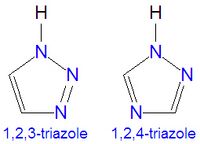
Triazole
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
| |||||||
| triazole | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antifungal drugs and fungicides | ||||||
| Properties: | basic, azole compound | ||||||
| Hazards: | see side effects & drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
The triazoles are two isomers, namely 1,2,3-triazole or 1,2,4-triazole, with the formula C2H3N3. They are aromatic ring compounds that are similar to the azoles pyrazole and imadazole, but they would have an additional nitrogen atom in the ring structure. Like the azoles, triazoles are used in many antifungal drugs and fungicides, and the triazole-based drugs are more selective for fungi than mammalian cells compared to the azole-based antifungal compounds.