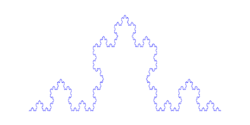
Fractal
In common parlance, fractal, from the Latin fractus,[1] meaning "broken", designates a highly irregular or "infinitely complex" shape that appears detailed and self-similar in some sense at all scales of magnification. Mathematicians avoid giving the strict definition,[2] and use the term fractal to refer to a geometric object that has (most of) the following features
- fine structure at each scale
- no easy description in the language of traditional Euclidean geometry
- self-similarity (at least approximately)
- the Hausdorff dimension greater than the topological dimension
- a relatively simple and recursive definition
- natural appearance (interpreted as "not smooth", "jagged", "with thorns" etc.)
Not all self-similar objects are fractals — for example, the real line (a straight Euclidean line) is formally self-similar but fails to have other fractal characteristics.
Introduction
History
Objects that are now described as fractals were discovered and described centuries ago. Ethnomathematics like Ron Eglash's African Fractals (ISBN 0-8135-2613-2) describes pervasive fractal geometry in indigeneous African craft work. In 1525, the German Artist Albrecht Dürer published The Painter's Manual, in which one section is on "Tile Patterns formed by Pentagons." The Dürer's Pentagon largely resembled the Sierpinski carpet, but based on pentagons instead of squares.
The idea of "recursive self-similarity" was originally developed by the philosopher Leibniz and he even worked out many of the details. In 1872, Karl Weierstrass found an example of a function with the nonintuitive property that it is everywhere continuous but nowhere differentiable — the graph of this function would now be called a fractal. In 1904, Helge von Koch, dissatisfied with Weierstrass's very abstract and analytic definition, gave a more geometric definition of a similar function, which is now called the Koch snowflake. In 1915, Waclaw Sierpinski constructed his triangle and, one year later, his carpet. Actually, these fractals were described as curves, which is hard to realize with the well known modern constructions. The idea of self-similar curves was taken further by Paul Pierre Lévy who, in his 1938 paper Plane or Space Curves and Surfaces Consisting of Parts Similar to the Whole, described a new fractal curve, the Lévy C curve.
Georg Cantor gave examples of subsets of the real line with unusual properties — these Cantor sets are also now recognised as fractals. Iterated functions in the complex plane had been investigated in the late 19th and early 20th centuries by Henri Poincaré, Felix Klein, Pierre Fatou, and Gaston Julia. However, without the aid of modern computer graphics, they lacked the means to visualize the beauty of many of the objects that they had discovered.
In the 1960s, Benoît Mandelbrot started investigating self-similarity in papers such as How Long Is the Coast of Britain? Statistical Self-Similarity and Fractional Dimension. This built on earlier work by Lewis Fry Richardson. In 1975, Mandelbrot coined the word fractal to denote an object whose Hausdorff-Besicovitch dimension is greater than its topological dimension. He illustrated this mathematical definition with striking computer-constructed visualizations. These images captured the popular imagination; many of them were based on recursion, leading to the popular meaning of the term "fractal".
Examples
A relatively simple class of examples is given by the Cantor sets, Sierpinski triangle and carpet, Menger sponge, dragon curve, space-filling curve, Koch curve. Additional examples of fractals include the Lyapunov fractal and the limit sets of Kleinian groups. Fractals can be deterministic (all the above) or stochastic (that is, non-deterministic). For example the trajectories of the Brownian motion in the plane have Hausdorff dimension 2.
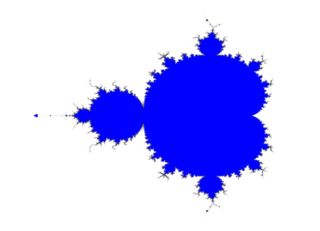
Chaotic dynamical systems are sometimes associated with fractals. Objects in the phase space of a dynamical system can be fractals (see attractor). Objects in the parameter space for a family of systems may be fractal as well. An interesting example is the Mandelbrot set. This set contains whole discs, so it has the Hausdorff dimension equal to its topological dimension of 2 —but what is truly surprising is that the boundary of the Mandelbrot set also has the Hausdorff dimension of 2 (while the topological dimension of 1), a result proved by M. Shishikura in 1991. A closely related fractal is the Julia set.
Hausdorff dimension
The following analysis of the Koch Snowflake suggests how self-similarity can be used to analyze fractal properties.
The total length of a number, N, of small steps, L, is the product NL. Applied to the boundary of the Koch snowflake this gives a boundless length as L approaches zero. But this distinction is not satisfactory, as different Koch snowflakes do have different sizes. A solution is to measure, not in meter, m, nor in square meter, m², but in some other power of a meter, mx. Now 4N(L/3)x = NLx, because a three times shorter steplength requires four times as many steps, as is seen from the figure. Solving that equation gives x = (log 4)/(log 3) ≈ 1.26186. So the unit of measurement of the boundary of the Koch snowflake is approximately m1.26186.
More generally, suppose that a fractal consists of N identical parts that are similar to the entire fractal with the scale factor of L and that the intersection between part is of the Lebesgue measure 0. Then the Hausdorff dimension of the fractal is . For example, the Hausdorf dimension of
- the Cantor set is ,
- the Sierpinski gasket is ,
- the Sierpinski carpet is ,
and so on. Even more generally one may assume that each of N parts is similar to the fractal with a different scale factor , . Then the Hausdorff dimension can be calculated by solving the following equation in the variable s:
Generating fractals
|

|

|
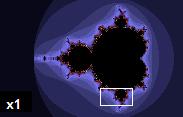
 Even 2000 times magnification of the Mandelbrot set uncovers fine detail resembling the full set. Even 2000 times magnification of the Mandelbrot set uncovers fine detail resembling the full set. |
Three common techniques for generating fractals are:
- Iterated function systems — These have a fixed geometric replacement rule. Cantor set, Sierpinski carpet, Sierpinski gasket, Peano curve, Koch snowflake, Harter-Heighway dragon curve, T-Square, Menger sponge, are some examples of such fractals.
- Escape-time fractals — Fractals defined by a recurrence relation at each point in a space (such as the complex plane). Examples of this type are the Mandelbrot set, the Burning Ship fractal and the Lyapunov fractal.
- Random fractals — Generated by stochastic rather than deterministic processes, for example, fractal landscapes, Lévy flight and the Brownian tree. The latter yields so-called mass- or dendritic fractals, for example, diffusion-limited aggregation or reaction-limited aggregation clusters.
Classification of fractals
Fractals can also be classified according to their self-similarity. There are three types of self-similarity found in fractals:
- Exact self-similarity — This is the strongest type of self-similarity; the fractal appears identical at different scales. Fractals defined by iterated function systems often display exact self-similarity.
- Quasi-self-similarity — This is a loose form of self-similarity; the fractal appears approximately (but not exactly) identical at different scales. Quasi-self-similar fractals contain small copies of the entire fractal in distorted and degenerate forms. Fractals defined by recurrence relations are usually quasi-self-similar but not exactly self-similar.
- Statistical self-similarity — This is the weakest type of self-similarity; the fractal has numerical or statistical measures which are preserved across scales. Most reasonable definitions of "fractal" trivially imply some form of statistical self-similarity. (Fractal dimension itself is a numerical measure which is preserved across scales.) Random fractals are examples of fractals which are statistically self-similar, but neither exactly nor quasi-self-similar.
Fractals in nature
Approximate fractals are easily found in nature. These objects display self-similar structure over an extended, but finite, scale range. Examples include clouds, snow flakes, mountains, river networks, and systems of blood vessels.
Trees and ferns are fractal in nature and can be modeled on a computer by using a recursive algorithm. This recursive nature is obvious in these examples — a branch from a tree or a frond from a fern is a miniature replica of the whole: not identical, but similar in nature.
The surface of a mountain can be modeled on a computer by using a fractal: Start with a triangle in 3D space and connect the central points of each side by line segments, resulting in four triangles. The central points are then randomly moved up or down, within a defined range. The procedure is repeated, decreasing at each iteration the range by half. The recursive nature of the algorithm guarantees that the whole is statistically similar to each detail.
High voltage breakdown within a 4″ block of acrylic creates a fractal Lichtenberg figure.
Fractal branching occurs on a microwave-irradiated DVD
Romanesco cauliflower showing very fine natural fractals
Applications
As described above, random fractals can be used to describe many highly irregular real-world objects. Other applications [1] of fractals include:
- Classification of histopathology slides in medicine
- Generation of new music
- Generation of various art forms
- Signal and image compression
- Seismology
- Computer and video game design, especially computer graphics for organic environments and as part of procedural generation
- Fractography and fracture mechanics
- Fractal antennas — Small size antennas using fractal shapes
- Neo-hippie t-shirts and other fashion.
- Generation of patterns for camouflage, such as MARPAT.
References
- ↑ The term fractal was coined by Benoît Mandelbrot in 1975. From Mandelbrot's Fractal Geometry of Nature: "I coined fractal from the Latin adjective fractus. The corresponding Latin verb frangere means 'to break' to create irregular fragments. It is therefore sensible - and how appropriate for our need! - that, in addition to 'fragmented' (as in fraction or refraction), fractus should also mean 'irregular', both meanings being preserved in fragment."
- ↑ K. Falconer, Techniques in Fractal Geometry, John Willey and Sons, 1997. ISBN 0-471-92287-0