding how cooperation arose and is maintained, particularly among large numbers of species, presents a challenge for practitioners of both molecular biology and evolutionary biology, as well as for theorists. Is cooperation best understood as the convergence of the immediate self-interest of multiple parties? Or can evolution lead to stable cases of short-term altruistic behavior, providing long-term benefit for all? These questions have been central in evolutionary biology since the time of Darwin, who regarded apparently altruistic behavior as a challenge for his theory. Especially puzzling was the extreme levels of cooperation and altruism, termed eusociality, in the haplodiploid insects and termites.
J. B. S. Haldane elucidated a fundamental principle underlying apparent altruistic behavior when he said that he would lay down his life to save two brothers or eight cousins, reflecting the one-half and one-eighth of his genes he shared with each, respectively. William D. Hamilton formalized these notions in his theory of kin selection, pointing out that the enhanced genetic relatedness of haplodiploid sisters, who share three-quarters of their genes, facilitates “altruism” in the haplodiploid species. Subsequent work has shown that kin selection can also work effectively under conditions of low relatedness and, furthermore, is not even necessary for cooperative behavior to arise. Cooperation can similarly be facilitated among unrelated individuals, for example, when the spatial range of interactions is restricted. Kin selection may play a role when limited spatial range is involved, but it is not essential [9]. On the other hand, a limited range of spatial interactions is no guarantee of cooperation; it can just as well lead to spite and selfish behavior, as in the production of allelopathic substances in microorganisms and plants [10]. For reviews of the selective mechanisms leading to cooperation and altruism, see [11–13].
The challenges in understanding cooperation and how it becomes reinforced over evolutionary time to produce stable mutualisms and even multicellularity is at the core of understanding biology. It is key to understanding how complexity arose evolutionarily, how organisms band together and profit from collective decision making, and how populations of diverse organisms interact to produce self-reinforcing networks of mutual benefit. It is also key to understanding the maintenance of ecological communities and patterns of nutrient cycling. The mathematical approaches of the past provide a foundation, but new mathematical techniques drawn from such diverse subjects as dynamical game theory and spatial stochastic processes will be needed to lay bare the essential truths. Considerable progress has been made in the past few years in developing the relevant mathematics, and we are at the threshold of dramatic advances in our understanding of cooperative behavior, one of the central and fundamental issues in biology.
References cited by Wingreen and Levin 2006
- 1. Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) Quorum sensing: Cell-to cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21: 319–346. Find this article online
- 2. Zhang CC, Laurent S, Sakr S, Peng L, Bedu S (2006) Heterocyst differentiation and pattern formation in cyanobacteria: A chorus of signals. Mol Microbiol 59: 367–375. Find this article online
- 3. Surette MG, Miller MB, Bassler BL (1999) Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Vibrio harveyi: A new family of genes responsible for autoinducer production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 1639–1644. Find this article online
- 4. Miller ST, Xavier KB, Campagna SR, Taga ME, Semmelhack MF, et al. (2004) Salmonella typhimurium recognizes a chemically distinct form of the bacterial quorum-sensing signal A1-2. Mol Cell 15: 677–687. Find this article online
- 5. Crespi BJ (2001) The evolution of social behavior in microorganisms. Trends Ecol Evol 16: 178–183. Find this article online
- 6. Kiers ET, Rousseau RA, West SA, Denison RF (2003) Host sanctions and the legume-rhizobium mutualism. Nature 425: 78–81. Find this article online
- 7. Visick KL, Foster J, Doino J, McFall-Ngai M, Ruby EG (2000) Vibrio fischeri lux genes play an important role in colonization and development of the host light organ. J Bacteriol 182: 4578–4586. Find this article online
- 8. Keller L, Surette MG (2006) Communication in bacteria: An ecological and evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Microbiol 4: 249–258. Find this article online
- 9. Durrett R, Levin SA (1994) The importance of being discrete (and spatial). Theor Popul Biol 46: 363–394. Find this article online
- 10. Chao L, Levin BR (1981) Structured habitats and the evolution of anti-competitor toxins in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 78: 6324–6328. Find this article online
- 11. Sachs JL, Mueller UG, Wilcox TP, Bull JJ (2004) The evolution of cooperation. Quart Rev Biol 79: 135–160. Find this article online
- 12. Lehmann L, Keller L (2006) The evolution of cooperation and altruism. A general framework and a classification of models. J Evol Biol In press.
- 13. West SA, Griffin AS, Gardner A, Diggle SP (2006) Social evolution theory for microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 4: 597–607. Find this article online
Series Editor: Simon. Levin, Princeton University, United States of AmericaCitation: Wingreen NS, Levin SA (2006) Cooperation among microorganisms. PLoS Biol 4(9): e299. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040299 Published: September 12, 2006 Copyright: © 2006 Wingreen and Levin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Ned S. Wingreen is Professor in the Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, United States. Simon A. Levin is Professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, United States. SAL is to whom correspondence should be addressed. E-mail: slevin--AT--princeton.edu
Methods and mechanisms of quorum sensing
Bacteria that use quorum sensing produce and secrete certain signaling compounds (called autoinducers or pheromones), one example of which are N-acyl homoserine lactones (AHL). These bacteria also have a receptor that can specifically detect the AHL (inducer). When the inducer binds the receptor, it activates transcription of certain genes, including those for inducer synthesis. There is a low likelihood of a bacterium detecting its own secreted AHL.
When only a few other bacteria of the same kind are in the vicinity, diffusion reduces the concentration of the inducer in the surrounding medium to almost zero, so the bacteria produce little inducer. With many bacteria of the same kind, the concentration of the inducer passes a threshold, whereupon more inducer is synthesised. This forms a positive feedback loop, and the receptor becomes fully activated. This induces the up regulation of other specific genes, such as luciferase in V. fishcheri. This is useful since a single V. fischeri bacterium that is luminescent would have no evolutionary advantage and would be wasting energy.
In Escherichia coli, AI-2 is produced by the lsr operon, encoding an ABC transporter which imports AI-2 into the cells during the early stationary (latent) phase of growth. AI-2 is then phosphorylated by lsrK and the newly produced phospho-AI-2 can either be internalized or used to suppress lsrR, an inhibitor of the lsr operon (thereby activating the operon). The lsr operon is also thought to be inhibited by dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) through its competitive binding to lsrR. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate has also been shown to inhibit the lsr operon through cAMP-CAPK-mediated inhibition. This explains why when grown with glucose E. coli will lose the ability to internalize AI-2 (because of catabolite repression). When grown normally, AI-2 presence is transient.
A first X-ray structure of a receptor (LuxP) was discovered in Vibrio harveyi in 2002, together with its inducer (AI-2), which is one of the few biomolecules containing boron (Nature 415, 545ff PDF). Autoinducer-2 is conserved among many bacterial species, including Escherichia coli, an enteric bacterium and model organism for Gram negative bacteria. Autoinducer-2 appears to be used for interspecies communication because of this conservation.
References
Citations
Further reading
- Banin, E., M. L. Vasil, and E. P. Greenberg (2005). Iron and Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 11076-81.
- Bassler BL (2006). Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria: a chemical discourse. Harvey Lect. 2004-2005 100: 123-142.
- Bassler BL and Losick R (2006). Bacterially speaking. Cell 125: 237-246.
- Camilli A and Bassler BL (2006). Bacterial small-molecule signaling pathways. Science 311: 1113-1116.
- Kolter, R. and E. P. Greenberg (2006). Microbial sciences: the superficial life of microbes. Nature 441: 300-2.
- Waters CM and Bassler BL (2005). Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21: 319-346.
- Waters CM, Bassler BL (2006). The Vibrio harveyi quorum-sensing system uses shared regulatory components to discriminate between multiple autoinducers. Genes Dev 20: 2754-2767.
- Xavier KB and Bassler BL (2005). Regulation of uptake and processing of the quorum-sensing autoinducer AI-2 in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 187: 238-248.
- Xavier KB and Bassler BL (2005). Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature 437: 750-753.
External links
- The Quorum Sensing Website
- Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. (Infect. Immunol. 68: 4839-4849) Free Full Text 2000
- Cell-to-Cell Communication in Bacteria
- Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University.
de:Quorum sensing es:Quorum sensing ja:クオラムセンシング pl:Quorum sensing
