Hip fracture: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Robert Badgett |
imported>Robert Badgett |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Surgical treatment is optimal.<ref name="pmid18646065">{{cite journal |author=Handoll HH, Parker MJ |title=Conservative versus operative treatment for hip fractures in adults |journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev |volume= |issue=3 |pages=CD000337 |year=2008 |pmid=18646065 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD000337.pub2 |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000337.pub2 |issn=}}</ref> | Surgical treatment is optimal, especially for intracapsular fractures.<ref name="pmid18646065">{{cite journal |author=Handoll HH, Parker MJ |title=Conservative versus operative treatment for hip fractures in adults |journal=Cochrane Database Syst Rev |volume= |issue=3 |pages=CD000337 |year=2008 |pmid=18646065 |doi=10.1002/14651858.CD000337.pub2 |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD000337.pub2 |issn=}}</ref> | ||
For incomplete intertrochanteric fractures, conservative therapy is an option.<ref name="pmid16129752">{{cite journal| author=Alam A, Willett K, Ostlere S| title=The MRI diagnosis and management of incomplete intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. | journal=J Bone Joint Surg Br | year= 2005 | volume= 87 | issue= 9 | pages= 1253-5 | pmid=16129752 | For incomplete intertrochanteric fractures, conservative therapy is an option.<ref name="pmid16129752">{{cite journal| author=Alam A, Willett K, Ostlere S| title=The MRI diagnosis and management of incomplete intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. | journal=J Bone Joint Surg Br | year= 2005 | volume= 87 | issue= 9 | pages= 1253-5 | pmid=16129752 | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 12 January 2010
In medicine, hip fractures are "fractures of the femur head; the femur neck; (femoral neck fractures); the trochanters; or the inter- or subtrochanteric region. Excludes fractures of the acetabulum and fractures of the femoral shaft below the subtrochanteric region (femoral fractures)."[1]
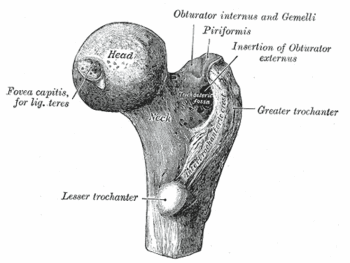
Classification

Upper right femur viewed from behind and above.
Intracapsular fractures
- Femoral head fracture
- Femoral neck fractures
Extracapsular fractures
- Intertrochanteric fractures
- Subtrochanteric fractures
Etiology
Osteoporosis and accidental falls are risk factors.
Treatment
Surgical treatment is optimal, especially for intracapsular fractures.[2]
For incomplete intertrochanteric fractures, conservative therapy is an option.[3]
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Hip fracture (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Handoll HH, Parker MJ (2008). "Conservative versus operative treatment for hip fractures in adults". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (3): CD000337. DOI:10.1002/14651858.CD000337.pub2. PMID 18646065. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Alam A, Willett K, Ostlere S (2005). "The MRI diagnosis and management of incomplete intertrochanteric fractures of the femur.". J Bone Joint Surg Br 87 (9): 1253-5. DOI:10.1302/0301-620X.87B9.16558. PMID 16129752. Research Blogging.