Amikacin: Difference between revisions
imported>Meg Taylor m (spelling: postive -> positive) |
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
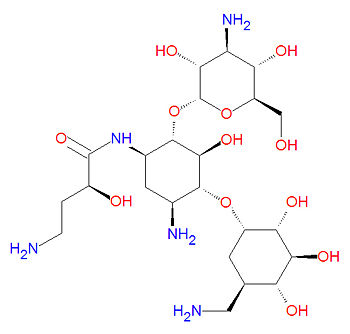
{{Image|Amikacin structure.jpg|right|350px|Amikacin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic}} | {{Image|Amikacin structure.jpg|right|350px|Amikacin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic}} | ||
'''Amikacin''', also called '''amikacina''', '''amikacine''', '''amikacinum''' and '''BB-K8''', is a broad-spectrum [[aminoglycoside]] type of [[antibiotic]] derived from [[kanamycin]] that is used to treat severe infections due to gram-negative aerobic bacteria. It is active against species of ''[[E. coli]]'', ''[[Acinetobacter]]'', ''[[Pseudomonas]]'', ''[[Proteus]]'', ''[[Providencia]]'' and ''[[Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia]]'' and some [[mycobacteria]]. It can be used for Gram-positive bacterial infections, but better treatment options are generally used. Like other aminoglycosides, it shows little effect on anaerobic bacteria, [[fungi]] and [[virus]]es. | '''Amikacin''', also called '''amikacina''', '''amikacine''', '''amikacinum''' and '''BB-K8''', is a broad-spectrum [[aminoglycoside]] type of [[antibiotic]] derived from [[kanamycin]] that is used to treat severe infections due to gram-negative aerobic bacteria. It is active against species of ''[[E. coli]]'', ''[[Acinetobacter]]'', ''[[Pseudomonas]]'', ''[[Proteus]]'', ''[[Providencia]]'' and ''[[Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia]]'' and some [[mycobacteria]]. It can be used for Gram-positive bacterial infections, but better treatment options are generally used. Like other aminoglycosides, it shows little effect on anaerobic bacteria, [[Fungus|fungi]] and [[virus]]es. | ||
== Chemistry == | == Chemistry == | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 21 June 2024
Amikacin, also called amikacina, amikacine, amikacinum and BB-K8, is a broad-spectrum aminoglycoside type of antibiotic derived from kanamycin that is used to treat severe infections due to gram-negative aerobic bacteria. It is active against species of E. coli, Acinetobacter, Pseudomonas, Proteus, Providencia and Klebsiella-Enterobacter-Serratia and some mycobacteria. It can be used for Gram-positive bacterial infections, but better treatment options are generally used. Like other aminoglycosides, it shows little effect on anaerobic bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Chemistry
Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S)-4-amino-N-[(1R,2S,3S,4R,5S)-5-amino-2-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-4-[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-6-(aminomethyl)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan- 2-yl]oxy-3-hydroxycyclohexyl]-2-hydroxybutanamide and it has chemical formula C22H43N5O13.
Drug interactions
An increased risk of nephrotoxicity occurs when amikacin is taken in combination with cephalosporin or related compounds, including ceforanide, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, cefalotin, cephapirin, cisplatin, cefamandole, cefazolin, cefonicid, cefoperazone, cefotetan, cefoxitin, ceftizoxime and cefradine. Amikacin also increases the effects of muscle relaxants including atracurium, doxacurium, gallamine Triethiodide, metocurine, mivacurium, pancuronium, pipecuronium, rocuronium, succinylcholine, tubocurarine and vecuronium. Increased Ototoxicity occurs when amikacin is used with bumetanide, furosemide, ethacrynic acid or torasemide. Thalidomide use increases renal toxicity.
Brand names
Amikacin is sold under the following brand names:
- Amicacin®
- Amiglyde-V®
- Amikavet®
- Amikin®
- Briclin®
External links
The most up-to-date information about Amikacin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Amikacin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Amikacin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Amikacin - Detailed information from DrugBank.