Cefazolin
|
| |||||||
| cefazolin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Cefazolin, also called cefazoline, cephazolin or CEZ, is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic sold under the brand name Ancef®. It is primarily used to treat bacterial skin infections, but can be used to treat moderately severe bacterial infections involving the lungs, bones, joints, stomach, blood, heart valves or the urinary tract. It is effective against staphylococci and streptococci species of Gram-positive bacteria. It is given by IV (parenterally).
Mechanism of action
Like other cephalosporins and penicillins, cefazolin binds to penicillin-binding proteins thus interfering with the final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis, the peptidoglycan layer, and causing autolysis of the cells by autolysins enzymes.
Chemistry
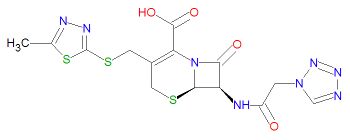
Cefazolin has the IUPAC chemical name (7R)-3-[(5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)sulfanylmethyl]-8-oxo-7-[[2-(tetrazol-1-yl) acetyl]amino]-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, molecular formula C14H14N8O4S3 and molecular mass 454.5072 g/mol. It is a cephalosporin and contains a beta-lactam moiety.
External links
The most up-to-date information about Cefazolin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Cefazolin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefazolin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Cefazolin - Detailed information from DrugBank.