Israel
| State of Israel | |
|---|---|
| מדינת ישראל Medīnat Yisrā'el دولة إسرائيل Dawlat Isrā'īl | |

| |
 File:Israel coat of arms.svg File:Israel coat of arms.svg
| |
| National anthem | "Hatikvah" ("The Hope") |
| Capital | Jerusalem [1] Template:Coor dm |
| Largest city | Jerusalem |
| Official language | Hebrew, Arabic |
| Government type | Parliamentary democracy |
| President | Moshe Katsav |
| Prime Minister | Ehud Olmert |
| Area | 22,1451 km² 8,5501 mi² (151th) (~2% % water) |
| Population | 7,026,0002 (98th) (May 2006 estimate) 5,548,523 (1995 census) |
| Population density | 324/km² (34th) 787 mi² |
| GDP (PPP) | Total:$163.45 billion (53rd) Per capita:$23,416 (28th) (2005 estimate) |
| HDI | 0.915 (high) (23rd) (2003) |
| Currency | New Israeli sheqel (₪) (ILS) |
| Time zone | IST (UTC+2) |
| Country codes | Internet TLD : .il Calling code : +972 |
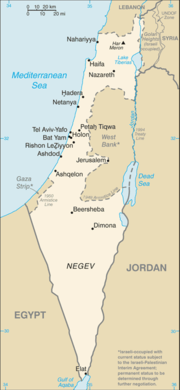
Israel (Hebrew: Template:Audio; Medinat Yisra'el; Template:Lang-ar, Dawlat Isrā'īl), officially the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia on the southeastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea. It is the Middle East's only parliamentary democracy and the nation state of the indigenous people of Eretz Yisrael (Hebrew: ארץ ישראל). As such, it is the world's only Jewish state, though its population includes citizens from many ethnic and religious backgrounds. (See also Israelis.)
Israel is bordered by Lebanon in the north, Syria and Jordan in the east, and Egypt in the south-west. It has a population of over seven million people, in an area of around 22,000 square kilometres (8500 square miles).
Israel has a technologically advanced economy and is ranked 23rd on the 2005 United Nations Human Development Index.
Name
The name "Israel" is rooted in the Hebrew Bible, Genesis 32:28, where Jacob is renamed Israel after successfully wrestling with a mysterious adversary.[2] The biblical nation fathered by Jacob was then called "The Children of Israel" or the "Israelites."
The modern country was named State of Israel, and its citizens are referred to as Israelis in English. Other rejected name proposals included Eretz Israel, Zion, Judea and New Judea.[3] The use of the term Israeli to refer to a citizen of Israel was decided by the Government of Israel in the weeks immediately after independence and announced by Foreign Minister Moshe Shertok.[4]
History
Historical roots
- See also: History of ancient Israel and Judah
The first historical record of the word "Israel" comes from an Egyptian stele documenting military campaigns in Canaan. Although this stele which referred to a people (the determinative for 'country' was absent) is dated to approximately 1211 BCE, [5] Jewish tradition holds that the Land of Israel has been a Jewish Holy Land and Promised land for 3,000 years. The land of Israel holds a special place in Jewish religious obligations, encompassing Judaism's most important sites — including the remains of the First and Second Temples of the Jewish King, Solomon. Connected with these two versions of the temple are religiously significant rites which stand as the origin for many aspects of modern Judaism. [6] Starting around the 11th century BCE the first of a series of Jewish kingdoms and states established intermittent rule over the region that lasted more than a millennium.

Under Assyrian, Babylonian, Persian, Greek, Roman, Byzantine, and (briefly) Sassanian rule, Jewish presence in the region dwindled because of mass expulsions. In particular, the failure of the Bar Kochba Revolt against the Roman Empire in 132 CE resulted in a large-scale expulsion of Jews. It was during this time that the Romans gave the name Syria Palaestina to the geographic area, in an attempt to erase Jewish ties to the land.[7] The Mishnah and Jerusalem Talmud, two of Judaism's most important religious texts, were composed in the region during this period. The Muslims conquered the land from the Byzantine Empire in 638 CE. The area was ruled by various Muslim states (interrupted by the rule of the Crusaders) before becoming part of the Ottoman Empire in 1517.
Zionism and Immigration
Waves of immigration occurred during the centuries. For example, in the years 1209-1211, the "aliyah of the Rabbis of France and England" to Acre became famous as in 1258 and 1266. Waves of Rabbinical students occurred in 1808 - 1809, who settled in Tiberias, Safed and then in Jerusalem.
Small waves of modern immigration occurred during the 18th and the 19th century out of religious motives. In 1860, the old Jewish community in Jerusalem started building neighborhoods outside the walls of the Old City. In 1878, the first modern agricultural settlement was founded in the form of Petah Tikva.
The first big wave of modern immigration to Israel, or Aliyah (עלייה) started in 1881 as Jews fled growing persecution, or followed the Socialist Zionist ideas of Moses Hess and others of "redemption of the soil." Jews bought land from Ottoman and individual Arab landholders. After Jews established agricultural settlements, tensions erupted between the Jews and Arabs.
Theodor Herzl (1860 – 1904), an Austrian Jew, founded the Zionist movement. In 1896, he published Der Judenstaat (The Jewish State), in which he called for the establishment of a national Jewish state. The following year he helped convene the first World Zionist Congress.
The establishment of Zionism led to the Second Aliyah (1904 – 1914) with the influx of around 40,000 Jews. In 1917, the British Foreign Secretary Arthur J. Balfour issued the Balfour Declaration that "view[ed] with favour the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people." In 1920, Palestine became a League of Nations mandate administered by Britain.
Jewish immigration resumed in third (1919 – 1923) and fourth (1924 – 1929) waves after World War I. A massacre of Jews by Arabs in 1929 killed 133 Jews, including 67 in Hebron.
The rise of Nazism in 1933 led to a fifth wave of Aliyah. The Jews in the region increased from 11% of the population in 1922 to 30% by 1940Template:Fact. 28% of the land was already bought and owned by Zionist organizations plus additional private land owned by JewsTemplate:Fact. The southern half of the country is the barren and mostly empty Negev desert. The subsequent Holocaust in Europe led to additional immigration from other parts of Europe. By the end of World War II, the number of Jews in Palestine was approximately 600,000.
In 1939, the British introduced a White Paper of 1939, which limited Jewish immigration over the course of the war to 75,000 and restricted purchase of land by Jews, perhaps in response to the Great Arab Uprising (1936-1939). The White Paper was seen as a betrayal by the Jewish community and Zionists, who perceived it as being in conflict with the Balfour Declaration of 1917. The Arabs were not entirely satisfied either, as they wanted Jewish immigration halted completely. However, the White Paper guided British policy until the end of the term of their Mandate. As a result, many Jews fleeing to Palestine to avoid Nazi persecution and the Holocaust were intercepted and returned to Europe. Two specific examples of this policy involved the ships Struma and Exodus. [3] These attempts by Jews to circumvent the blockade and flee Europe became known as Aliya Beth.
Jewish Underground groups
As tensions grew between the Jewish and Arab populations, and with little apparent support from the British Mandate authorities, the Jewish community began to rely on itself for defense.
Arab nationalists, opposed to the Balfour declaration, the mandate, and the Jewish National Home, instigated riots and pogroms against Jews in Jerusalem, Hebron, Jaffa, and Haifa. As a result of the 1921 Arab attacks, the Haganah was formed to protect Jewish settlements. The Haganah was mostly defensive in nature, which among other things caused several members to split off and form the militant group Irgun (initially known as Hagana Bet) in 1931. The Irgun adhered to a much more active approach, which included attacks and initiation of armed actions against the British, such as attacking British military headquarters, the King David Hotel, which killed 91 people. Haganah, on the other hand, often preferred restraint. A further split occurred when Avraham Stern left the Irgun to form Lehi, (also known as the Stern Gang) which was much more extreme in its methods. Unlike the Irgun, they refused any co-operation with the British during World War II and even attempted to work with the Nazis to secure European Jewry's emigration to Israel.
These groups had an enormous impact on events and procedures in the period preceding the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, such as Aliya Beth — the clandestine immigration from Europe, the forming of the Israel Defense Forces, and the withdrawal of the British, as well as to a great degree forming the foundation of the political parties which exist in Israel today.
Establishment of the State

In 1947, following increasing levels of violence together with unsuccessful efforts to reconcile the Jewish and Arab populations, the British government decided to withdraw from the Palestine Mandate. The UN General Assembly approved the 1947 UN Partition Plan dividing the territory into two states, with the Jewish area consisting of roughly 55% of the land, and the Arab area roughly 45%. Jerusalem was planned to be an international region administered by the UN to avoid conflict over its status.
Immediately following the adoption of the Partition Plan by the UN General Assembly on November 29, 1947, David Ben-Gurion tentatively accepted the partition, while the Arab League rejected it. Scattered attacks on civilians of both sides soon turned into widespread fighting between Arabs and Jews, this civil war being the first "phase" of the 1948 War of Independence.
The State of Israel was proclaimed on May 14 1948, one day before the expiry of the Palestine Mandate.
Israel was admitted as a member of the United Nations on May 11, 1949.
War of Independence and migration
- See also: Jewish refugees, Palestinian refugee, Palestinian exodus, and Arab-Israeli conflict
Following the State of Israel's establishment, the armies of Egypt, Syria, Jordan, Lebanon, and Iraq joined the fighting and began the second phase of the 1948 Arab – Israeli War. From the north, Syria, Lebanon, and Iraq, were all but stopped relatively close to the borders. Jordanian forces, invading from the east, captured East Jerusalem and laid siege on the city's west. However, forces of the Haganah successfully stopped most invading forces, and Irgun forces halted Egyptian encroachment from the south. At the beginning of June, the UN declared a one-month ceasefire during which the Israel Defense Forces were officially formed. After numerous months of war, a ceasefire was declared in 1949 and temporary borders, known as the Green Line, were instituted. Israel had gained an additional 26% of the Mandate territory west of the Jordan River. Jordan, for its part, held the large mountainous areas of Judea and Samaria, which became known as the West Bank. Egypt took control of a small strip of land along the coast, which became known as the Gaza Strip.
During and after the war, then Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion set about establishing order by dismantling the Palmach and underground organizations like the Irgun and Lehi. Those two groups were classified as terror organizations after the murder of Folke Bernadotte, a Swedish diplomat.
Large numbers of the Arab population fled the newly-created Jewish State during the Palestinian exodus, which is referred to by many Palestinian groups and individuals as the Nakba (Arabic: النكبة), meaning "disaster" or "cataclysm". Many historians suggest that the Palestinians fled because of orders from Arab generals. Many Palestinians left under the belief that the Arab armies would prevail and they would return.[8] Moreover, Israel offered — in the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel — to the Arab inhabitants of the State of Israel the full and equal citizenship and due representation in all its provisional and permanent institutions, but many refused.
Estimates of the final refugee count range from 600,000 to 900,000 with the official United Nations count at 711,000.[9] The continuing conflict between Israel and the Arab world resulted in a lasting displacement that persists to this day.
Immigration of Holocaust survivors and Jewish refugees from Arab lands doubled Israel's population within a year of independence. Over the following years approximately 850,000 Sephardi and Mizrahi Jews fled or were expelled from surrounding Arab countries and Iran. Of these, about 600,000 settled in Israel; the remainder went to Europe and the Americas. See: Jewish exodus from Arab lands
1950s and 1960s
Between 1954 and 1955, under Moshe Sharett as prime minister, the Lavon Affair, a failed attempt to bomb targets in Egypt, caused political disgrace in Israel. Compounding this, in 1956, Egypt nationalized the Suez Canal, much to the chagrin of the United Kingdom and France. Following this and a series of Fedayeen attacks, Israel created a secret military alliance with those two European powers and declared war on Egypt. After the Suez Crisis, the three collaborators faced international condemnation, and Israel was forced to withdraw its forces from the Sinai Peninsula.
In 1955, Ben-Gurion once again became prime minister and served as such until his final resignation in 1963. After Ben-Gurion's resignation, Levi Eshkol was appointed to the post.
In 1961, the Nazi war criminal Adolf Eichmann, who had been largely responsible for the Final Solution, the planned extermination of the Jews of Europe, was captured in Buenos Aires, Argentina, and brought to trial in Israel. Eichmann became the only person ever sentenced to death by the Israeli courts.
On the political field, tensions once again arose between Israel and her neighbors in May 1967. Syria, Jordan, and Egypt had been hinting at war, and Egypt expelled UN Peacekeeping Forces from the Gaza Strip. When Egypt closed the strategic Straits of Tiran to Israeli vessels, Israel deemed it a casus belli for pre-emptively attacking Egypt on June 5. After the ensuing Six-Day War between Israel and its Arab neighbors, the Jewish State emerged triumphant. Israel had defeated the armies of three large Arab states and decimated their air forces. Territorially, Israel conquered the West Bank, Gaza Strip, Sinai Peninsula, and Golan Heights. The Green Line of 1949 became the administrative boundary between Israel and her Occupied Territories, also called Disputed Territories. However, Israel has spread its administrative domain to East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights. The Sinai was later returned to Egypt following the signing of a peace treaty.
In 1967 Israeli aircraft attacked the USS Liberty, killing 34 American servicemen. American and Israeli investigations into the incident concluded that the attack was a tragic accident involving confusion over the identity of the Liberty.
In 1969 Golda Meir, Israel's first and, to date, only female prime minister was elected.
- See also: Positions on Jerusalem, Jerusalem Law, Golan Heights, and Israeli-occupied territories
1970s
Between 1968 and 1972, a period known as the War of Attrition, numerous scuffles erupted along the border between Israel and Syria and Egypt. Furthermore, in the early-1970s, Palestinian groups embarked on an unprecedented wave of attacks against Israel and Jewish targets in other countries. The climax of this wave occurred at the 1972 Munich Olympic Games, when, in the Munich massacre, Palestinian militants held hostage and killed members of the Israeli delegation. Israel responded with Operation Wrath of God, in which agents of Mossad assassinated most of those who were involved in the massacre.
Finally, on October 6 1973, on the Jewish fast day of Yom Kippur, the Egyptian and Syrian armies launched a surprise attack against Israel. However, despite early successes against an unprepared Israeli army, Egypt and Syria failed to accomplish their goal of regaining the territories lost in 1967. Yet after the war, a number of years of relative calm ensued, which fostered the environment in which Israel and Egypt could make peace.
In 1974, Yitzhak Rabin, with Meir's resignation, became Israel's fifth prime minister. Then, in the 1977 Knesset elections, the Ma'arach, the ruling party since 1948, created a storm by leaving the government. The new Likud party, led by Menachem Begin, became the new ruling party.
Then, in November of that year, Egyptian President Anwar Sadat, making a historic visit to the Jewish State, spoke before the Knesset — the first recognition of Israel by its Arab neighbors. Following the visit, the two nations conducted negotiations which led to the signing of the Camp David Accords. In March 1979, Begin and Sadat signed the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty in Washington, DC. As laid out in the treaty, Israel withdrew from the Sinai Peninsula and evacuated the settlements established there during the 1970s. It was also agreed to lend autonomy to Palestinians across the Green Line.
- See also: War of Attrition, Munich Massacre, Yom Kippur War, Anwar Sadat, and Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty
1980s
On July 7 1981, the Israeli Air Force bombed the Iraqi nuclear reactor at Osiraq in an attempt to foil Iraqi efforts at producing an atomic bomb. This operation was known as Operation Opera.
In 1982, Israel launched an attack against Lebanon, which had been embroiled in the Lebanese Civil War since 1975. The official reason for the attack was to defend Israel's northernmost settlements from terrorist attacks, which had been occurring frequently. However, after establishing a forty-kilometer barrier zone, the IDF continued northward and even captured the capital, Beirut. Israeli forces expelled Palestinian Liberation Organization forces from the country, forcing the organization to relocate to Tunis. Unable to deal with the stress of the ongoing war, Prime Minister Begin resigned from his post in 1983 and was replaced by Yitzhak Shamir. Though Israel withdrew from most of Lebanon in 1986, a buffer zone was maintained until May 2000 when Israel unilaterally withdrew from Lebanon.
The rest of the 1980s were spent constantly shifting from the right, led by Yitzhak Shamir, to the left under Shimon Peres. Peres, for example, was prime minister from 1984, but handed the position over to Shamir in 1986. The First Intifadah then broke out in 1987 and was accompanied by waves of violence in the Occupied Territories. Following the outbreak, Shamir once again was elected prime minister, in 1988.
- See also: 1982 Lebanon War, Lebanese Civil War, and PLO
1990s
During the Gulf War, Iraq hit Israel with 39 Scud missiles, even though Israel was not a member of the coalition and was not involved in the fighting. The missles didn't kill Israeli citizens directly, but there were some deaths from wrong use of the gas masks provided, one Israeli died from a heart attack following a hit, and one Israeli died from a Patriot missile hit. During the war, Israel also provided gas masks for the Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza. [10] The PLO however supported Saddam Hussein. [11] Palestinians in the West Bank and Gaza marched and famously stood on their rooftops while Skads were falling and cheered Saddam Hussein calling for him to bomb Israel with chemical weapons [12] [13] [14]. Ultimately, Palestinians also used the gas masks against Israeli use of tear gas in the coming years. [15]
The early 1990s were marked by the beginning of a massive immigration of Soviet Jews, who, according to the Law of Return, were entitled to become Israeli citizens upon arrival. About 380,000 arrived in 1990-91 alone. Although initially favouring the right, the new immigrants became the target of an aggressive election campaign by Labor, which blamed their employment and housing problems on the ruling Likud. As a result, in the 1992 elections the immigrants voted en masse for Labor, letting the left achieve a 61-59 majority in the 1992 Knesset elections.
Following the elections, Yitzhak Rabin became prime minister, forming a left-wing government coalition. During the election campaign his Labor party promised Israelis a significant improvement in personal security and achievement of a comprehensive peace with the Arabs "within six to nine months" after the elections. By the end of 1993 the government abandoned the framework of Madrid and signed the Oslo Accords with the PLO. In 1994, Jordan became the second of Israel's neighbours to make peace with it.
The initial wide public support for the Oslo Accords began to wane as Israel was struck by an unprecedented wave of attacks supported by the militant Hamas group, which opposed the accords. Public support slipped even further. On November 4, 1995, a Jewish nationalist militant named Yigal Amir assassinated Rabin.
Public dismay with the assassination created a backlash against Oslo opponents and significantly boosted the chances of Shimon Peres, Rabin's successor and Oslo architect, to win the upcoming 1996 elections. However, a new wave of suicide bombings combined with Arafat's statements extolling the Muslim nationalist militant Yahya Ayyash, made the public mood swing once again and in May 1996 Peres narrowly lost to his challenger from Likud, Benjamin Netanyahu.
Although seen as a hard-liner opposing the Oslo Accords, Netanyahu withdrew from Hebron and signed the Wye River Memorandum giving wider control to the Palestinian National Authority. During Netanyahu's tenure, Israel experienced a lull in attacks against Israel's civilian population by Palestinian groups, but his government fell in 1999. Labor's Ehud Barak beat Netanyahu by a wide margin in the 1999 elections and succeeded him as prime minister.
- See also: Israel-Jordan Treaty of Peace
2000s
Template:Current-section Template:Sectfact
Barak initiated unilateral withdrawal from Lebanon in 2000. This process was intended to frustrate Hezbollah attacks on Israel by forcing them to cross Israel's border. Barak and Yassir Arafat once again conducted negotiations with President Clinton at the July 2000 Camp David summit. However, the talks failed. Barak offered to form a Palestinian State initially on 73% of the West Bank and 100% of the Gaza Strip. In ten to 25 years, the West Bank area would expand to 90% (94% excluding greater Jerusalem). [4] [5]
After the collapse of the talks, Palestinians began a second uprising, known as the Al-Aqsa Intifadah, just after the leader of the opposition Ariel Sharon visited the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. The failure of the talks and the outbreak of a new war caused many Israelis on both the right and the left to turn away from Barak, and also discredited the peace movement.
Ariel Sharon became the new prime minister in March 2001 and consequently was re-elected, along with his Likud party in the Knesset elections of 2003. Sharon initiated a plan to unilaterally withdraw from the Gaza Strip. This disengagement was executed between August and September 2005.
Israel also is building a West Bank Barrier to defend the country from attacks by Palestinian armed groups. The barrier, which is planned to measure 681 kilometers, meanders past the Green Line and effectively annexes 9.5% of the West Bank.[16] The barrier has been met with some criticism from the international community and numerous protest demonstrations by the Israeli left.
After Ariel Sharon suffered a severe hemorrhagic stroke, the powers of the office were passed to Ehud Olmert, who was designated the "Acting" Prime Minister. On April 14, 2006, Olmert was elected Prime Minister after his party, Kadima, Hebrew for "forward," won the most seats in the 2006 legislative elections.
On June 28, 2006, Hamas militants dug a tunnel under the border from the Gaza Strip and attacked an IDF post, capturing an Israeli soldier and killing two others. In response, Israel began Operation Summer Rains, which consisted of heavy bombardment of Hamas targets as well as bridges, roads, and the only power station in Gaza. Israel has also deployed troops into the territory. Israel’s critics have accused it of disproportionate use of force and collective punishment of innocent civilians and not giving diplomacy a chance. Israel argues that they have no other option to get their soldier back and put an end to the rocket attacks into Israel.
The 2006 Israel-Lebanon conflict refers to the military conflict in Lebanon and northern Israel, primarily between Hezbollah and Israel, which started on 12 July 2006. The conflict began with a cross-border Hezbollah raid and shelling, which resulted in the capture of two and killing of three Israeli soldiers. Israel held the Lebanese government responsible for the attack, as it was carried out from Lebanese territory, and initiated an air and naval blockade, airstrikes across much of the country, and ground incursions into southern Lebanon. Hezbollah continuously launched rocket attacks into northern Israel and engaged the Israeli Army on the ground with hit-and-run guerrilla attacks. A ceasefire came into effect at 05:00 UTC, 14 August 2006, although violations of the ceasefire have occurred from both sides. The conflict killed over 1000 Lebanese civilians[17], 440 Hezbollah militants[18], and 119 Israeli soldiers[19], as well as 44 Israeli civilians[19], and caused massive damage to the civilian infrastructure and cities of Lebanon and damaged thousands of buildings across northern Israel, many of which were completely destroyed.[20] [21] [22]
Geography and Climate
Israel is bordered by Lebanon in the north, Syria and Jordan in the east, and Egypt in the south-west. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean in the west and the Gulf of Eilat (also known as the Gulf of Aqaba) in the south.
During the Six-Day War of 1967, Israel captured the West Bank from the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, the Golan Heights from Syria, Gaza Strip (which was under Egyptian occupation), and Sinai from Egypt. It withdrew all troops and settlers from Sinai by 1982 and from the Gaza Strip by September 12 2005. The future status of the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights remains to be determined.
The sovereign territory of Israel — excluding all territories captured by Israel in 1967 — is 20,770 km² or 8,019 mi² in area. (1% is water). The total area under Israeli law — including East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights — is 22,145 km² or 8,550 mi²; with a little less than one per cent being water. It should be noted however that UN resolution 497 states the application of Israeli law to the Golan Heights is "null and void and without international legal effect". The total area under Israeli control — including the military-controlled and Palestinian-governed territory of the West Bank — is 28,023 km² or 10,820 mi² (~1% water).
The climate of the coastal areas can be very different from that of the mountainous areas, particularly during the winter months. The high mountains in the north, like Mount Hermon in the Golan Heights, can get cold, wet and often snowy and even Jerusalem experiences snow spells every couple of years. The coastal regions, where Tel Aviv and Haifa are located, have a typical Mediterranean climate with cool, rainy winters and hot, dry summers.

Metropolitan areas
- See also: Districts of Israel and List of cities in Israel
As of 2006, The Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics defines three metropolitan areas: Tel Aviv (population 3 million), Haifa (population 980,600) and Jerusalem, the Capital (population 706,368).
Government
Template:Morepolitics Israel is a democratic republic with universal suffrage that operates under the parliamentary system.
Legislature

Israel's unicameral legislative branch is a 120-member parliament known as the Knesset. Membership in the Knesset is allocated to parties based on their proportion of the vote, via a proportional representation voting system. Elections to the Knesset are normally held every four years, but the Knesset can decide to dissolve itself ahead of time by a simple majority, known as a vote of no-confidence. Twelve parties currently hold seats.
- See also: List of political parties in Israel
Executive
The President of Israel is Head of State, serving as a largely ceremonial figurehead. The President selects the leader of the majority party or ruling coalition in the Knesset as the Prime Minister, who serves as head of government.[23]
Constitution and legal system
Israel has not completed a written constitution. Its government functions according to the laws of the Knesset, especially the "Basic Laws of Israel" (currently there are 14). These are slated to become the foundation of a future official constitution. In mid-2003, the Knesset's Constitution, Law, and Justice Committee began drafting an official constitution. The effort is still underway as of early 2006. [24]
Israel's legal system mixes influences from Anglo-American, Continental and Jewish law, as well as the declaration of the State of Israel.
As in Anglo-American law, the Israeli legal system is based on the principle of stare decisis (precedent). It is an adversarial system, not an inquisitorial one, in the sense that the parties (for example, plaintiff and defendant) are the ones that bring the evidence before the court. The court does not conduct any independent investigation on the case.
As in Continental legal systems, the jury system was not adopted in Israel. Court cases are decided by professional judges. Additional Continental Law influences can be found in the fact that several major Israeli statutes (such as the Contract Law) are based on Civil Law principles. Israeli statute body is not comprised of Codes, but of individual statutes. However, a Civil Code draft has been completed recently, and is planned to become a bill.
Religious tribunals (Jewish, Sharia'a, Druze and Christian) have exclusive jurisdiction on annulment of marriages.
Judiciary

Israel's Judiciary branch is made of a three-tier system of courts. At the lowest level are Magistrate Courts, situated in most cities. Above them are District Courts, serving both as appellate courts and as courts of first instance, situated in five cities: Jerusalem, Tel Aviv, Haifa, Be'er Sheva and Nazareth.
At the top of the judicial pyramid is the Supreme Court of Israel seated in Jerusalem. The current Chief Justice of the Supreme Court is Aharon Barak. The Supreme Court serves a dual role as the highest court of appeals and as the body for a separate institution known as the High Court of Justice (HCOJ). The HCOJ has the unique responsibility of addressing petitions presented to the Court by individual citizens. The respondents to these petitions are usually governmental agencies (including the Israel Defense Forces). The result of such petitions, which are decided by the HCOJ, may be an instruction by the HCOJ to the relevant Governmental agency to act in a manner prescribed by the HCOJ.
A committee composed of Knesset members, Supreme Court Justices, and Israeli Bar members carries out the election of judges. The Courts Law requires judges to retire at the age of seventy. The Chief Justice of the Supreme Court, with the approval of the Minister of Justice, appoints registrars to all courts.
Israel is not a member of the International Criminal Court as it fears it could lead to prosecution of Israeli settlers in the occupied territories.
Military
Israel's military consists of a unified Israel Defense Forces (IDF), known in Hebrew by the acronym Tzahal (צה"ל). Historically, there have been no separate Israeli military services. The Navy and Air Force are subordinate to the Army. There are other paramilitary agencies that deal with different aspects of Israel's security (such as Magav and Shin Bet). The IDF was based on paramilitary underground armies, chiefly Haganah.
The IDF is one of the best funded military forces in the Middle East and ranks among the most battle-trained armed forces in the world, having been involved in five major wars and numerous border conflicts. In terms of personnel, the IDF's main resource is the training quality of its soldiers and expert institutions, rather than sheer numbers of soldiers. It also relies heavily on high-tech weapons systems, some developed and manufactured in Israel for its specific needs, and others imported (largely from the United States).
Most Israelis (males and females) are drafted into the military at age 18. Exceptions are Israeli Arabs, those who cannot serve because of injury or disability, women who declare themselves married, or those who are religiously observant. Compulsory service is three years for men, and two years for women. Circassians and Bedouin also actively enlist in the IDF. Since 1956, Druze men have been conscripted in the same way as Jewish men, at the request of the Druze community. Men studying full-time in religious institutions can get a deferment from conscription. Most Haredi Jews extend these deferments until they are too old to be conscripted, a practice that has fueled much controversy in Israel.
Following compulsory service, Israeli men become part of the IDF reserve forces, and are usually required to serve several weeks every year as reservists until their 40s.
Nuclear Capability
There is much speculation regarding the nuclear capabilities of Israel. Since the middle of the 20th century, the Negev Nuclear Research Center has been operational and capable of producing weapons grade nuclear material. This site has never been under the watch of the International Atomic Energy Agency, so it is therefore widely believed that Israel has a large stockpile of nuclear weapons. The IAEA has stated outright that it believes Israel "to be a state possessing nuclear weapons," but the Israeli government has never confirmed or denied this assertion. Although size of nuclear arsenal is debated, it is generally accepted that Israel possesses more than one hundred devices. Israel has not ratified the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty.
The supposed number of stationary nuclear weapons in 2002 is 200 (compared with 190 in Great Britain). [25]
Data on Israeli nuclear deployment capability is much more freely available than hard data on their nuclear program. Israel leads the Middle East in medium-range ballistic missile development. The Jericho series of ballistic missile was begun in the 1970s, with three major designs built to date; Jericho I, II, and III. The Jericho II series has been in service since the mid 1980s and has a confirmed range of 1500 km. The latest missile design, the Jericho III, has a conservative range estimate of 4500 km.
In addition to ballistic missile technology, Israel maintains a fleet of Dolphin class submarines capable of carrying nuclear munitions.
Economy
Israel has a technologically advanced market economy with substantial government participation. It depends on imports of fossil fuels (crude oil, natural gas, and coal), grains, beef, raw materials, and military equipment. Despite limited natural resources, Israel has intensively developed its agricultural and industrial sectors over the past 20 years. Israel is largely self-sufficient in food production except for grains and beef. Diamonds, high technology, military equipment, software, pharmaceuticals, fine chemicals, and agricultural products (fruits, vegetables and flowers) are leading exports. Israel usually posts sizable current account deficits, which are covered by large transfer payments from abroad and by foreign loans (although some economists would say the deficit is a sign of Israel's advancing markets). Israel possesses extensive facilities for oil refining, diamond polishing, and semiconductor fabrication.
Roughly half of the government's external debt is owed to the United States, which is its major source of economic and military aid. A relatively large fraction of Israel's external debt is held by individual investors, via the Israel Bonds program. The combination of American loan guarantees and direct sales to individual investors, allow the state to borrow at competitive and sometimes below-market rates.
The influx of Jewish immigrants from the former USSR topped 750,000 during the period 1989 – 1999, bringing the population of Israel from the former Soviet Union to one million, one-sixth of the total population, and adding scientific and professional expertise of substantial value for the economy's future. The influx, coupled with the opening of new markets at the end of the Cold War, energized Israel's economy, which grew rapidly in the early 1990s. But growth began slowing in 1996 when the government imposed tighter fiscal and monetary policies and the immigration bonus petered out. Those policies brought inflation down to record low levels in 1999.
Twenty-four percent of Israel's workforce holds university degrees - ranking third in the industrialized world, after the U.S. and Netherlands - and 12 percent hold advanced degrees.[26]
The important diamond industry has been affected by changing industry conditions and shifts of certain industry activities to the Far East.
As Israel has liberalized its economy and reduced taxes and spending, the gap between the rich and poor has grown. As of 2005, 20.5% of Israeli families (and 34% of Israeli children) are living below the poverty line, though around 40% of those are lifted above the poverty line through transfer payments.Template:Fact
Israel's GDP per capita, as of 28 July, 2005, was $20,551.20 per person (42nd in the world). Israel's overall productivity was $54,510.40, and the amount of patents granted was 74/1,000,000 people.
As of May 2006 average monthly wages per employee were: 7,333 shekels or 1,655 USD. Percent of unemployed persons - first quarter 2006: 8.7%
Science and technology
Israeli contributions to science and technology have been significant. Since the establishment of the State of Israel, Israel has worked in science and engineering. Israeli scientists have contributed in the areas of genetics, computer sciences, electronics, optics, engineering and other high-tech industries. Israeli science is well known for its military technology. Israel has pioneered in advanced agricultural technology. Israel has a high reputation in theoretical physics and is also known for its well-developed and revolutionary medicine.
Four Israelis have won science Nobel Prizes. Biologists Avram Hershko and Aaron Ciechanover of the Technion shared the Chemistry prize in 2004. Israeli-American psychologist Daniel Kahneman had previously won the 2002 prize in Economics. In 2005 Robert Aumann from The Hebrew University also won the prize in Economics.
High technology industries have taken a pre-eminent role in the economy, particularly in the last decade. Israel’s limited natural resources and strong emphasis on education have also played key roles in directing industry towards high technology fields. As a result of the country’s success in developing cutting edge technologies in software, communications and the life sciences, Israel is frequently referred to as a second Silicon Valley. Israel (as of 2004) receives more venture capital investment than any country of Europe, and has the largest VC/GDP rate in the world, seven times that of the United States. Israel has the largest number of startup companies in the world after the U.S. Outside the U.S. and Canada, Israel has the largest number of NASDAQ listed companies. Israel also has the highest percentage in the world of home computers per Capita.
Israel produces more scientific papers per capita than any other nation - 109 per 10,000 people.[27] It also boasts one of the highest per capita rates of patents filed.
Israel is ranked 3rd in Research and development spending, 8th in technological readiness (companies spending on R&D, the creativity of its scientific community, personal computer and internet penetration rates), 11th in innovation, 16th in High technology exports, 17th in technological achievement in Nation Master's list of countries in the world by economy standards.

Tourism
Another leading industry is tourism, which benefits from the plethora of important historical sites for Judaism and Christianity and from Israel’s warm climate and access to water resources. Tourism in Israel includes a rich variety of historical and religious sites in the Holy Land, as well as modern beach resorts, archaeological tourism, heritage tourism and ecotourism. See also Template:Wikitravel.
Population
Demographics
According to Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics, as of May 2006, of Israel's 7 million people, 77% were Jews, 18.5% Arabs, and 4.3% "others".[28] Among Jews, 68% were Sabras (Israeli-born), mostly second- or third-generation Israelis, and the rest are olim — 22% from Europe and the Americas, and 10% from Asia and Africa, including the Arab countries. [29]
Israel has two official languages; Hebrew and Arabic. Hebrew is the major and primary language of the state and is spoken by the majority of the population. Arabic is spoken by the Arab minority and by some members of the Mizrahi Jewish community. English is studied in school and is spoken by the majority of the population as a second language. Other languages spoken in Israel include Russian, Yiddish, Ladino, Romanian, Polish, French, Italian, Dutch, German, Amharic and Persian. American and European popular television shows are commonly presented. Newspapers can be found in all languages listed above as well as others.
As of 2004, 224,200 Israeli citizens lived in the West Bank in numerous Israeli settlements, (including towns such as Ma'ale Adummim and Ariel, and a handful of communities that were present long before the 1948 Arab-Israeli War and were re-established after the Six-Day War such as Hebron and Gush Etzion). Around 180,000 Israelis lived in East Jerusalem, [30] which came under Israeli law following its capture from Jordan during the Six-Day War. About 8,500 Israelis lived in settlements built in the Gaza Strip, prior to their forcible removal by the government in the summer of 2005 as part of Israel's unilateral disengagement plan.
Culture of Israel
The culture of Israel is inseparable from long history of Judaism and Jewish history which preceded it.
Tel Aviv, Haifa, Herzliyyāh, and Jerusalem have excellent art museums, and many towns and kibbutzim have smaller high-quality museums. The Israel Museum in Jerusalem houses the Dead Sea Scrolls along with an extensive collection of Jewish religious and folk art. The Museum of the Diaspora is located on the campus of Tel Aviv University.
Israel has artist colonies in Safed, Jaffa, and Ein Hod.
Of the three major repertory companies, the most famous, Habima Theater, was founded in 1917.
- See also: Archaeology of Israel, Israel Antiquities Authority, Jewish cuisine, Israeli wine, and Kibbutz
Sports
Sports in Israel, as in other countries, are an important part of the national culture. The Israeli sporting culture is much like that of European countries. Israeli athletics go back as far as before the establishment of the state of Israel. While football (soccer) and basketball are considered the most popular sports in Israel, the nation has reached many achievements in other sports, such as handball and athletics, and Israelis are also involved in hockey, rugby and a wide variety of other athletic activities.
Israel has won 6 olympic medals so far.
Literature
Israeli literature is mostly written in Hebrew and the history of Israeli literature is mostly the product of the revival of the Hebrew language as a spoken language in modern times. Since the middle of the nineteenth century, the Hebrew language was increasingly used for speaking as well as writing modern forms of prose, poetry and drama. Every year thousands of new books are published in Hebrew and most of them are original to the Hebrew language.
Shmuel Yosef Agnon won the Nobel Prize in literature in 1966.
Music
The Israeli music is very versatile and combines elements of both western and eastern music. It tends to be very eclectic and contains a wide variety of influences from the Diaspora and more modern cultural importation. Hassidic songs, Asian and Arab pop, especially Yemenite singers, and hip hop or heavy metal.
The National/folk songs are very canonical and often deal with Zionist hopes and dreams and glorify the life of idealistic Jewish youth who intend on building a home and defending their homeland.
Israel is well known for its famous classical orchestras and the Israeli Philharmonic Orchestra under the management of Zubin Mehta has a worldwide reputation. Dudu Fisher, Itzhak Perlman and Pinchas Zukerman are some of the more renowned classical musicians from Israel.
Music styles popular in Israel include Pop, Rock, Heavy Metal, Hip hop and rap, Trance (especially Goa trance and psychedelic trance), Oriental Mizrahi music and Ethnic music.
Israel has won the Eurovision Song Contest 3 times.
- See also: Hatikvah
Religion in Israel
According to Israel's Central Bureau of Statistics, at the end of 2005, 76% of Israelis were Jews by religion (Judaism), 19.7% were Arabs (including Muslims, Christians and Druze) and the remaining 4.3% "others" (including mostly family members of FSU immigrants and some ethnic Jews which were not classified by religion, as well as non-Arab Christians) . [28]
Roughly 12% of Israeli Jews defined as haredim (ultra-orthodox religious); an additional 9% are "religious"; 35% consider themselves "traditionalists" (not strictly adhering to Jewish Halakha); and 43% are "secular" (termed "hiloni"). Among the seculars, 53% believe in God. However, 78% of all Israelis participate in a Passover seder. [31]
Israelis tend not to align themselves with a movement of Judaism (such as Reform Judaism or Conservative Judaism) but instead tend to define their religious affiliation by degree of their religious practice.
Among Arab Israelis, 82.6% were Muslim, 8.8% were Christian and 8.4% were Druze. [28]
- See also: Holidays and events in Israel
The Baha'i world centre, which includes the Universal House of Justice, in Haifa attracts pilgrimage from all over the world. [32] Apart from a few hundred staff, Baha'is do not live in Israel.
Human rights
Template:POV-section
The Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel proclaimed that the state "...will foster the development of the country for the benefit of all its inhabitants; it will be based on freedom, justice and peace as envisaged by the prophets of Israel; it will ensure complete equality of social and political rights to all its inhabitants irrespective of religion, race or sex; it will guarantee freedom of religion, conscience, language, education and culture; it will safeguard the Holy Places of all religions; and it will be faithful to the principles of the Charter of the United Nations."[33] However, like many democracies, Israel often struggles with issues of minority rights, especially when it comes to the often contentious issues surrouinding the treatment of Israel's large Arab minority, which constitutes 15% of Israel's population.[34][35]
Various countries, international bodies, non-governmental organizations and individuals have evaluated and often criticized Israel's human rights record, often in relation to the ongoing Arab-Israeli conflict and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Groups such as Amnesty International[36] and Human Rights Watch[37] are highly critical of Israel's policies. In turn, these groups were accused of anti-Israel bias: in the AI, in the HRW. According to 2005 US Department of State report on Israel, "The government generally respected the human rights of its citizens; however, there were problems in some areas..." [38] In 2006, the Freedom House rated political rights in Israel as "1" (1 representing the most free and 7 the least free rating), civil liberties as "2" and gave it the freedom rating of "Free". Other areas, controlled by Israel through military occupation but not considered with the country's main territory were rated as "6", "5", and "Not Free." [39]
Within Israel, policies of its government are often subjected to criticism by its press (the only country ranked "Free" (28 on the scale 1-100) in the region in 2005 by Freedom House[40]) as well as a vast variety of political, human rights and watchdog groups such as Association for Civil Rights in Israel, B'Tselem, Machsom Watch, Women in Black, Women for Israel's Tomorrow, among others. According to the Reporters Without Borders, "The Israeli media were once again in 2005 the only ones in the region that had genuine freedom to speak out."[41]
Foreign relations
High priorities in the foreign policy of Israel include seeking an end to hostilities with Arab forces and gaining wide acceptance as a sovereign state with an important international role.
The State of Israel joined the United Nations on May 11, 1949 (See also Israel and the United Nations). Today, Israel has diplomatic relations with 161 states. [42]
Annotated list of Israeli media sources
Template:Col-2General references to the Israeli media:- The Printed Media: Israel's Newspapers Summary from the Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs
- List of Israeli newspapers
- Azure [6] English edition of the quarterly journal offering essays and criticism on Israeli and Jewish public policy, culture and philosophy
- Globes [7] English-language website of Israel's business and technology daily
- Haaretz [8] Online English edition of the relatively highbrow Hebrew-language newspaper, Haaretz has a liberal editorial stance similar to that of The Guardian.
- IsraelInsider [9] - Independent, right wing outlet. Target audience is American Jewry.
- Jerusalem Newswire [10] Independent, right-wing Christian-run news outlet
- The Jerusalem Post [11] Israel's oldest English-language newspaper, considered to have a right-of-center editorial slant
- The Jerusalem Report [12] Left-of-center English weekly newspaper
- YNetNews [13] English-language website of Israel's largest newspaper Yedioth Ahronoth
- Globes [14] business daily
- Haaretz [15] Relatively highbrow Israeli newspaper with a liberal editorial stance similar to that of The Guardian
- Hamodia Daily newspaper serving Israel's Haredi community. English editions are also published in the U.S. and the U.K. and serve local Jewish Orthodox communities in those countries. Hamodia is not available online.
- Hazofe [16] daily newspaper with a religious Zionist point of view
- Maariv [17] Second largest Israeli newspaper, centrist.
- Makor Rishon [18] highbrow conservative weekly newspaper, conceived as a right-wing alternative to Ha'aretz
- Tchelet [19] Hebrew edition of Azure, a quarterly journal covering Israeli public policy
- Yated Ne'eman Daily newspaper serving the Haredi community
- Yedioth Ahronoth [20] Israel's largest newspaper, centrist
- Israel Nachrichten [21] The German-language daily from Tel Aviv for the 100,000 German-speaking Jews in Israel
- Al-Ittihad Arabic-language daily newspaper
- Israel Broadcasting Authority, TV News in Hebrew, some English.
- JerusalemONLINE video news update from Israel in English by Channel 2 News.
- Radio Israel
- Arutz Sheva news site representing the settler community, right-wing religious (English)
- Kol Israel - Voice of Israel Also produced by the IBA. In Hebrew, French, English, Spanish, Ladino, Russian, Persian, Yiddish, etc.
- IsraCast - Independent, multimedia broadcast and distribution network that focuses on Israeli foreign affairs and defense issues (English)
- Israelisms Podcast [22] Weekly podcast about everyday life and politics in Israel (English)
- DailyAlert [23] daily digest of Israeli and world media reports on Israel and the Middle East prepared by the Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs for The Conference of Presidents of Major American Jewish Organizations
- IsraPundit[24] Pro-Israel news and views from right-wing perspective.
- Israel Habara Committee
- Jewish Telegraphic Agency [25], New York-based news agency covering worldwide Jewish news, centrist (English)
References and footnotes
- ↑ Jerusalem is the official capital, and the location of the presidential residence, government offices and the Knesset, Israel's Parliament. In 1980, the Knesset asserted Jerusalem's status as the nation's "eternal and indivisible capital", by passing the Basic Law: Jerusalem — Capital of Israel. However, the United Nations does not recognize this designation. The bulk of the international community argues that the city is still legally an international corpus separatum and the final issue of the status of Jerusalem will be determined in future Israeli-Palestinian negotiations. The Palestinian Authority claims East Jerusalem as the capital of their future state. Most countries maintain their embassies in Tel Aviv (CIA Factbook), and the two remaining countries with embassies in Jerusalem have announced that they will move them to Tel Aviv too (Ynet). See Positions on Jerusalem for more information.
- ↑ this adversary was "a man", and later "God" according to Genesis 32:24–30; or "the angel", according to Hosea 12:4
- ↑ The Palestine Post December 7, 1947, page 1. "Popular Opinion" column.
- ↑ On the Move, TIME Magazine, May 31, 1948.
- ↑ The Stones Speak: The Merneptah Stele. Retrieved on 2006-04-08.
- ↑ The Land of Israel. Retrieved on 2006-04-08.
- ↑ Lehmann, Clayton Miles (Summer 1998). Palestine: History: 135-337: Syria Palaestina and the Tetrarchy. The On-line Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces. University of South Dakota. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ The Arab Refugees, The New York Post. November 30, 1948. Reproduction.
- ↑ General Progress Report and Supplementary Report of the United Nations Conciliation Commission for Palestine, Covering the Period from 11 December 1949 to 23 October 1950, published by the United Nations Conciliation Commission, October 23 1950. (U.N. General Assembly Official Records, Fifth Session, Supplement No. 18, Document A/1367/Rev. 1) The Committee believed the estimate to be "as accurate as circumstances permit", and attributed the higher number on relief to, among other things, "duplication of ration cards, addition of persons who have been displaced from area other than Israel-held areas and of persons who, although not displaced, are destitute".
- ↑ Court ruling Israeli High Court of Justice ruling mentioning how it enforced handing masks to all Palestinians during the Gulf War as a principle of equality Template:He icon
- ↑ Mideast Mirror, August 6, 1990
- ↑ Associated Press, August 12, 1990
- ↑ article An article in Ha'artez talking about the Palestinians' support for Nasrallah mentioning that in the 90's Saddam captivated the hearts of the Palestinians because of his goal to eradicate Israel. Template:He icon
- ↑ [1] An article in Ma'ariv talking about an anti Israel wide demonstration of Arabs citing their famous song from the Gulf War era: "Ya Saddam Ya Habib - destroy Tel Aviv". Template:He icon
- ↑ [2] Yediot Ahronot article: Israeli Deputy Minister of Defense says that in case Israel is 100% sure of another Iraqi attack (in 2002) , gas masks will be provided for the Palstinians , and mentioned their use against tear gas. Template:He icon
- ↑ B'Tselem separation barrier statistics
- ↑ Humanitarian Assistance to Lebanon. United States Agency for International Development Disaster Assistance (1 September 2006). Retrieved on 2006-09-03.
- ↑ Template:Http://www.upi.com/InternationalIntelligence/view.php?StoryID=20060906-045027-8532r
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Israel-Hizbullah conflict: Victims of rocket attacks and IDF casualties, Israel, Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
- ↑ Mideast War, by the numbers. Guardian / Associated Press (2006-08-18). Retrieved on 2006-08-25.
- ↑ Hizballah's Rocket Campaign Against Northern Israel: A Preliminary Report. Jerusalem Center for Public Affairs (2006-08-31). Retrieved on 2006-09-08.
- ↑ Assessing the Environmental Costs of the War in the North - Summer 2006. Ministry of Environmental Protection (2006-08-30). Retrieved on 2006-09-14.
- ↑ For a short period in the 1990s the Prime Minister was directly elected by the electorate. This change was not viewed a success and was abandoned.
- ↑ Constitution for Israel. Retrieved on 2006-04-08.
- ↑ Source: the French-German textbook Histoire/Geschichte - Europa und die Welt seit 1945, Klett 2006 and Nathan 2006, German version p. 311. ISBN 3-12-416510-1.
- ↑ The Israel you don't see on the evening news. Israel Embassy. Retrieved on 2006-07-20.
- ↑ BOYCOTT ISRAEL? DO IT PROPERLY.., Mideast Outpost, 2004-12-31.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Israel. Population, by religion and population group. Retrieved on 2006-04-08. Template:PDFlink Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "pdf2" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Israel. Jews and others, by origin, continent of birth and period of immigration. Retrieved on 2006-04-08. Template:PDFlink
- ↑ Settlements information, Foundation for Middle East Peace. East Jerusalem Population and Area, 2000-2002. Retrieved on 2006-04-08.
- ↑ Religion in Israel: A Consensus for Jewish Tradition by Daniel J. Elazar (JCPA)
- ↑ Haifa - Carmel Mountain (video)
- ↑ wikiquote:Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel
- ↑ A Status Report – Equality for Arab Citizens of Israel. The Association for Civil Rights In Israel (2002). Retrieved on August 2, 2006.
- ↑ Human Rights. A joint project of the Knesset and the Jewish Agency for Israel, operated in North America by the Israeli American Jewish Forum.. Retrieved on August 25, 2006.
- ↑ Israel and the Occupied Territories. AI Report 2005. Amnesty International (2006). Retrieved on 2006-09-03.
- ↑ Israel/Palestinian Authority. Human Rights Watch (2006). Retrieved on 2006-09-03.
- ↑ Israel and the Occupied Territories. Country Reports on Human Rights Practices - 2005. Israel and the Occupied Territories. Released by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor (March 8, 2006). Retrieved on July 27, 2006.
- ↑ Freedom in the World 2006 (Template:PDFlink). Freedom House (2005-12-16). Retrieved on 2006-07-27.
See also Freedom in the World 2006, List of indices of freedom}} - ↑ Press Freedom Rankings by Region 2005. Freedom House (2005). Retrieved on 2006-08-12.
- ↑ Israel - Annual report 2006. Reporters Without Borders (2006). Retrieved on 2006-08-12.
- ↑ Israel's Diplomatic Missions Abroad (Israeli MFA)
See also
|
External links
Template:Sisterlinks Template:Portal
General information
- The Jewish History Resource Center Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- BBC News Country Profile - Israel and Palestinian Territories
- Israel (Jewish Virtual Library )
- CIA World Factbook - Israel
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, Israel - Country Page
- US State Department - Israel includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports
- Columbia University Libraries - Israel directory category of the WWW-VL
- Israel Lexicon definitions, events and terms related to Israel, Israel Profile (YnetNews)
- Israel21c: A focus beyond the conflict
Government
- Government Portal of Israel
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Israel
- The President of the state of Israel
- Prime Minister's Office
- Bureau of Statistics
- Israel Defence Force site
- Israel Security Fence Project
Legislation and the legal system
- The Knesset (Parliament)
- Basic Laws, legal code of Israel
- Israeli Commercial, Banking, Tort and Insurance Laws in English
History
- State of Israel The Jewish History Resource Center, Project of the Dinur Center for Research in Jewish History, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem
- The birth of Israel from the BBC
- Israel Museum, Jerusalem
- Historical documents (MFA)
- Authentic historical recordings (Isracast)
Economy, science, and technology
- Standard and Poor's Israel Economic Information
- DUNS 100, the hundred largest companies in Israel
- Israel Science and Technology Homepage
- IsraCast: Science and Technology News From Israel (isracast.com, English)
Society
- Israel Women's Network
- Gay Middle East - Israel section
- Israeli Arabs and Israeli Society, discussion with Ori Nir, correspondent for Haaretz and the Forward.
- Freedom of Religion in Israeli Society and Politics by Prof. Shimon Shetreet, former minister of Religious Affairs.
- Neve Shalom/Wahat al-Salam the Oasis of Peace, an experimental Arab-Jewish cooperative village.
- Israel Movement for Progressive Judaism, Reform Judaism in Israel
Template:Southwest Asia
Template:Middle East
Template:Mediterranean
Template:Asia
af:Israel ang:Israhēl ar:إسرائيل an:Israel ast:Israel zh-min-nan:Í-sek-lia̍t-kok be:Ізраіль br:Israel bg:Израел ca:Israel cs:Izrael cy:Israel da:Israel de:Israel et:Iisrael el:Ισραήλ es:Israel eo:Israelo eu:Israel fa:اسرائیل fr:Israël fy:Israel ga:Iosrael gd:Israel gl:Israel - ישראל got:𐌹𐍃𐍂𐌰𐌴𐌻/Israel ko:이스라엘 hr:Izrael io:Israel ilo:Israel id:Israel ia:Israel is:Ísrael it:Israele he:ישראל ka:ისრაელი kw:Ysrael ht:Izrayèl ku:Îsraîl lad:Medinat Yisrael la:Israel (civitas) lv:Izraēla lb:Israel lt:Izraelis li:Israël hu:Izrael mk:Израел ms:Israel na:Israel fj:Isireli nl:Israël ja:イスラエル no:Israel nn:Israel oc:Israèl ug:ئىسرائىلىيە pam:Israel ps:اسرايل nds:Israel pl:Izrael pt:Israel ro:Israel ru:Израиль sq:Izraeli scn:Israeli simple:Israel sk:Izrael sl:Izrael sr:Израел sh:Izrael fi:Israel sv:Israel tl:Israel ta:இசுரேல் th:ประเทศอิสราเอล vi:Israel tr:İsrail uk:Ізраїль ur:اسرائیل uz:Isroil yi:מדינת ישראל zh-yue:以色列 zh:以色列